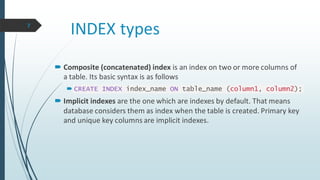
MySQL indexes are used to enhance retrieval performance for large tables. Indexes are similar to a book index and work by creating a lookup table for the indexed column(s). This speeds up queries with WHERE clauses that filter on indexed columns. However, indexes also slow down write operations like INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE. The optimal approach is to only create indexes on columns frequently used in queries, and avoid indexing columns with many NULL values or those frequently modified. The CREATE INDEX statement is used to index single or multiple columns, while DROP INDEX removes indexes no longer needed.