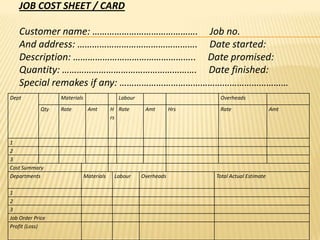
This document provides an overview of a job order cost system. It describes job order costing as a method used when production is done according to customer orders rather than for stock. Each job has a unique cost that is tracked from start to finish using a job cost sheet. The objectives are to determine the accurate cost of each job and identify profitable versus unprofitable jobs to aid future estimates. The key aspects of job order costing include distinct work orders for each job, tracking direct and overhead costs accumulated to each job, and comparing estimated versus actual costs for process improvement and pricing future jobs.