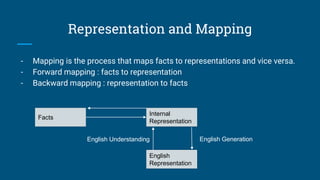
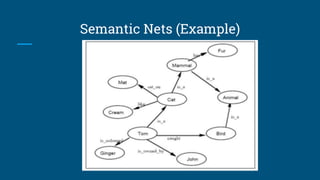
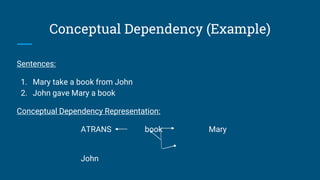
The document discusses structured knowledge representation methods, including mapping processes such as forward and backward mapping, and the properties of effective knowledge representation like adequacy and efficiency. It outlines various approaches such as semantic nets, frames, and conceptual dependency, detailing their advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it explains how structured representations can capture knowledge from natural language and depict relationships among elements.