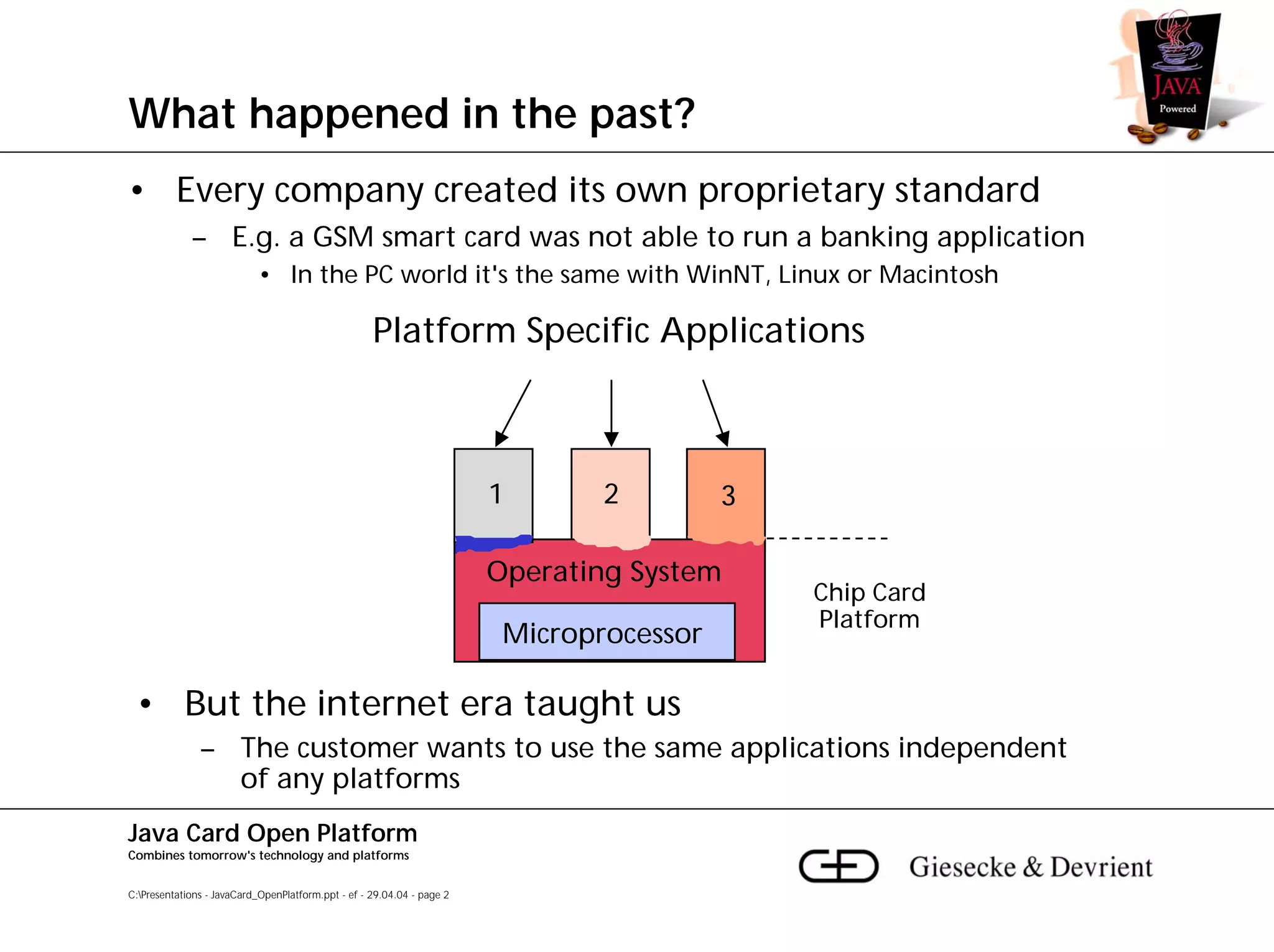
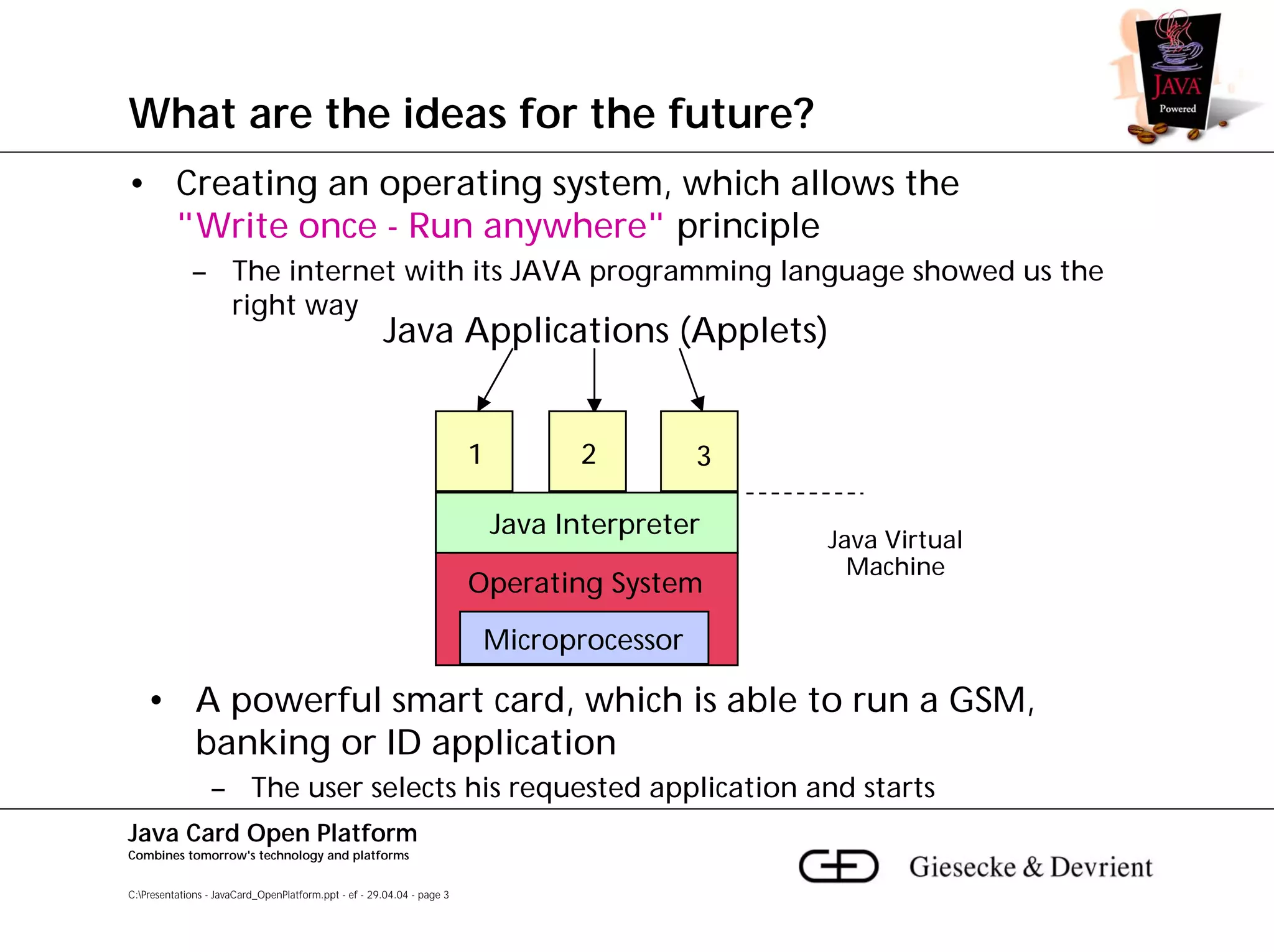
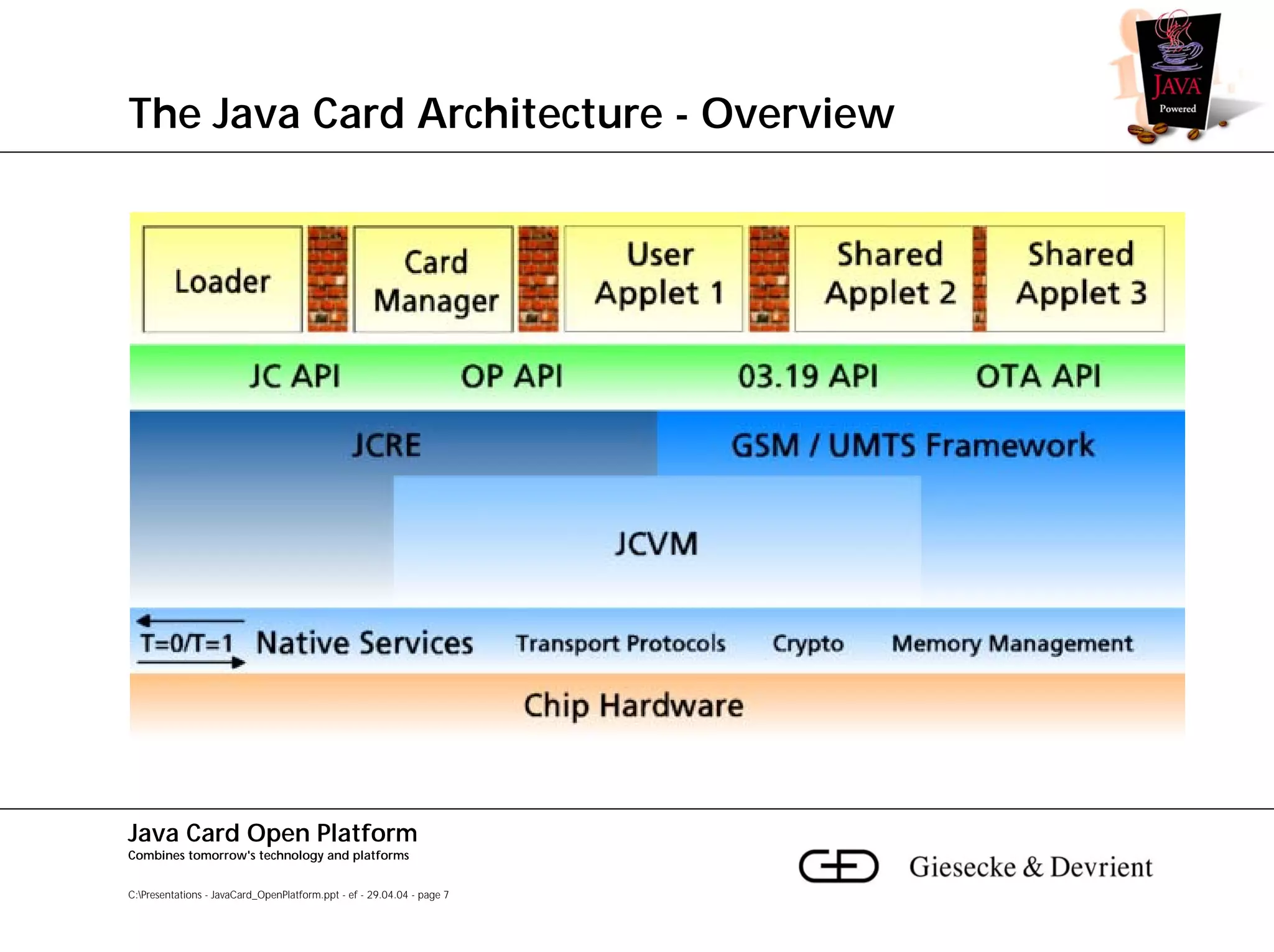
