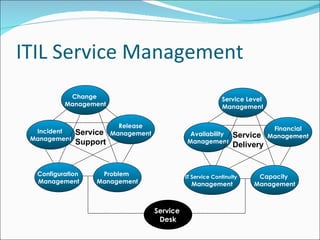
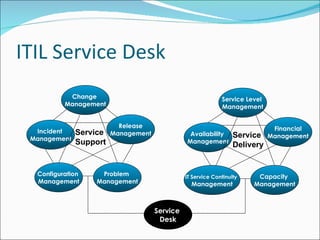
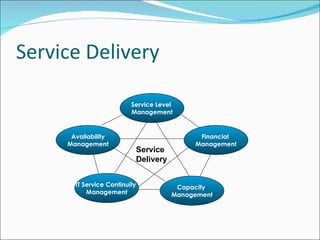
The document provides an overview of ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) service management processes. ITIL processes are divided into two main components: Service Support which focuses on day-to-day operations, and Service Delivery which focuses on long-term planning and improvement. Key processes include Change Management, Release Management, Incident Management, Problem Management, and Configuration Management. The goals, definitions, and activities of each process are described at a high level.