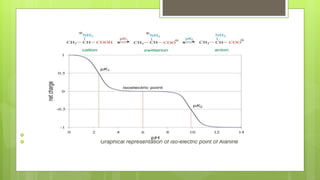
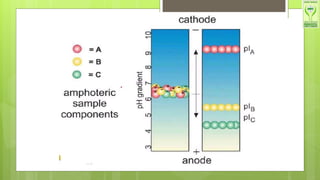
The document discusses iso-electric focusing, a technique for protein separation based on iso-electric points, which was discovered by H. Sevennson. It outlines the principle, instrumentation, advantages, and disadvantages of the method, and highlights its applications in various fields, including enzymology and forensic genetics. The document emphasizes that iso-electric focusing is the first step in 2D gel electrophoresis for protein separation.