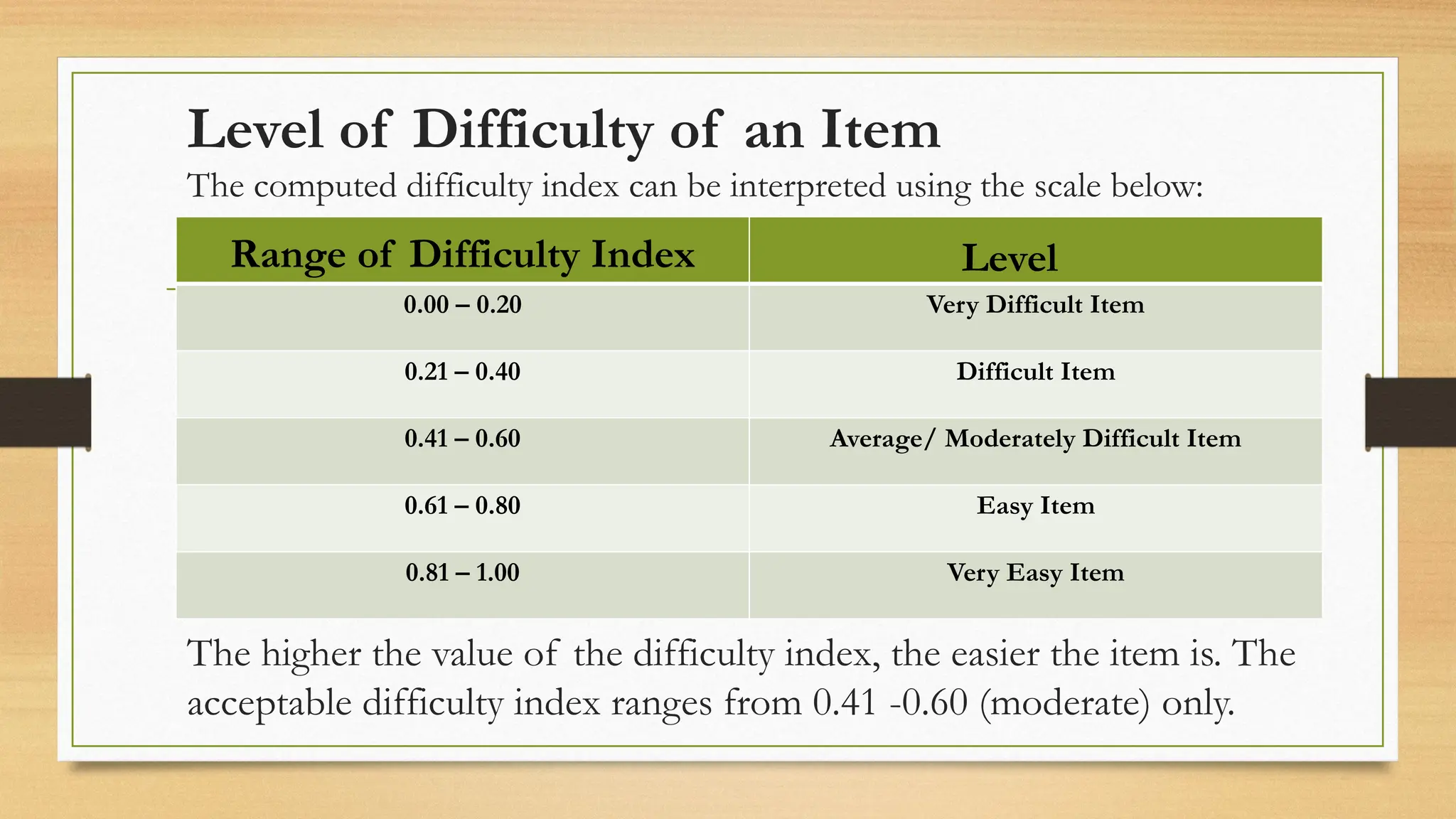
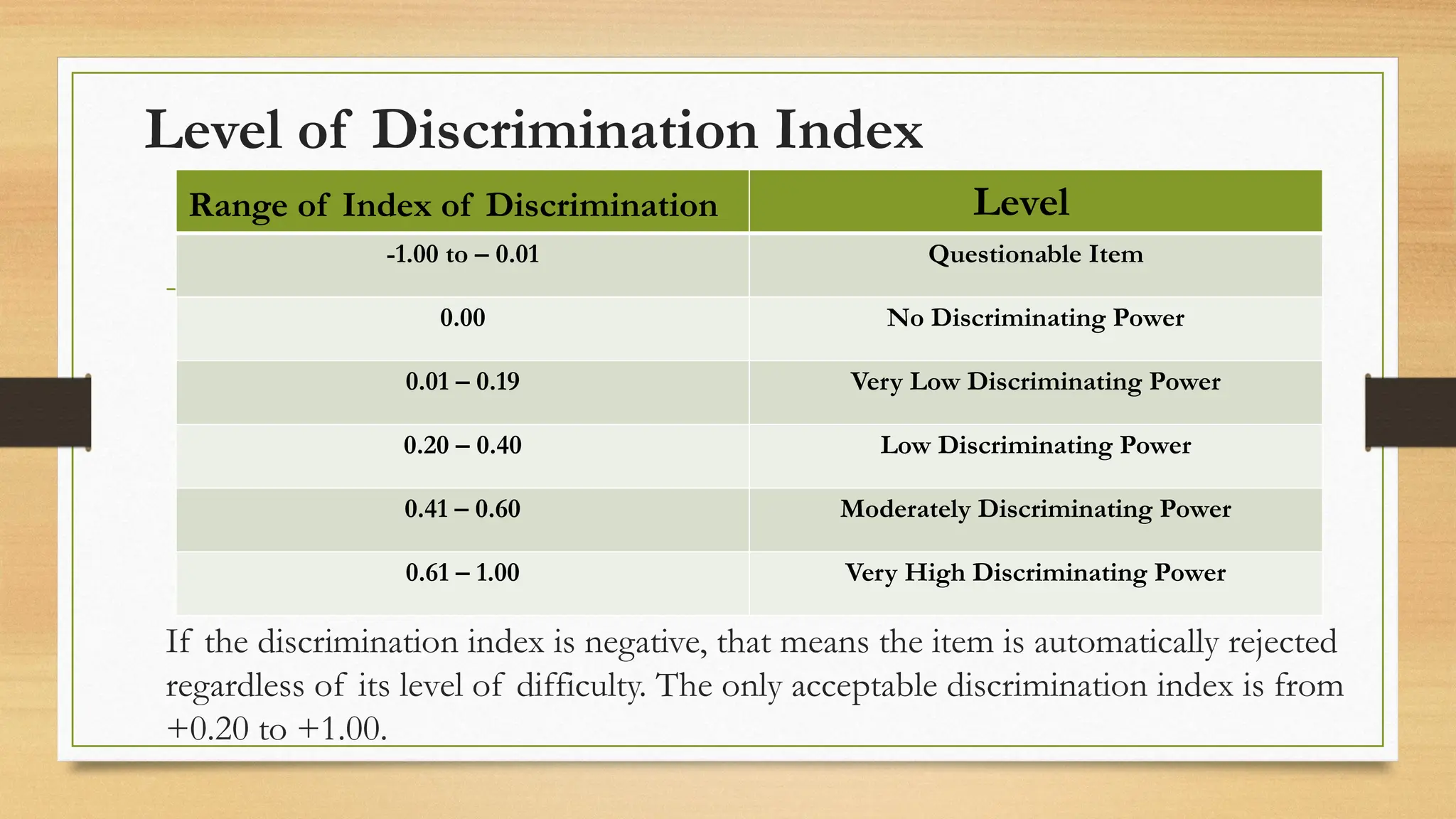
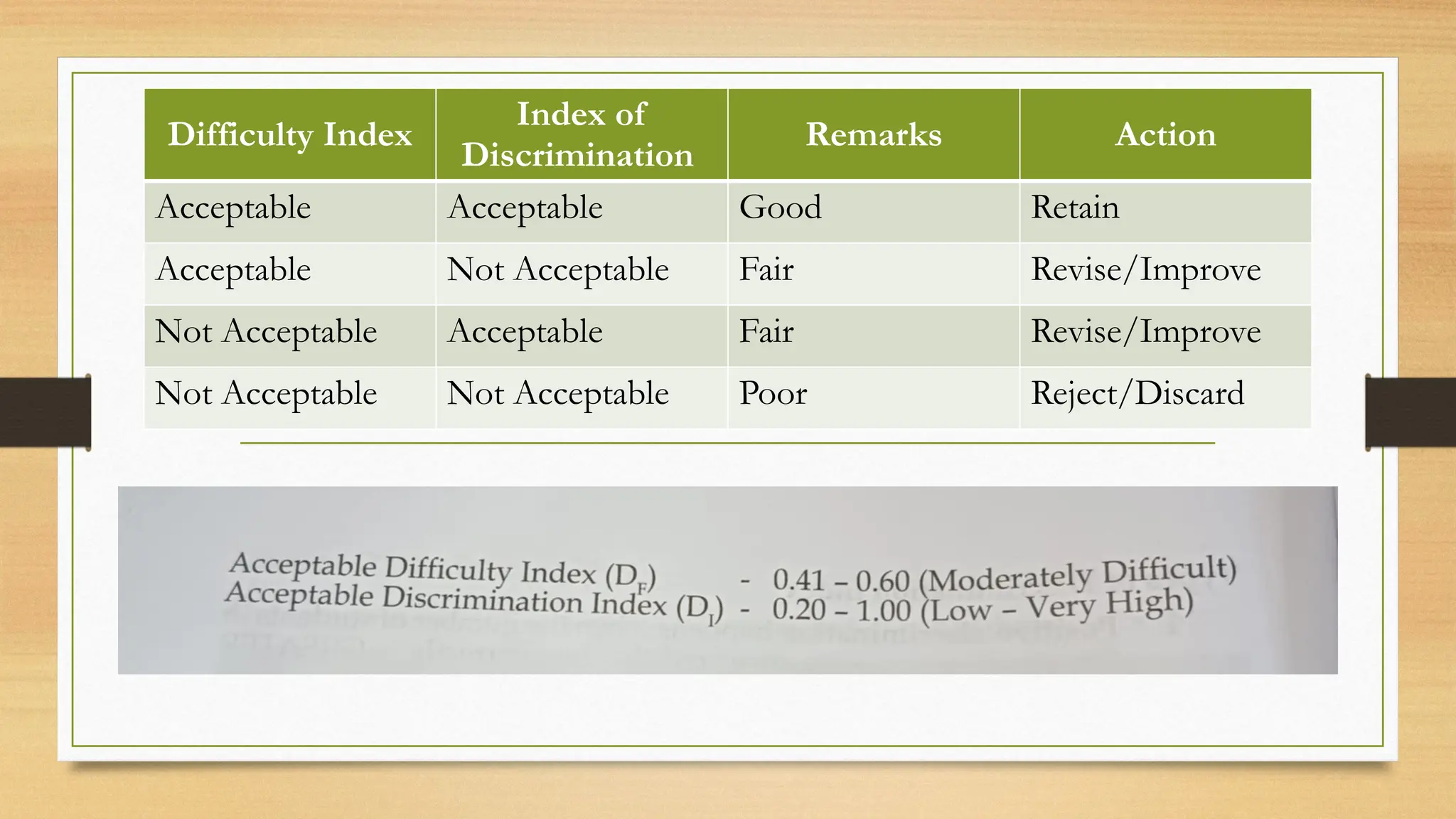
