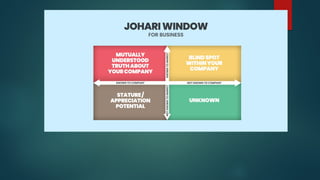
The Johari Window model, developed by psychologists Joseph Luft and Harrington Ingham in 1955, is a tool for understanding self-awareness and interpersonal relationships through four areas: open self, blind self, hidden self, and unknown self. Its primary goal is to increase the open self area, thereby building trust and facilitating personal growth through feedback and self-disclosure. However, the model has drawbacks, such as the potential for misuse of shared personal information and varying cultural attitudes toward openness and feedback.