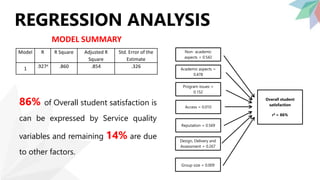
The dissertation investigates undergraduate students' satisfaction with service quality at the Faculty of Management Studies and Commerce, University of Jaffna. It identifies key factors influencing satisfaction, conducts data analysis through various hypotheses, and exposes relationships between service quality dimensions and overall satisfaction. The research concludes that there are significant relationships between several dimensions of service quality and student satisfaction, with recommendations for improvement in specific areas.