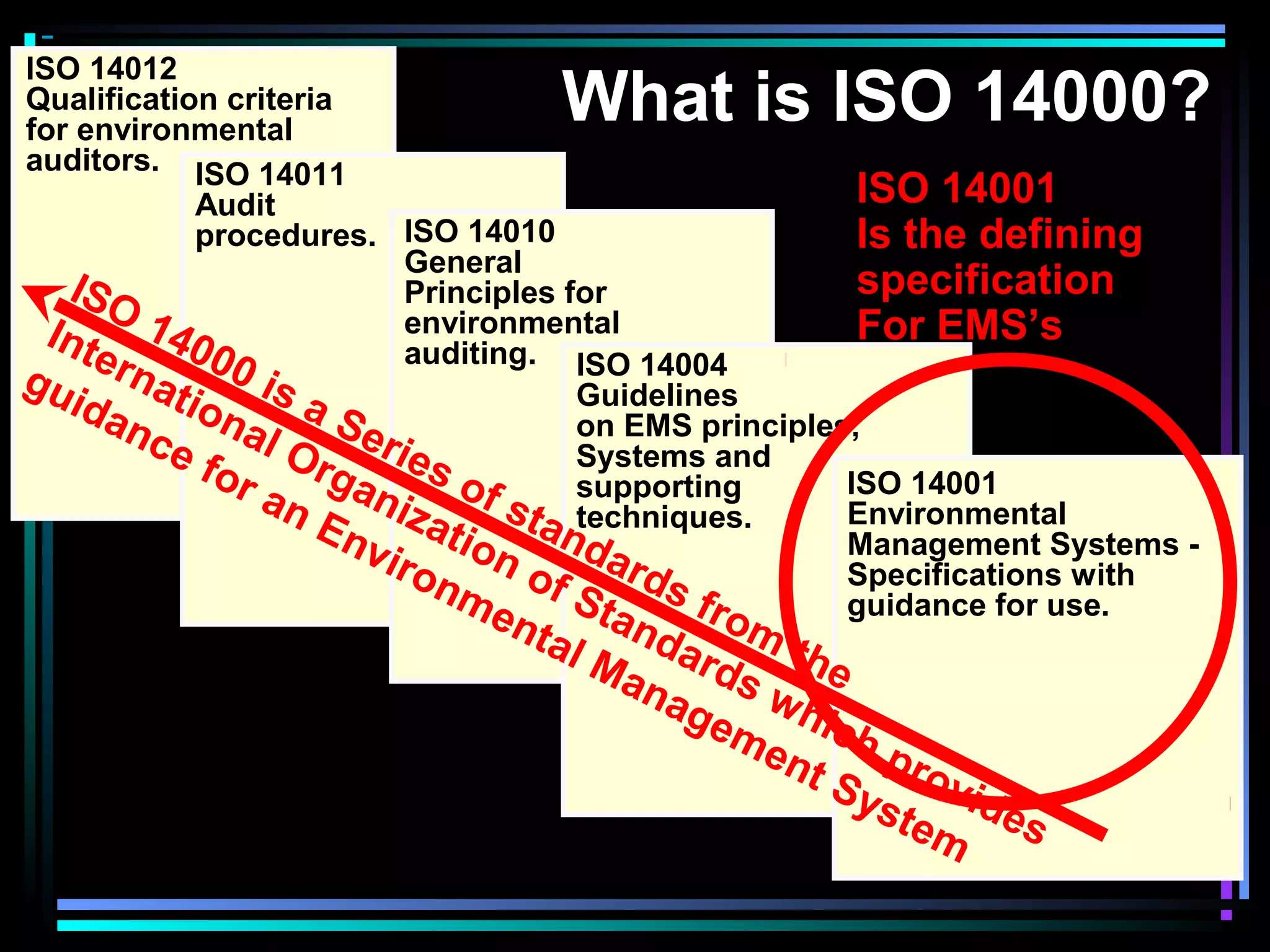
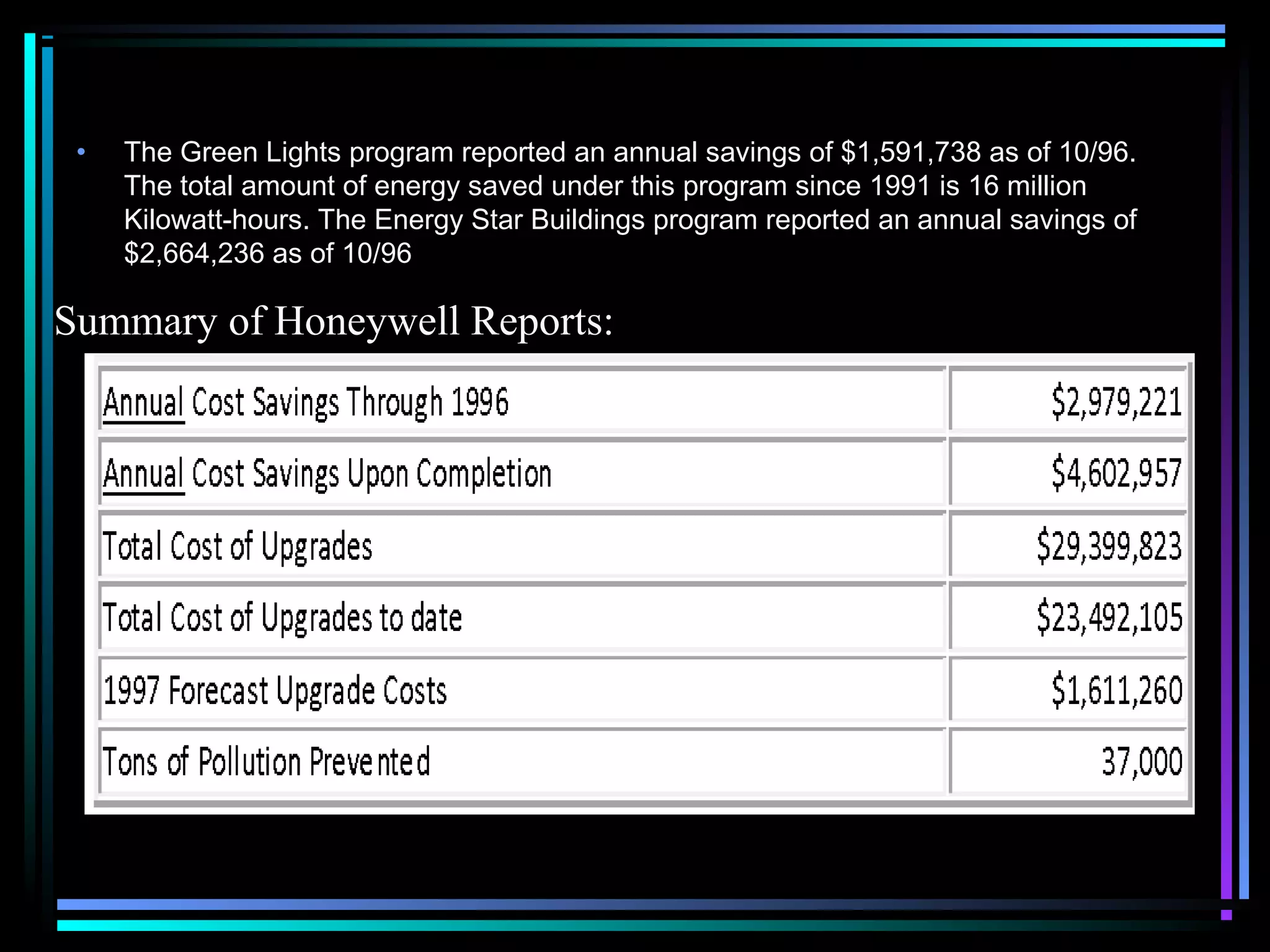
ISO 14000 is a family of standards related to environmental management. It provides guidance for organizations to minimize environmental impacts, comply with regulations, and continually improve environmental performance. The standards cover environmental management systems, auditing, labeling, and life cycle analysis. Key elements of an environmental management system include identifying environmental impacts, setting objectives and targets, defining roles and responsibilities, training, documentation, audits, management reviews, and continual improvement. An example is provided of Honeywell's efforts to improve environmental performance through programs to reduce releases, manage wastes, and save energy.