Embed presentation
Download to read offline



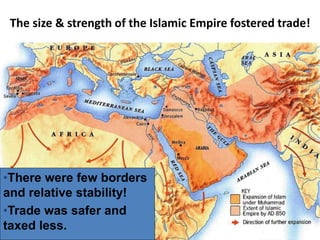










The Islamic Empire fostered extensive trade networks through its size, stability, and control of key trade routes like the Silk Road and Indian Ocean. This led to economic growth and cultural exchange as Arabic and Islamic influences spread. While political and linguistic elements changed over time and place, core religious continuities in Islam like the Quran, Five Pillars, and emphasis on Muhammad remained consistent. After Muhammad's death, a political split emerged between the Sunni and Shia sects over leadership succession.













