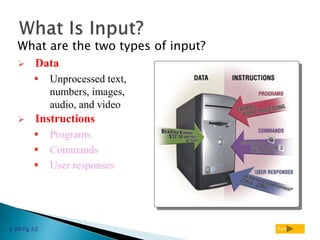
The document discusses input devices, which are hardware components used to enter data or instructions into a computer. It covers various types of input devices, including keyboards, mice, trackballs, touchpads, joysticks, and voice recognition, explaining their functions and uses. Additionally, it outlines the operation of these devices, including commands and alternatives like keyboard shortcuts.