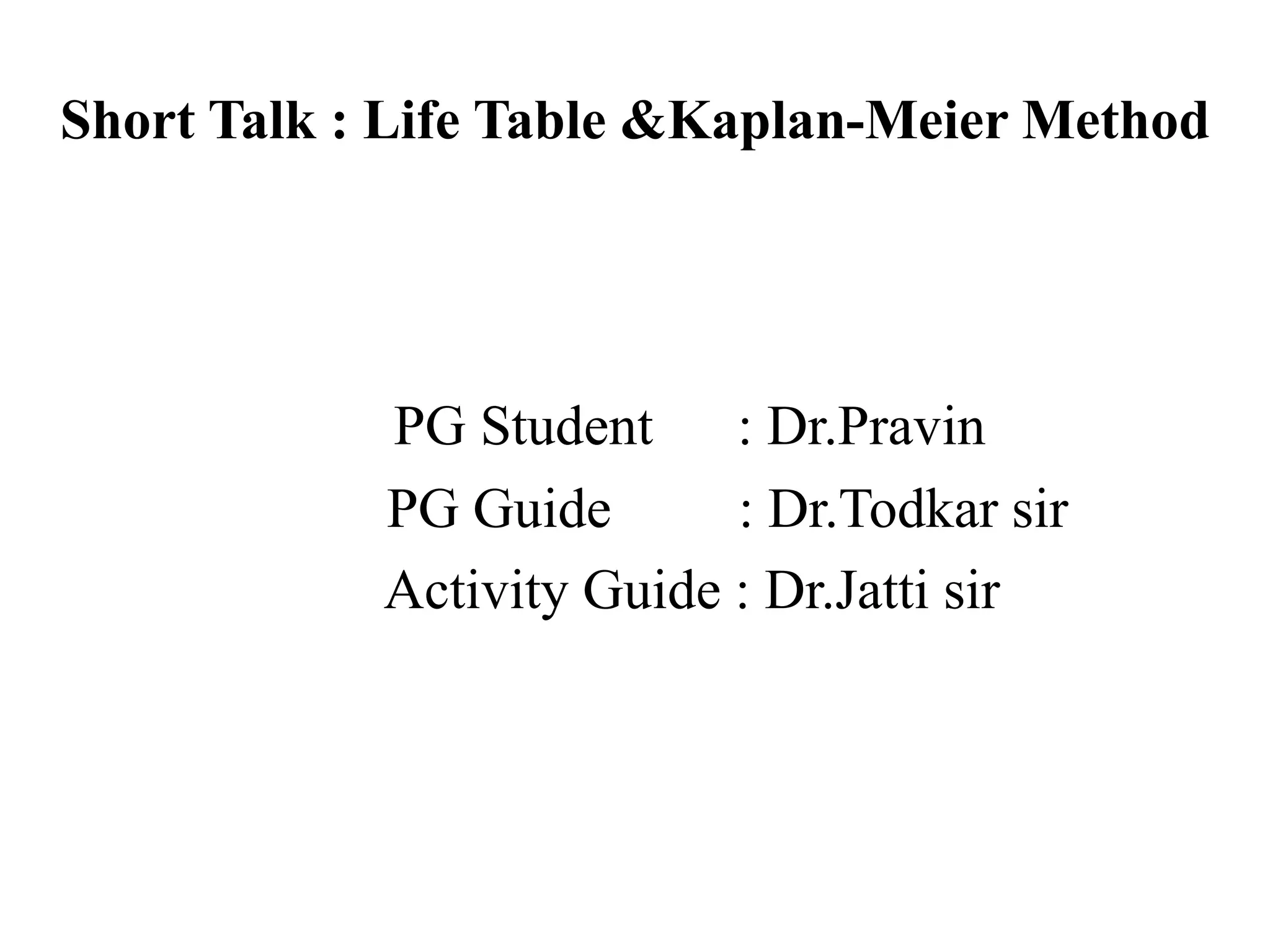
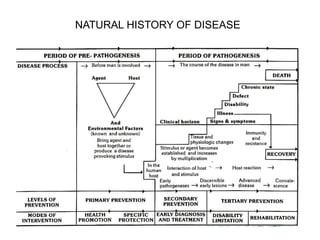
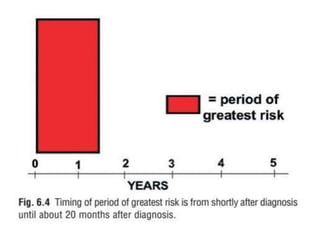
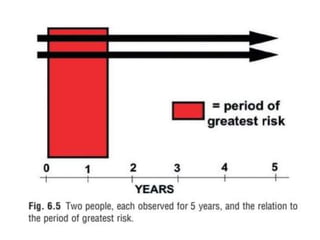
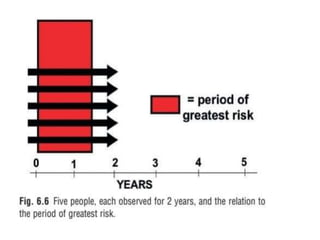
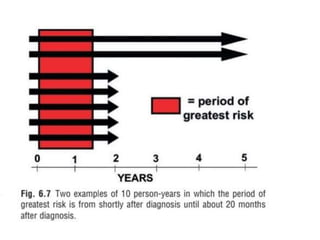
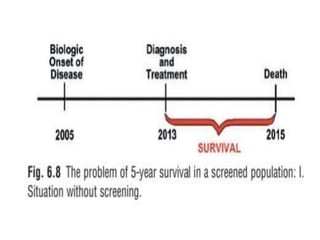
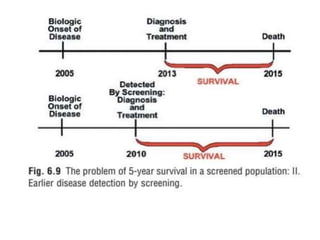
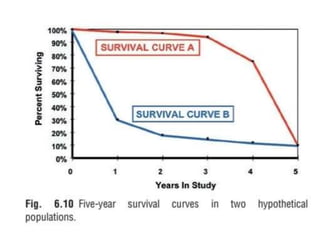
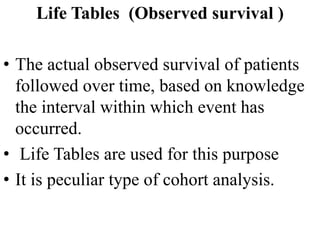
1. The document discusses various methods for expressing disease prognosis, including life tables and the Kaplan-Meier method.
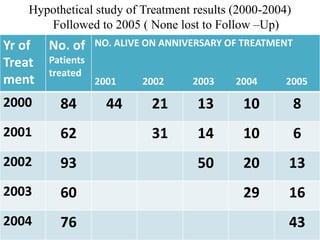
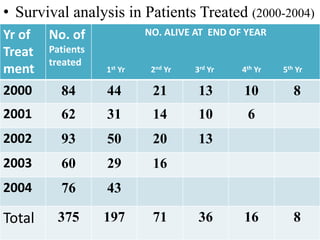
