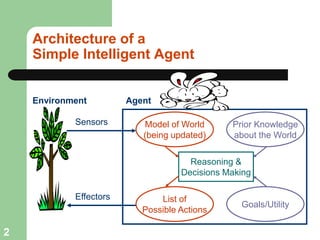
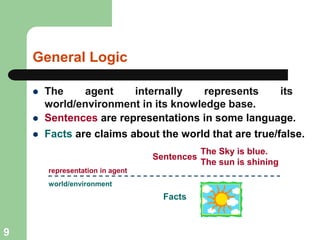
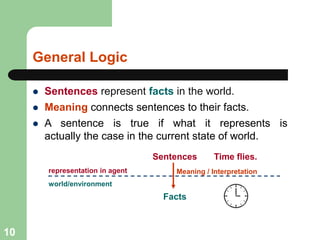
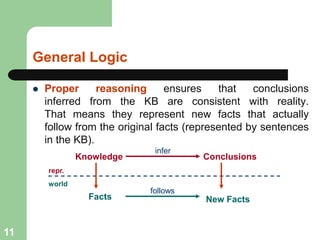
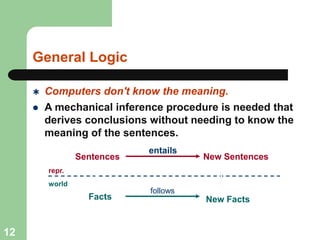
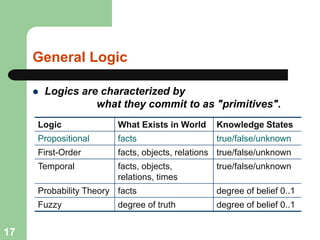
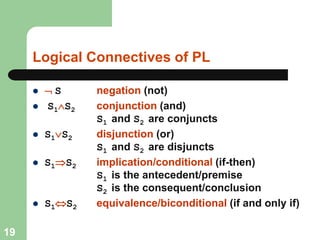
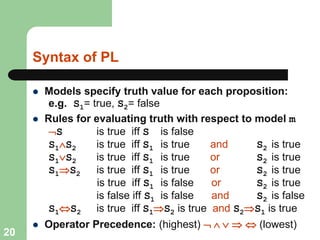
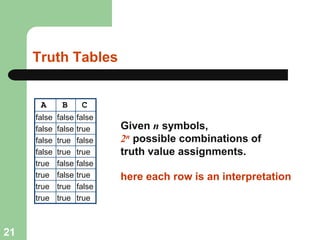
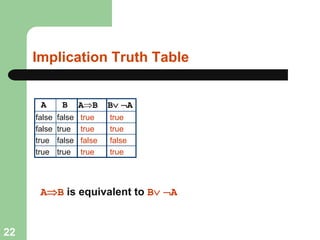
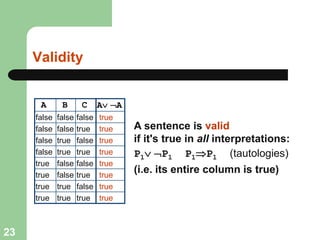
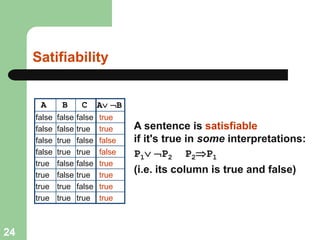
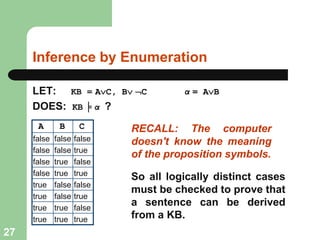
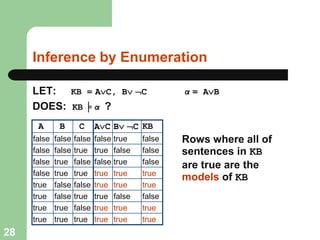
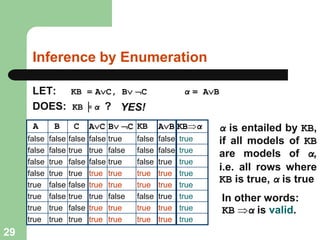
This document discusses logical agents and knowledge representation in artificial intelligence. It describes the architecture of a simple logical agent that uses sensors to perceive the environment, effectors to take actions, and a knowledge base to represent its knowledge and make reasoning and decisions. The knowledge base contains facts about the world represented as sentences in a formal logic. The agent can ask the knowledge base questions and incorporate new percepts to update its internal representation of the world. Logical inference allows the agent to deduce new facts that follow logically from the knowledge base without needing to understand the meaning of the sentences. Different types of logic like propositional, first-order, and temporal logic are discussed for knowledge representation.