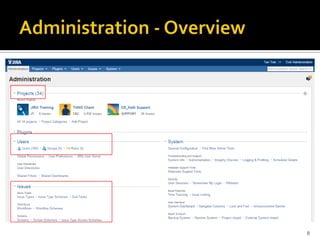
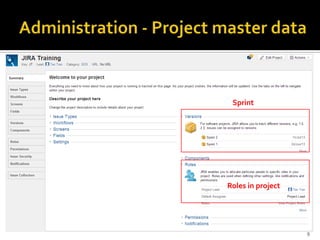
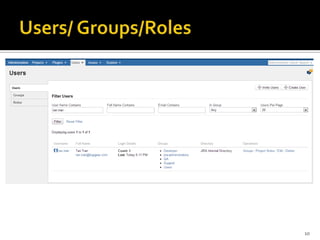
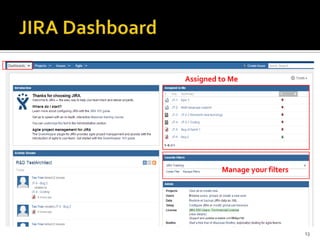
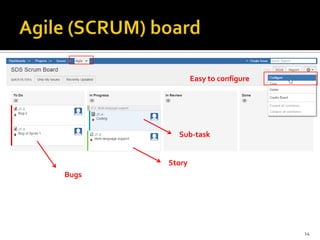
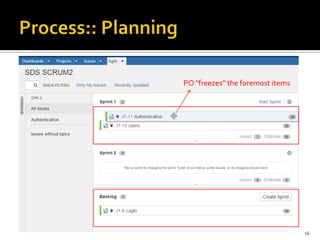
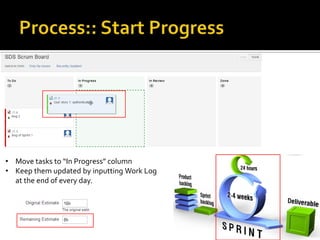
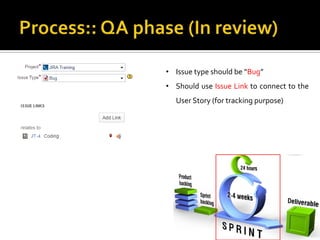
The document introduces JIRA and how it can be used for project and issue tracking. It provides an overview of how JIRA can be used by administrators to manage projects, users, and issues. It also describes how project members can use JIRA for agile planning and development with features like dashboards, backlogs, and SCRUM boards. The document includes a demo section and concludes with a discussion of integrating JIRA with the SCRUM framework for agile software development.