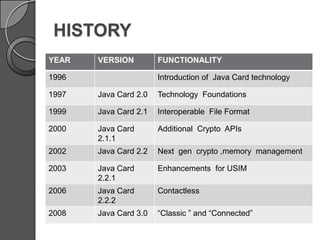
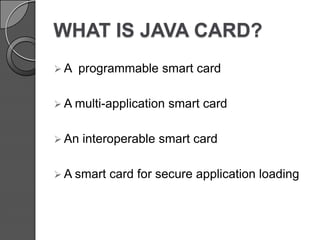
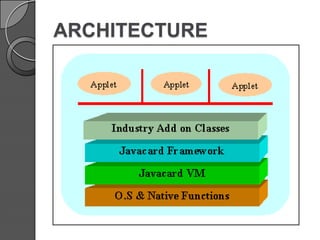
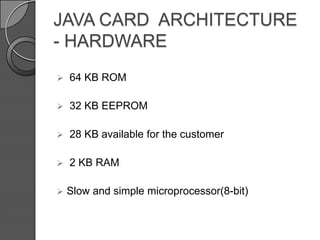
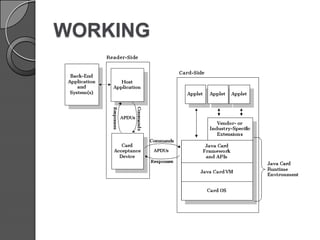
This document discusses Java Card technology. It provides an introduction to Java Card, describing it as a technology that allows Java-based applications to run securely on smart cards. The document then covers Java Card's history and versions, architecture, working, applications in areas like finance and mobile communication, and challenges related to its limited memory and capabilities compared to Java. It concludes that Java Card adds a new platform for Java and is a significant advancement, while also noting security threats must be addressed.