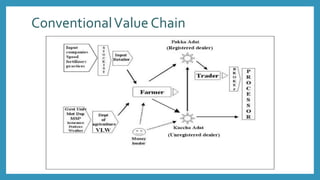
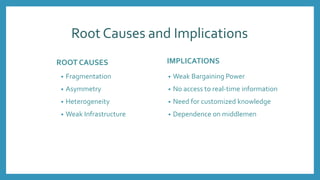
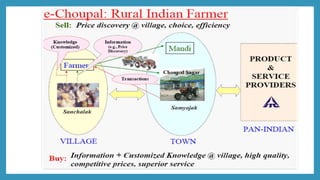
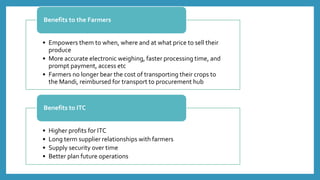
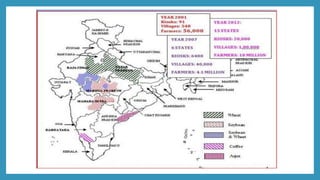
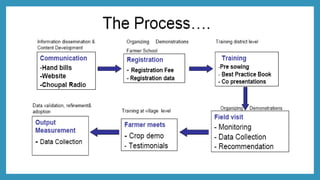
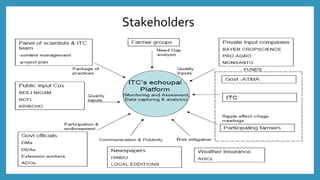
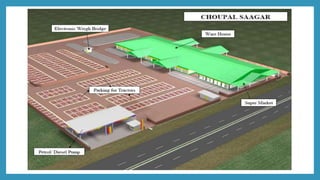
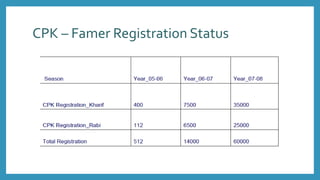
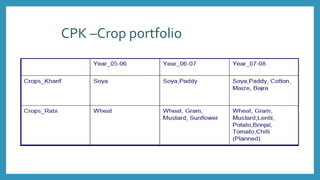
ITC launched its e-Choupal initiative in 2000 to address inefficiencies in the agricultural supply chain in India. The key aspects of the e-Choupal model are: (1) it establishes internet kiosks in rural areas managed by local farmers called "Sanchalaks" to provide farmers price information and facilitate sales, (2) it creates transparency in the supply chain and eliminates middlemen, (3) it has expanded to provide farmers additional services and products through initiatives like Choupal Pradarshan Khet, Choupal Saagar, and Choupal Fresh. The e-Choupal model has benefited both farmers through better prices and access to information and ITC through improved