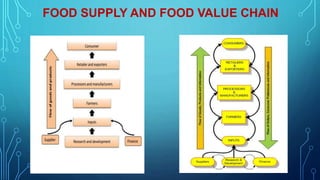
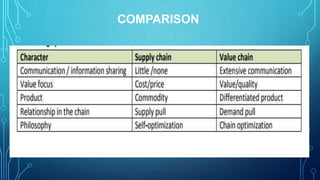
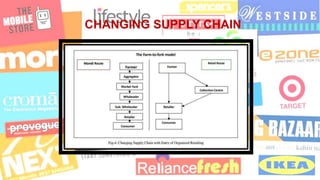
The document discusses the prospects and challenges of the agricultural supply chain in India. It outlines problems in the current supply chain such as poor infrastructure, lack of adequate warehousing and cold storage facilities, and access to finance for farmers. It then discusses opportunities to improve the supply chain through public-private partnerships for warehousing, expanding cold storage, strengthening information systems, and enabling farmers. The document also compares food supply chains to more sustainable value chains and provides case studies of different models linking farmers to markets.