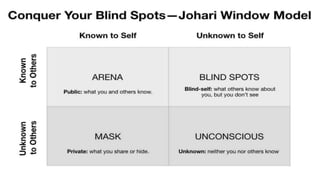
The document discusses the Johari window model, which was developed in 1955 by American psychologists Joseph Luft and Harrington Ingham. The model helps people understand their relationship with themselves and others through four regions or "panes" of self-knowledge: open self (known to self and others), blind self (unknown to self but known to others), hidden self (known to self but unknown to others), and unknown self (unknown to self and others). The goal of the model is to increase open self-knowledge through self-disclosure and feedback from others, while decreasing the size of the other regions.