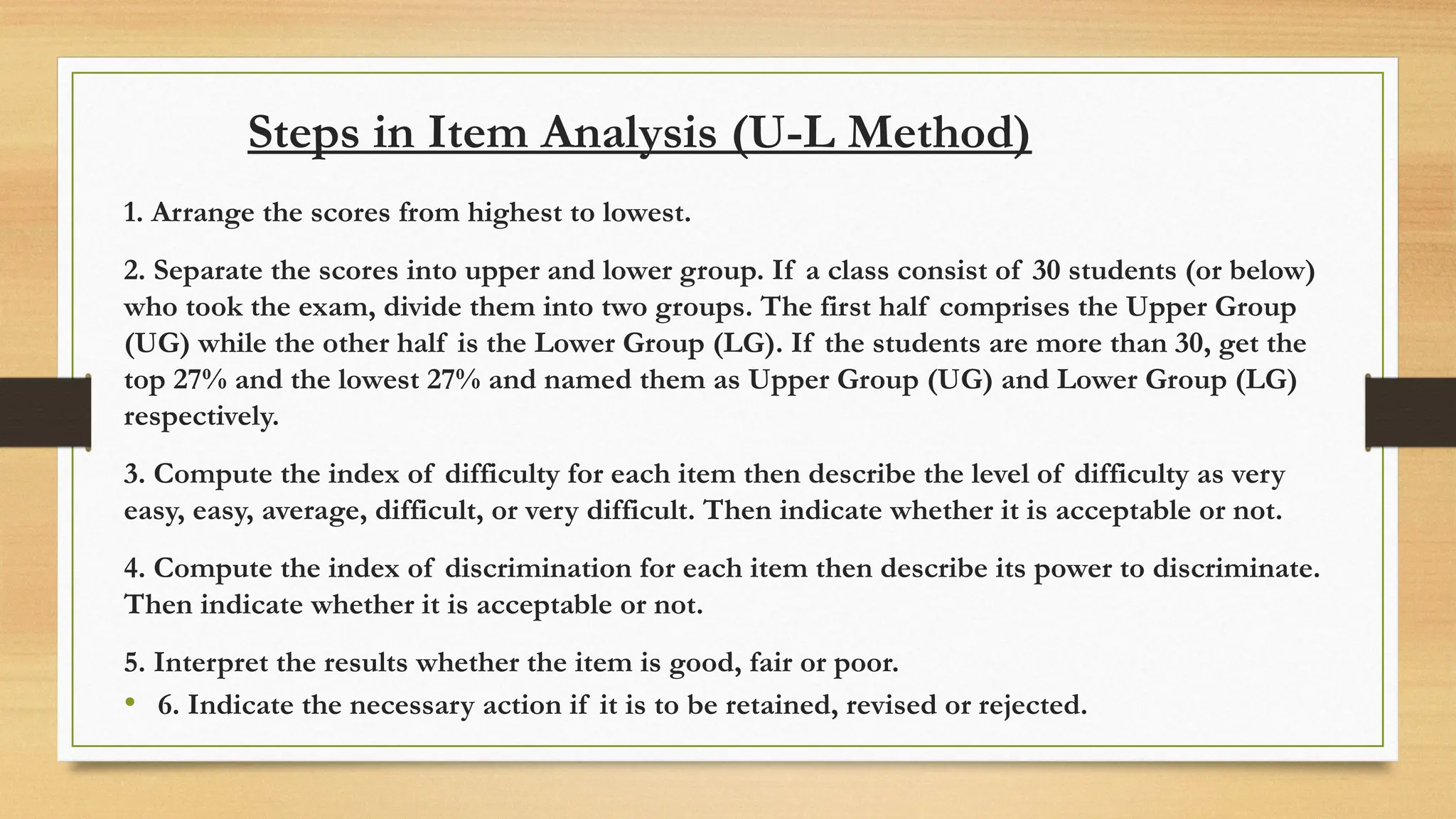
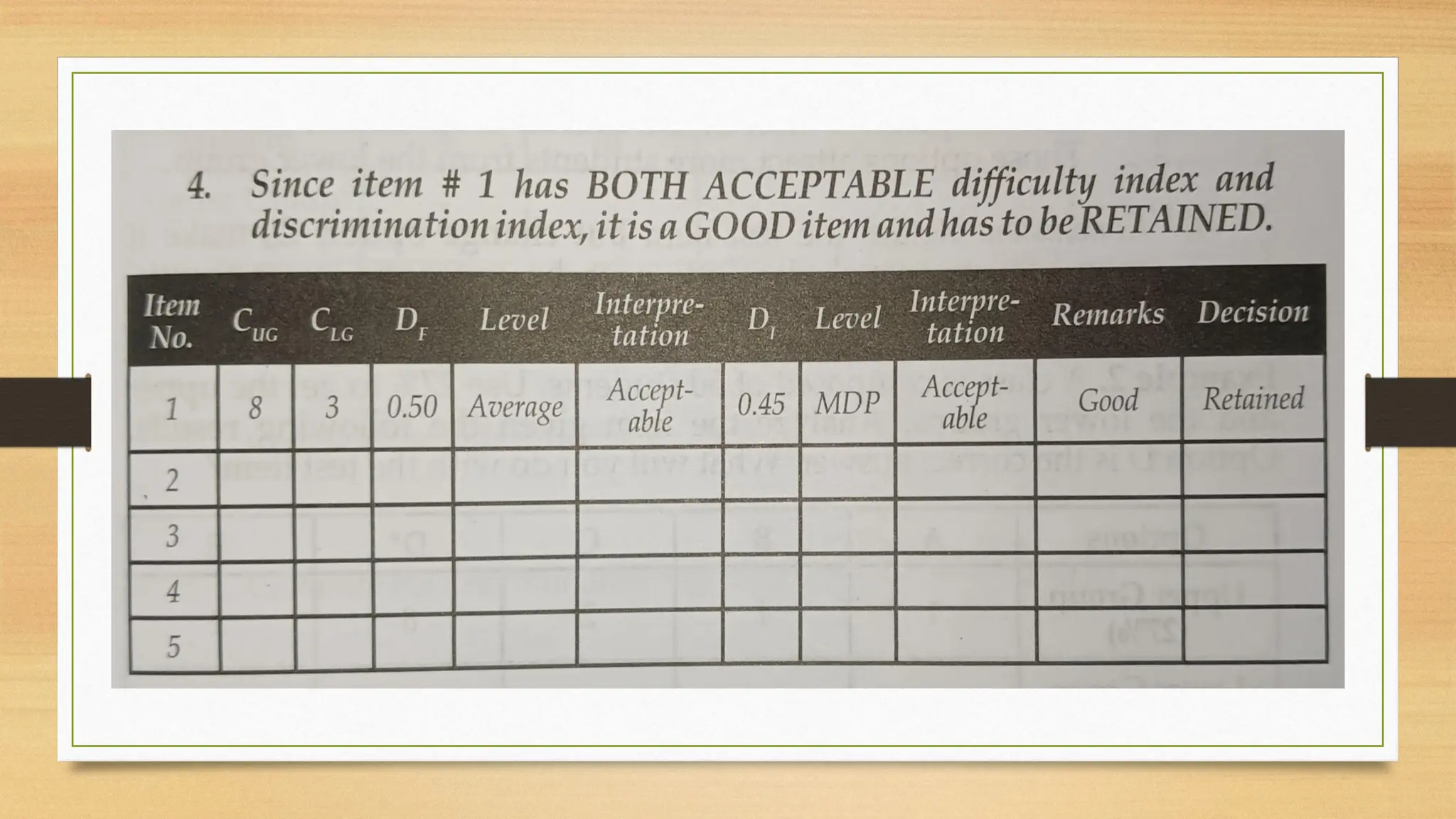
