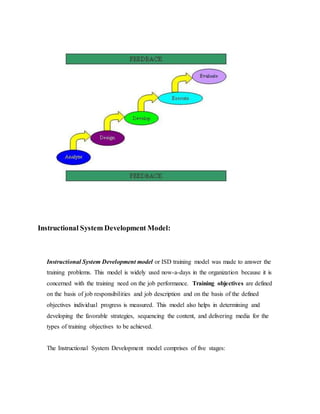
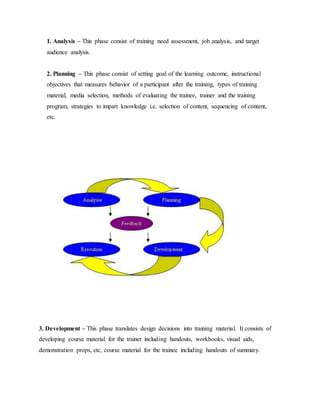
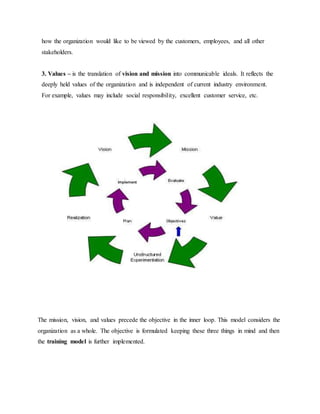
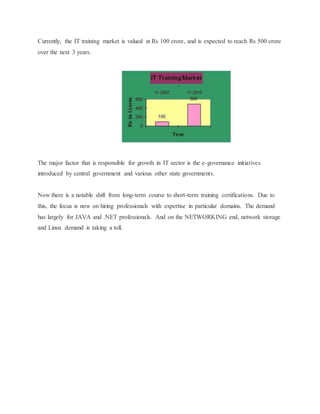
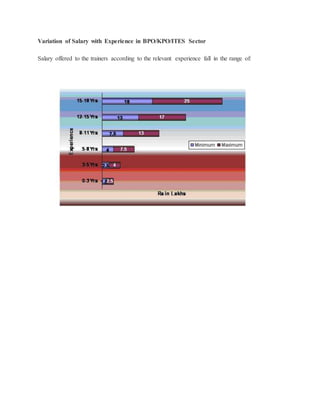
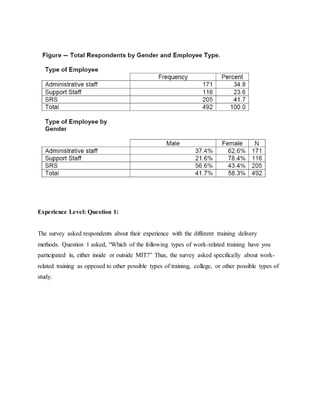
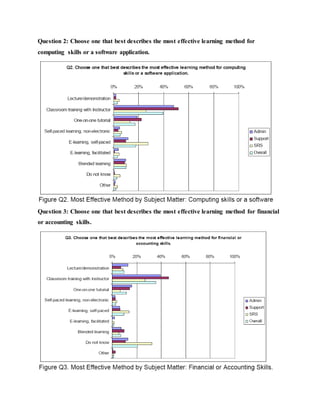
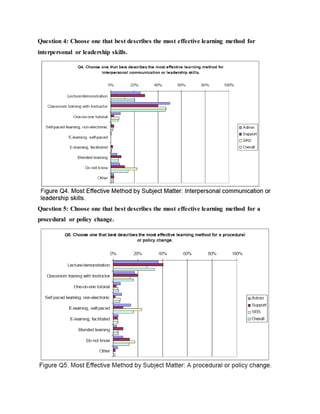
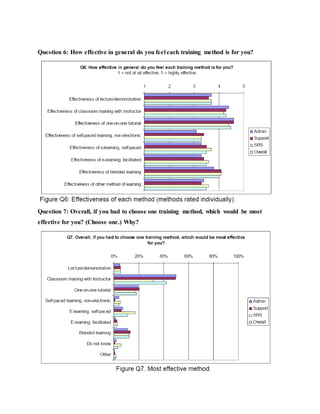
This document discusses job training methods and processes at an IT firm. It begins by introducing the importance of training for employees and businesses. It then provides background on the growth of the IT sector in India and the increased need for training and skills development. The rest of the document discusses various training models, domains, methods, and essential aspects of training in the IT industry. It also includes surveys on effective training delivery methods and the variation of trainer salaries with experience in the IT sector.