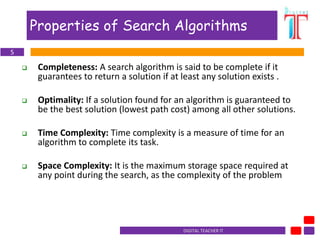
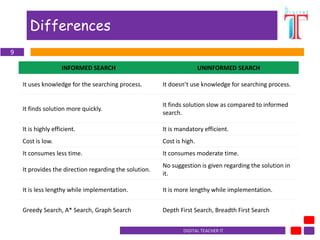
The document discusses search strategies in artificial intelligence. It defines key terms like search space, start state, goal test, and search tree. It describes properties of search algorithms like completeness, optimality, time complexity, and space complexity. It differentiates between uninformed searches, which do not use domain knowledge, like breadth-first search and depth-first search, and informed searches, which use heuristics to guide the search more efficiently, like greedy search and A* search. The document outlines the differences between informed and uninformed searches.