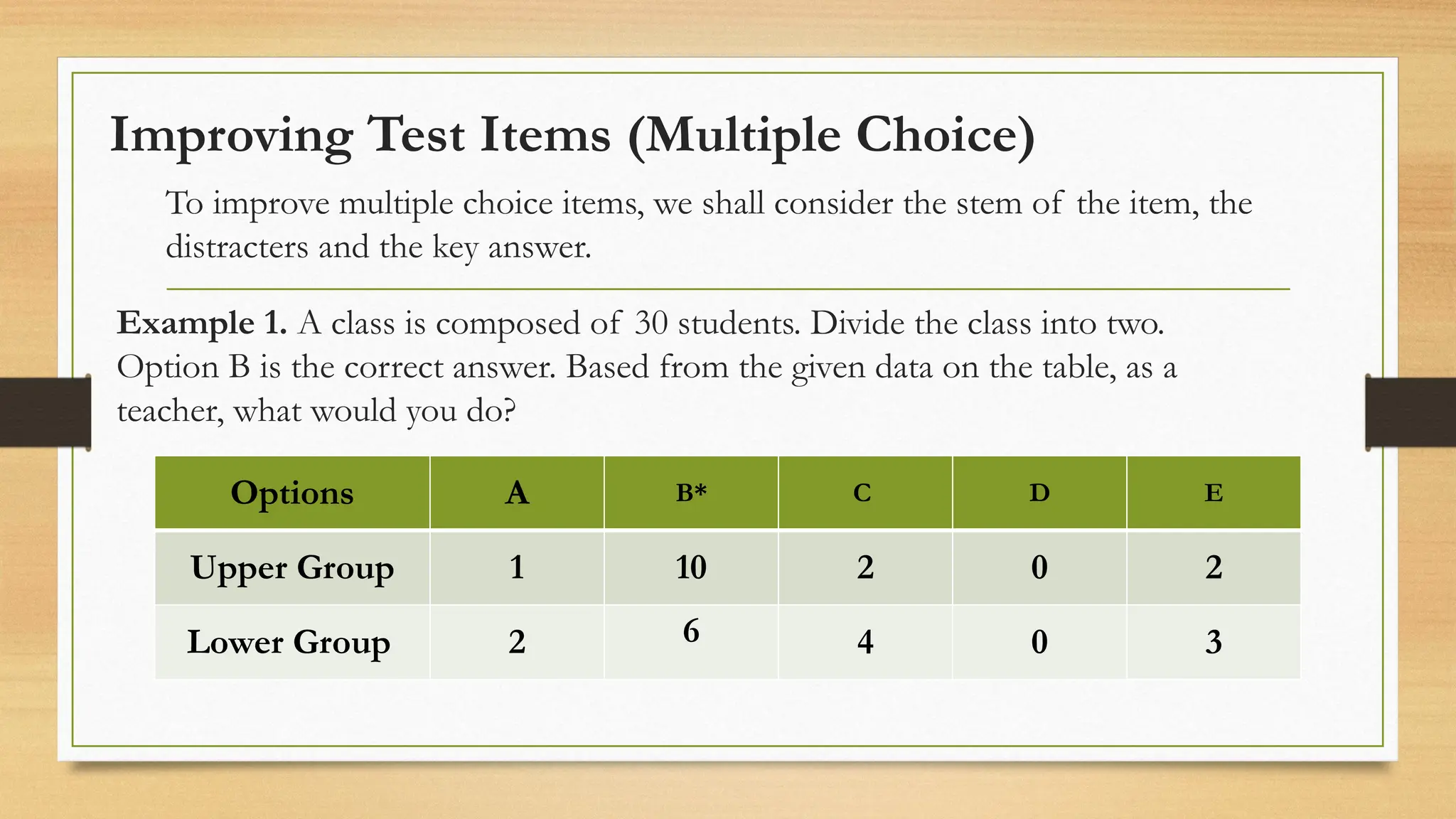
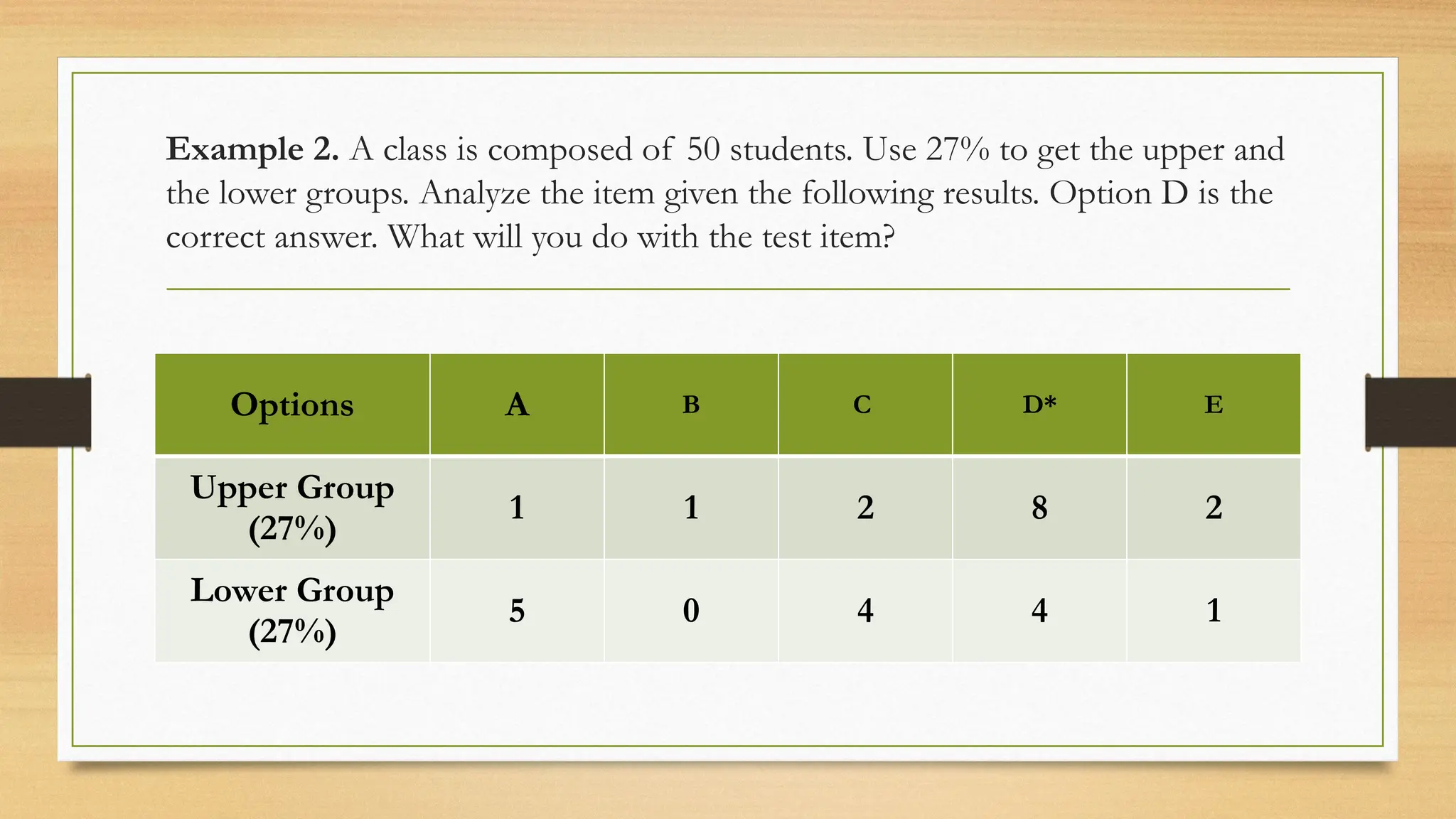
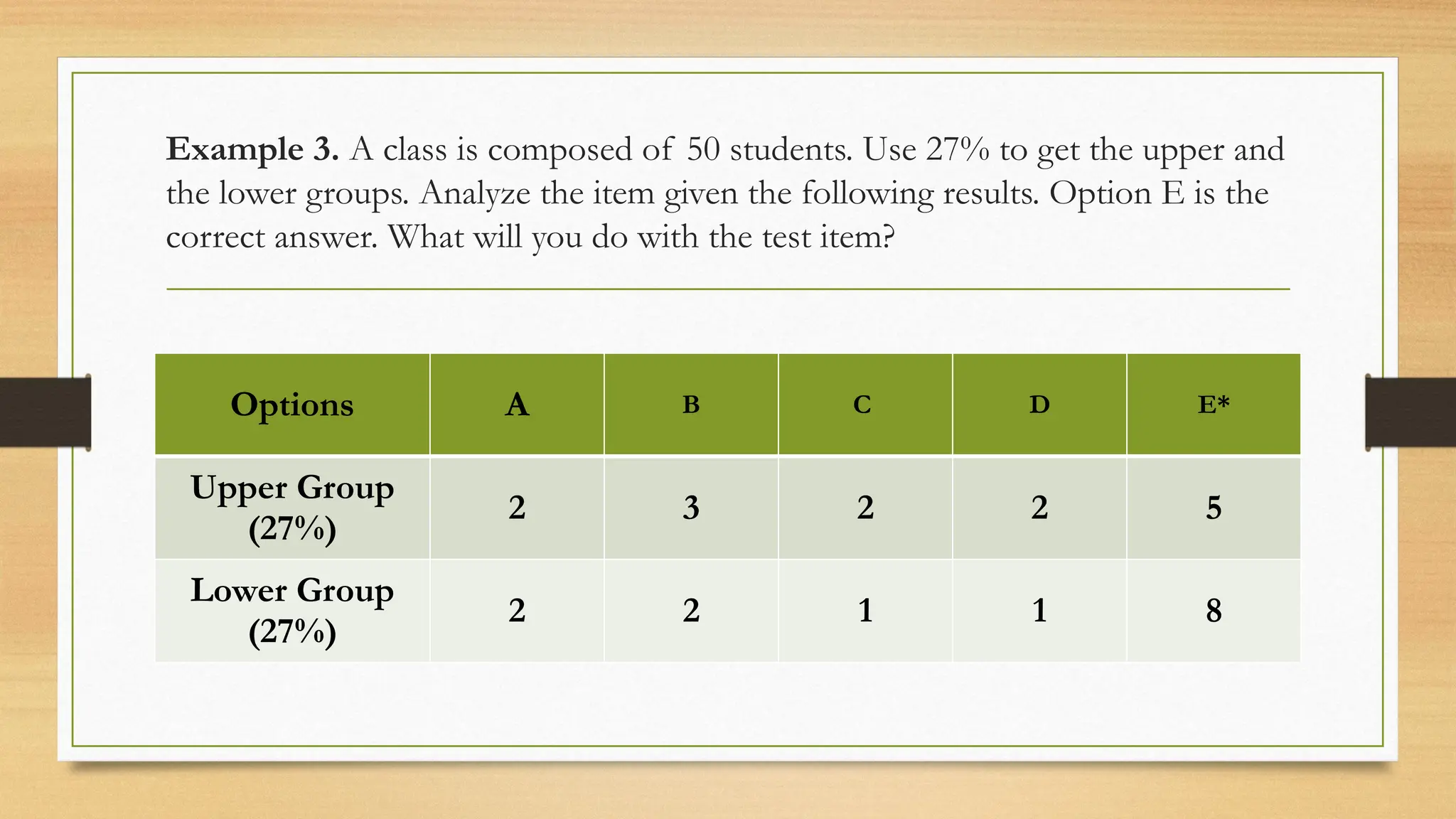
