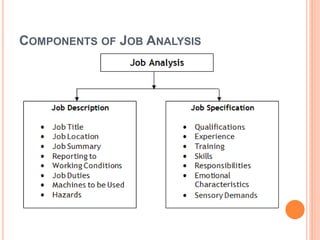
This document discusses job analysis and talent management. It defines job analysis as the process of gathering and analyzing job information. Key components are job descriptions outlining duties and responsibilities, and job specifications outlining required qualifications. Benefits include improved recruitment and performance evaluation. Methods for collecting job analysis data include observation, diaries, workshops, surveys, interviews, and online questionnaires. Talent management refers to attracting, developing, and retaining skilled employees. It is connected to job analysis through recruitment by using job data to attract qualified candidates, performance management by setting standards, compensation by designing fair pay, and career development by guiding employee skills.