Between 200 BCE and 200 CE:
1) The Mauryan Empire declined, dividing India into smaller kingdoms that were invaded by foreign dynasties like the Indo-Greeks, Saka, Parthians, and Kushanas.
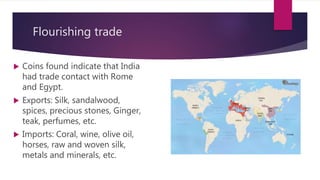
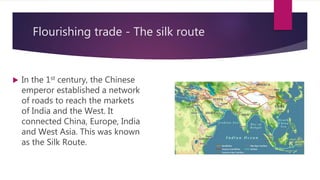
2) Trade flourished along routes like the Silk Road, exporting goods like spices and importing items like wine and metals.
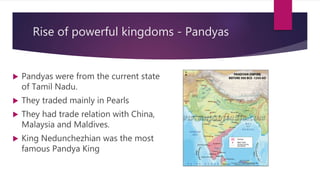
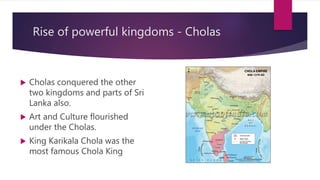
3) Powerful kingdoms like the Cheras, Pandyas, and Cholas rose in Southern India, benefiting from increased trade via sea routes.
4) Religions and culture spread across trade networks and through foreign rulers, with Buddhism spreading extensively through missionaries and travelers.