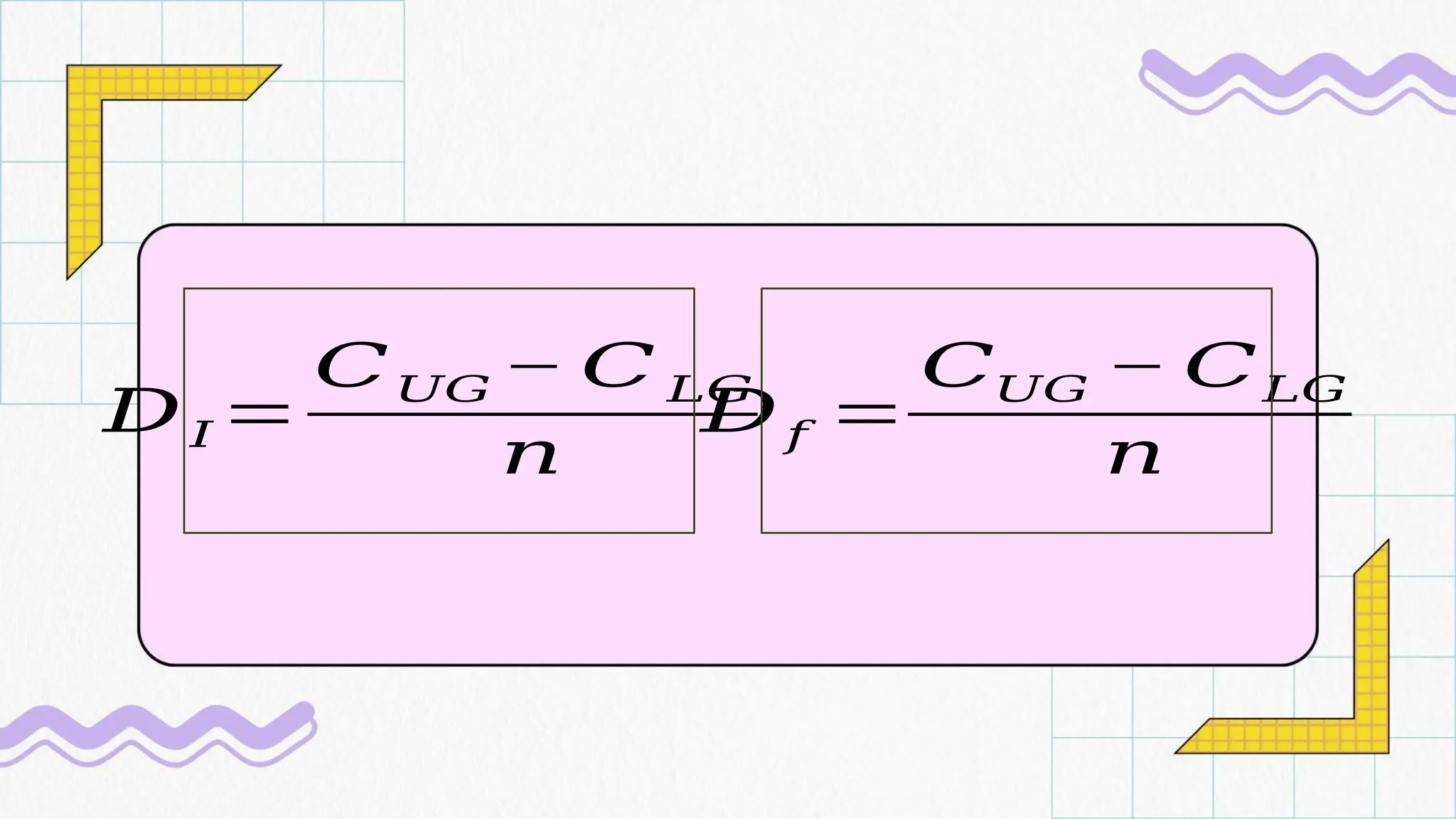The document details processes for administering, analyzing, and improving test items, focusing on difficulty and discrimination indices to evaluate item quality. It introduces two types of item analysis: quantitative, which assesses the difficulty and discrimination power of items, and qualitative, which involves proofreading tests for errors. The document also provides instructional guidelines on how to interpret indices and improve test items based on analysis results.