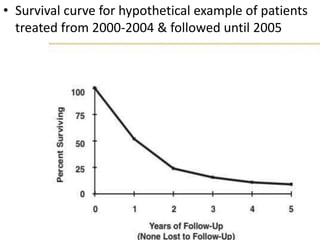
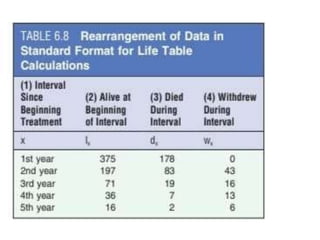
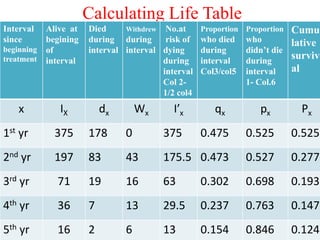
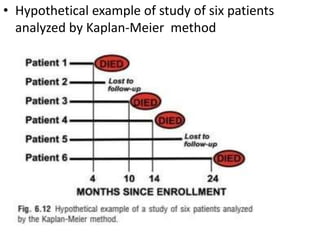
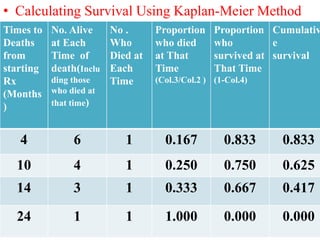
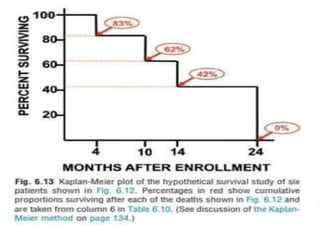
2. It provides examples of how to calculate survival probabilities using both a hypothetical life table and the Kaplan-Meier method based on data from patients treated between 2000-2004.
3. Both methods allow estimation of survival functions over time but the Kaplan-Meier method uses the exact times of events rather than predetermined intervals.