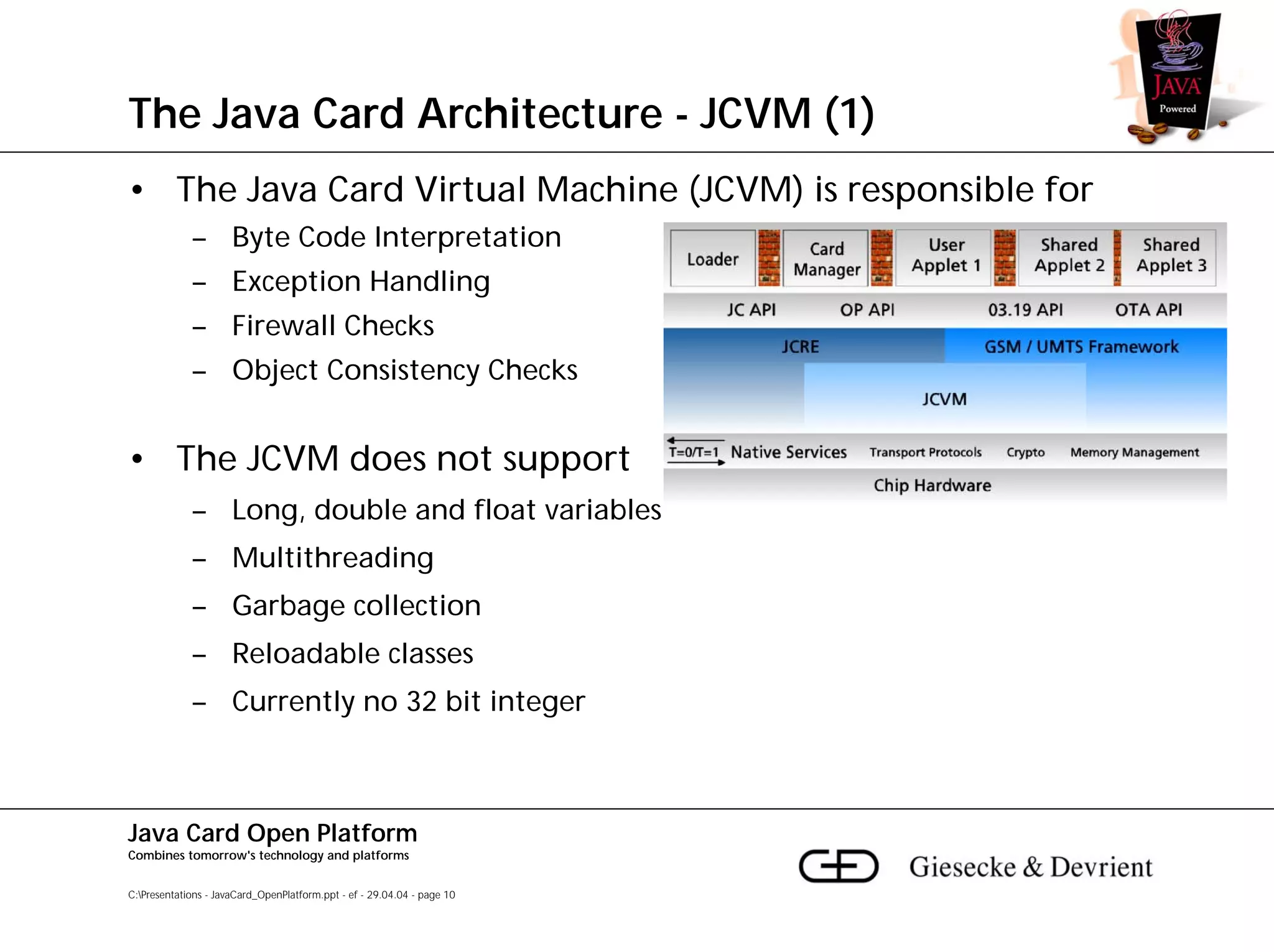
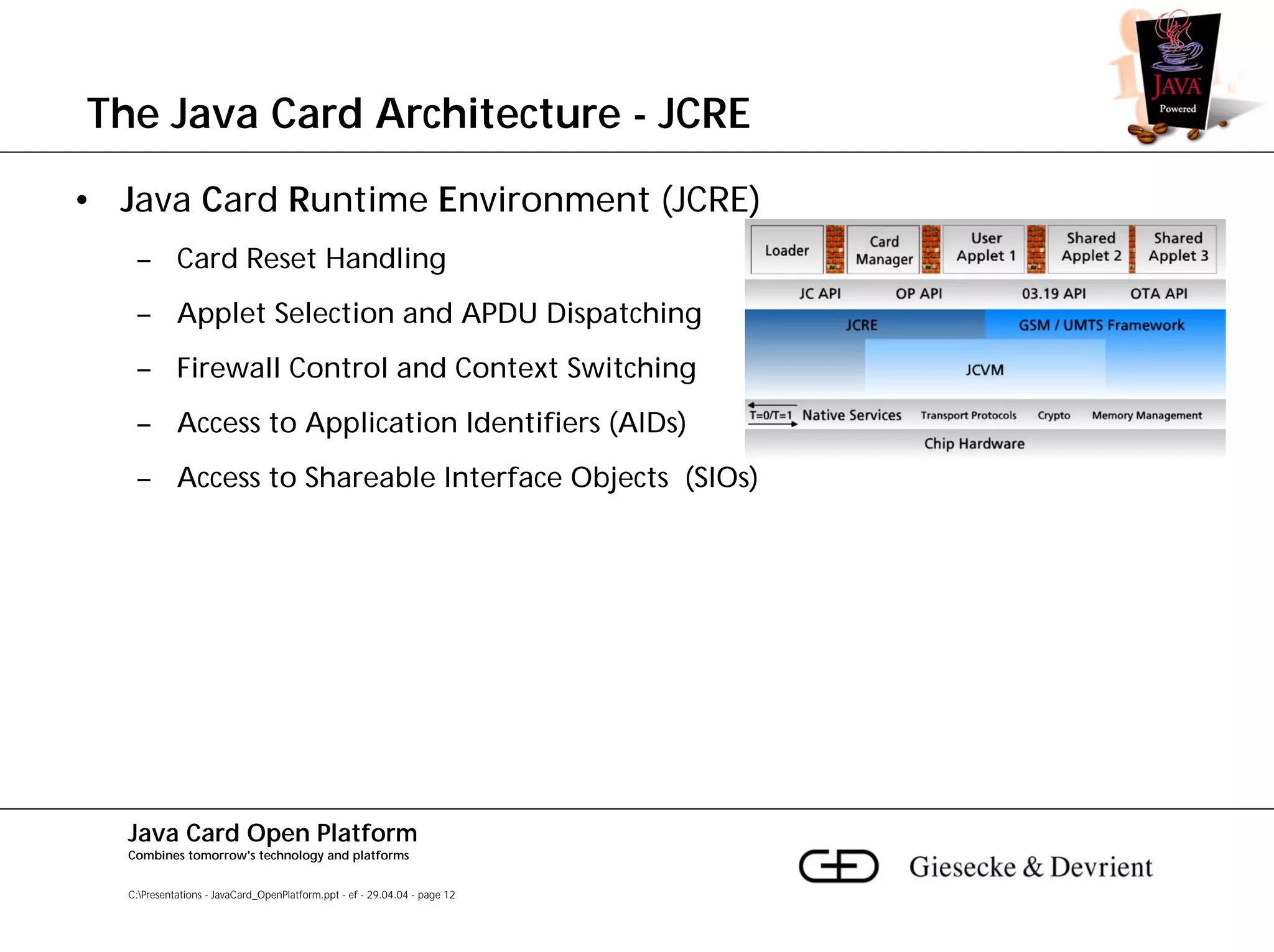
