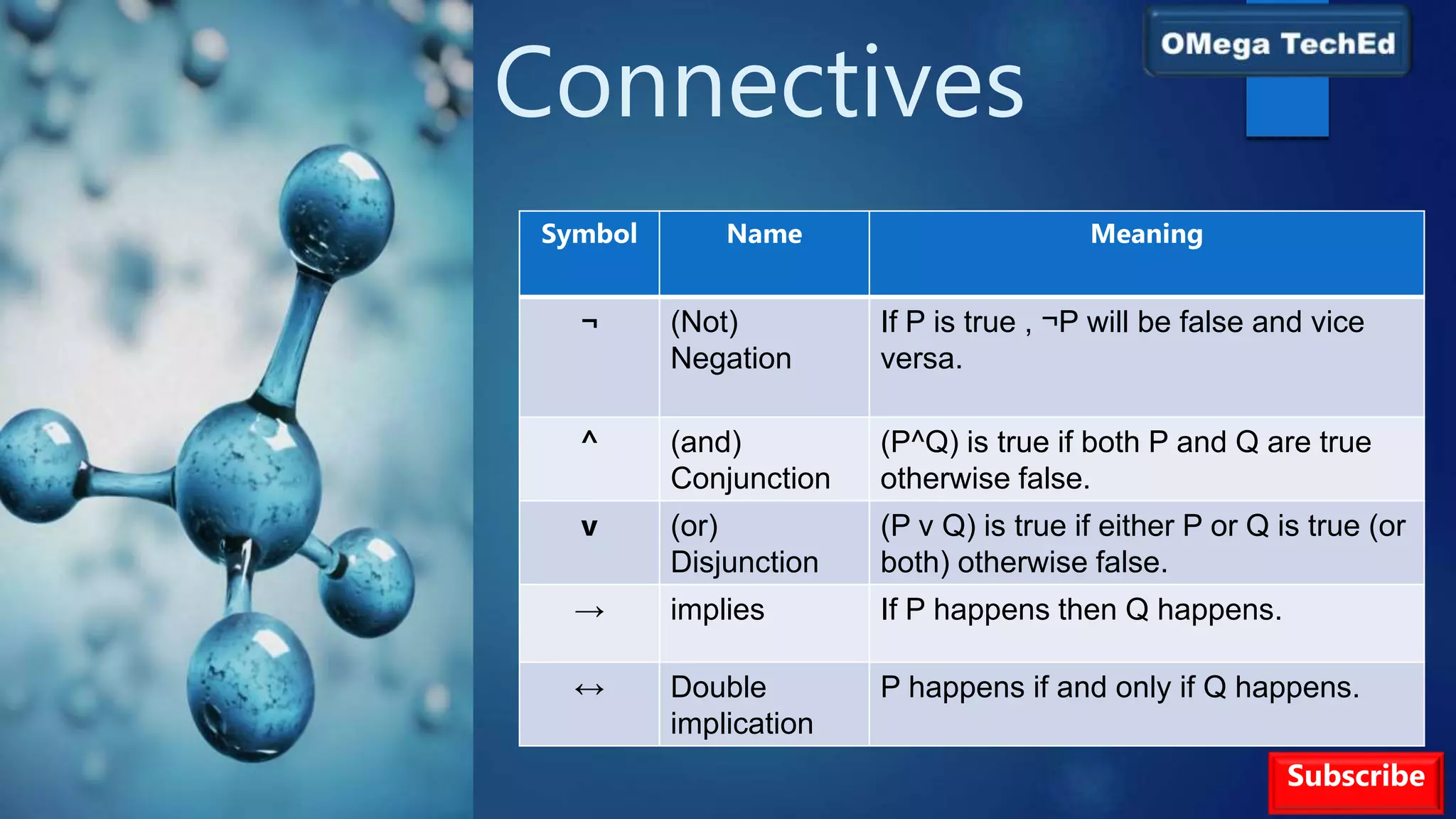
Knowledge-based agents can accept new tasks in the form of explicitly described goals and adapt to changes in their environment by updating relevant knowledge. They maintain a knowledge base of facts about the environment and use an inference engine to deduce new information and determine what actions to take. The knowledge base stores sentences expressed in a knowledge representation language and the inference engine applies logical rules to deduce new facts or answer queries. Propositional logic is often used to represent knowledge, where sentences consist of proposition symbols connected by logical connectives like AND, OR, and NOT.