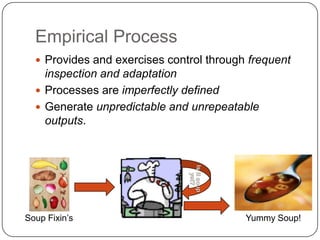
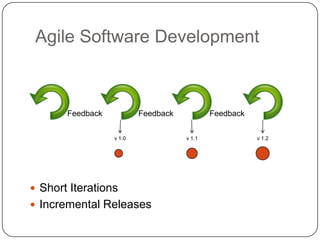
The document provides an overview of Scrum and the agile development process, contrasting empirical and defined processes, and emphasizing the significance of frequent inspection and adaptation. It outlines Scrum roles, responsibilities, and core practices, including the product backlog, user stories, sprint planning, daily standups, and retrospectives. The emphasis is on agility, collaboration, and self-organization within cross-functional teams to respond effectively to changing requirements.