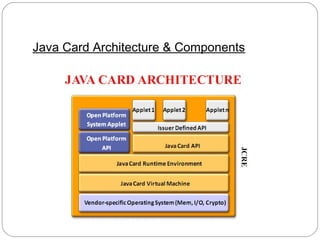
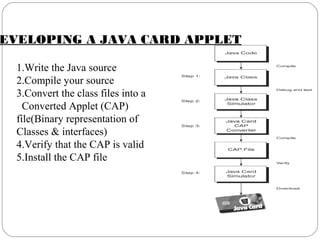
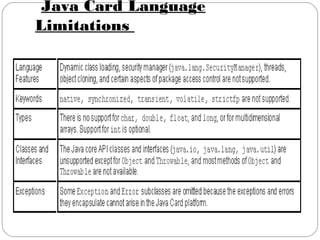
Java Card technology allows Java-based applications to run securely on smart cards. A Java Card is a programmable smart card that supports running multiple applications using the Java programming language. Key features of Java Card include support for small data types and one-dimensional arrays, as well as object-oriented features, while not supporting large data types, characters, strings, or dynamic class loading. Java Card provides advantages like interoperability, security, and compatibility with existing standards.