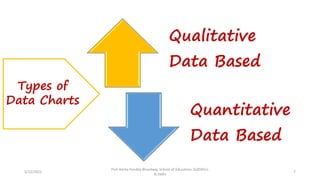
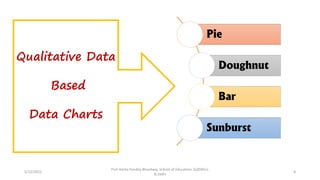
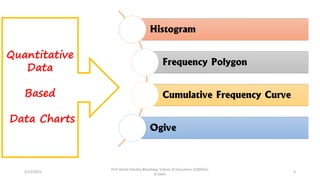
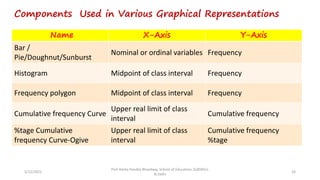
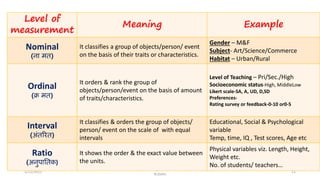
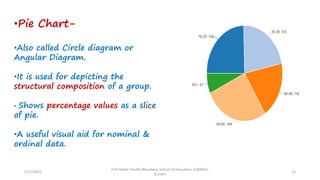
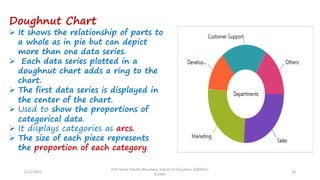
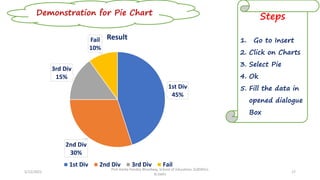
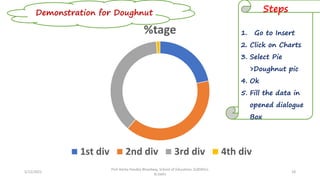
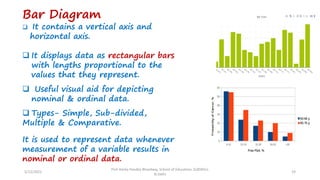
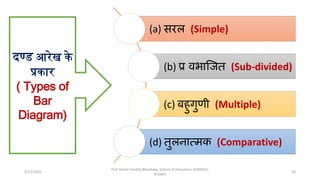
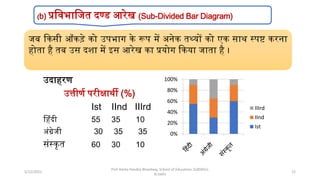
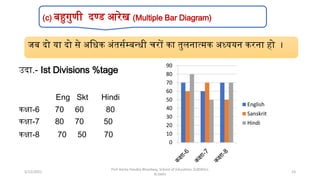
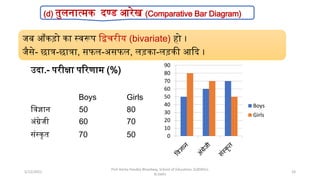
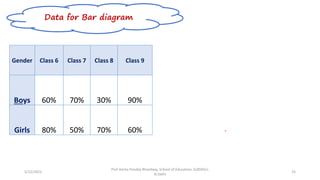
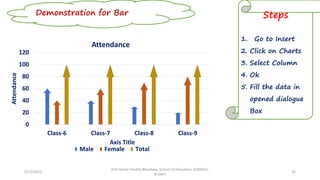
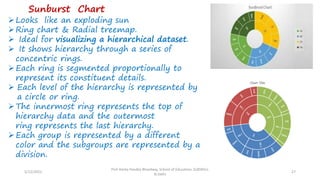
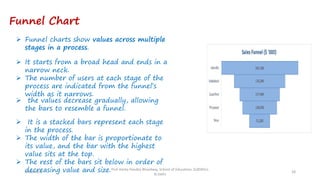
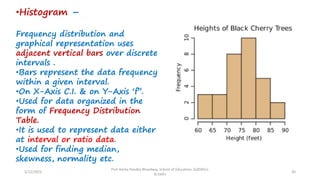
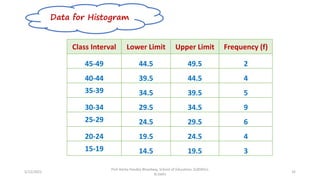
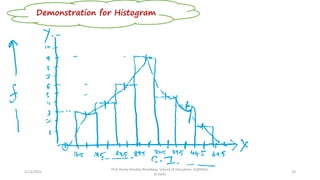
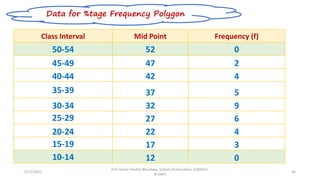
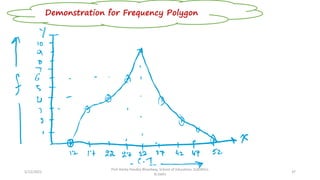
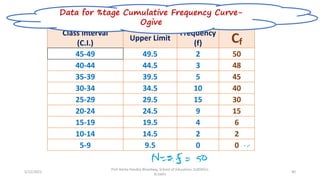
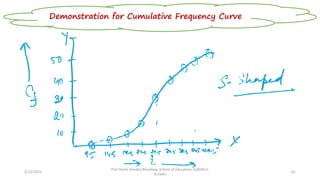
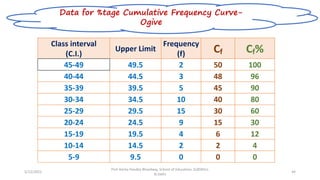
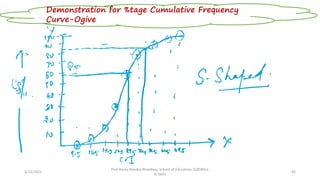
The document discusses various types of pictorial data presentation charts for qualitative and quantitative data. It describes charts like pie charts, bar diagrams, histograms etc. and provides examples of how each chart can be used to represent different types of data. Steps for creating pie, doughnut, bar charts in MS Office are demonstrated. Qualitative data charts include pie, doughnut, bar and sunburst charts while quantitative charts include histogram, frequency polygon, cumulative frequency curve and ogive.