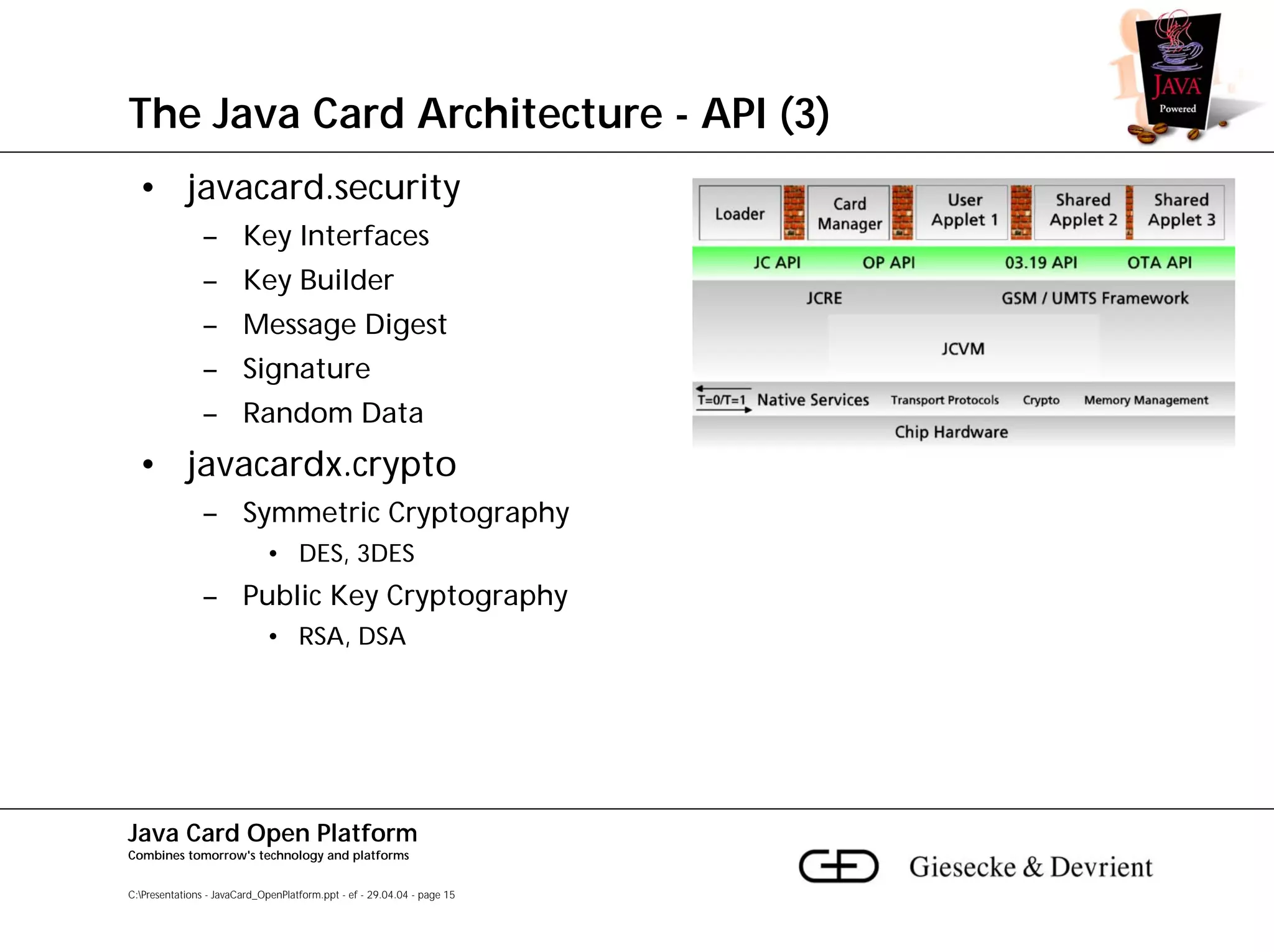
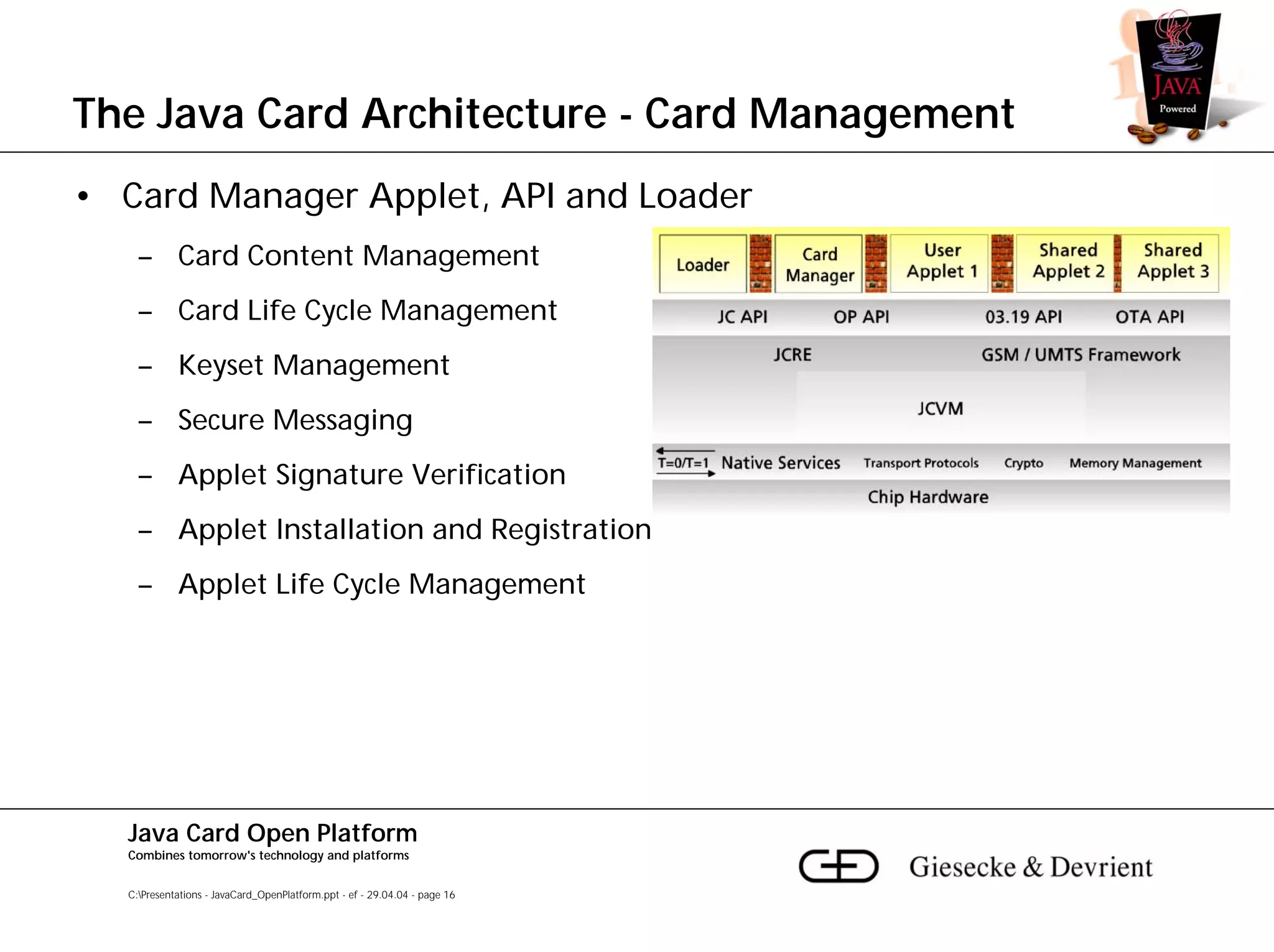
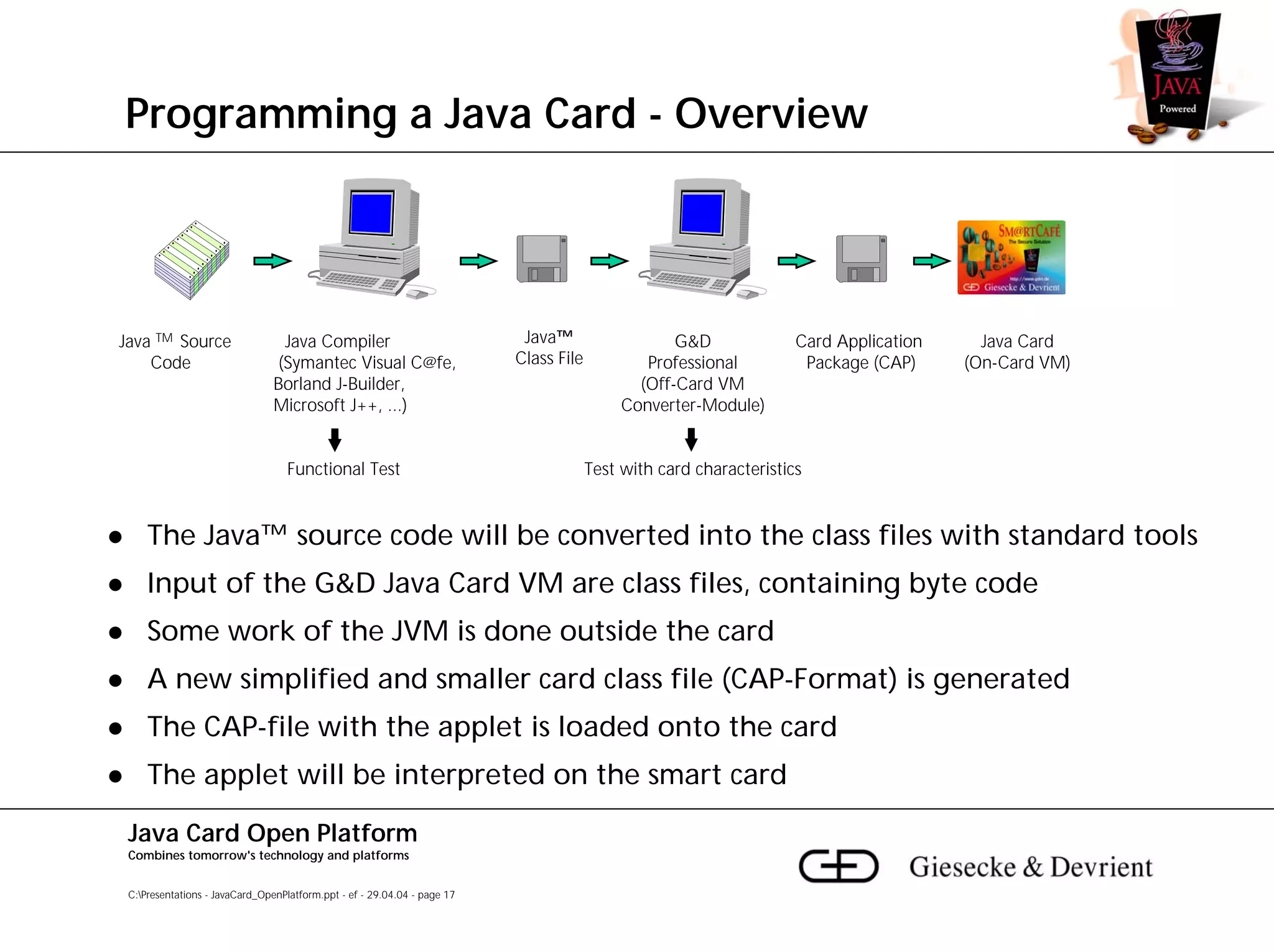
This document discusses Java Card, an open platform for smart cards that allows "write once, run anywhere" functionality. It provides background on Java Card, including that it allows multi-application smart cards and secure application loading. It then summarizes the Java Card architecture, including the hardware features, native functions, Java Card Virtual Machine (JCVM), Java Card Runtime Environment (JCRE), Java Card APIs, and card management. Finally, it provides an overview of the Java Card programming process.