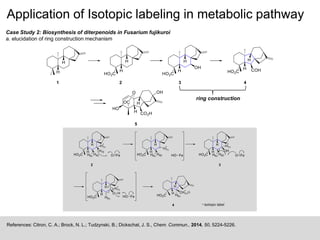
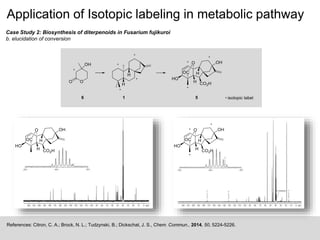
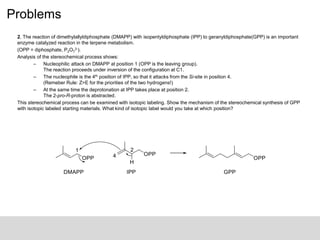
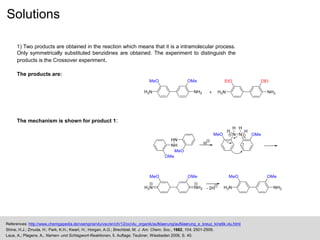
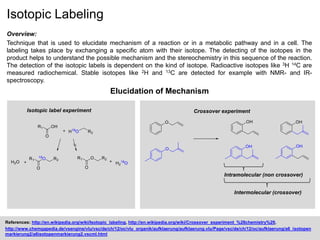
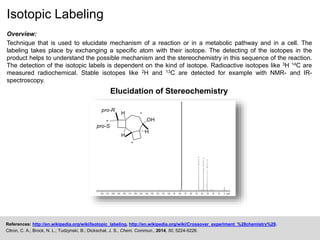
The document discusses isotopic labeling as a technique to elucidate reaction mechanisms and metabolic pathways by exchanging specific atoms with their isotopes. It details the detection methods for various isotopes and presents case studies on sulfur volatile production in marine bacteria and biosynthesis of diterpenoids in fungi. Additionally, it emphasizes the application of isotopic labeling in understanding stereochemistry and reaction mechanisms through experimental studies.
![Application of Isotopic labeling in metabolic pathway
References: Brock, N. L.; Mencke, M.; Klapschinski, T. ; Dickschat, J. S., Org. Biomol. Chem., 2014, 12, 4318-4323; Brock, N. L.; Citron, C. A.; Zell,
C.;Berger, M.; Wagner-Doebler, I.; Petersen, J.; Brinkhoff, T.; Simon, M.; Dickschat, J. S., Beilstein J. Org. Chem., 2013, 9, 942-950.
Case Study 1: Sulfur volatiles production from the Roseobacter clade
Dimethylsulfoniopropionate (DMSP) is one of the most important organic sulfur metabolite in marine environment and is degraded
by marine bacteria in two competing pathways. Demethylation Pathway forms methanethiol (MeSH), while the Cleavage Pathway
forms dimethylsulfide (DMS). For the distinct conclusion on the sulfur source for the volatile sulfur compounds, [34S]DMSP was
synthesized and used in a feeding experiment.
Demethylation
Pathway
Cleavage
Pathway
The sulfur volatiles emitted by the bacteria were analysed by GC-MS and the data revealed that DMSP is efficiently degraded to
MeSH via Demethylation pathway.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/isotopiclabeling-170124162833/85/Isotopic-labeling-4-320.jpg)