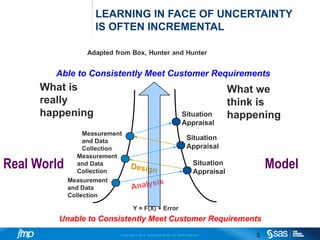
The document discusses statistical models, highlighting their role in relating inputs to outcomes while differentiating between predictable variation (signal) and non-predictable variation (noise). It emphasizes the importance of effective model building and the challenges posed by larger datasets and complexities in data. JMP is presented as a powerful tool for statistical modeling, offering scalability, simplicity, and efficiency in data analysis.