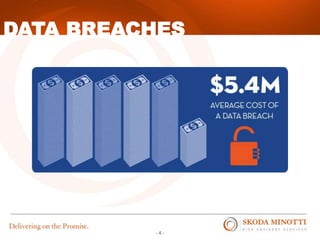
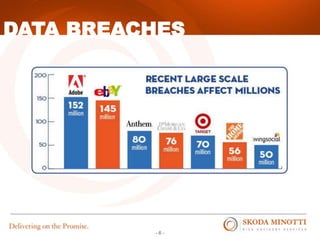
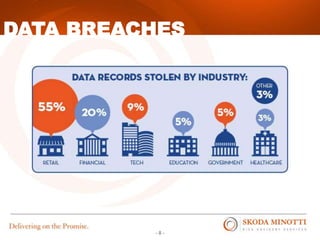
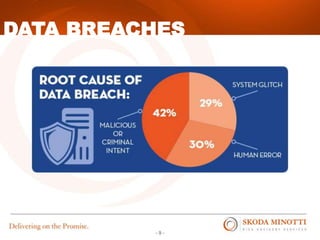
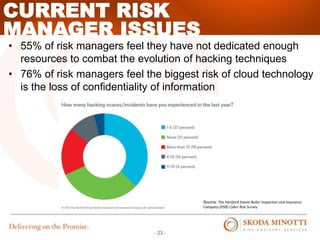
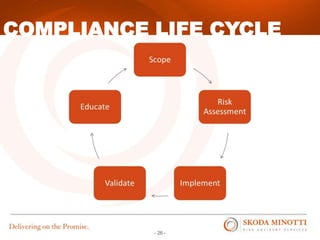
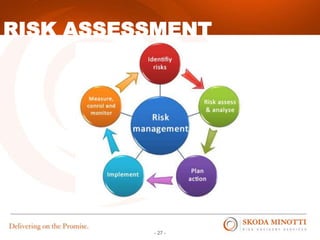
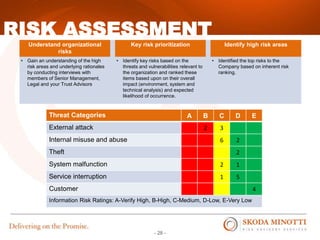
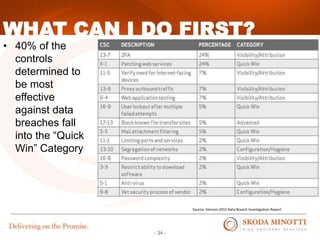
This document provides an overview of IT security essentials and data security best practices. It discusses common data security concerns, including access controls, encryption, APIs, auditing and more. Specific frameworks and standards are also reviewed, such as PCI DSS, NIST and ISO. The document outlines steps for conducting a risk assessment and implementing controls. It emphasizes quick wins can be achieved through controls in areas like access management, encryption, patching and monitoring. Overall the document serves to educate about the threat landscape, compliance obligations and how to establish an effective data security program.