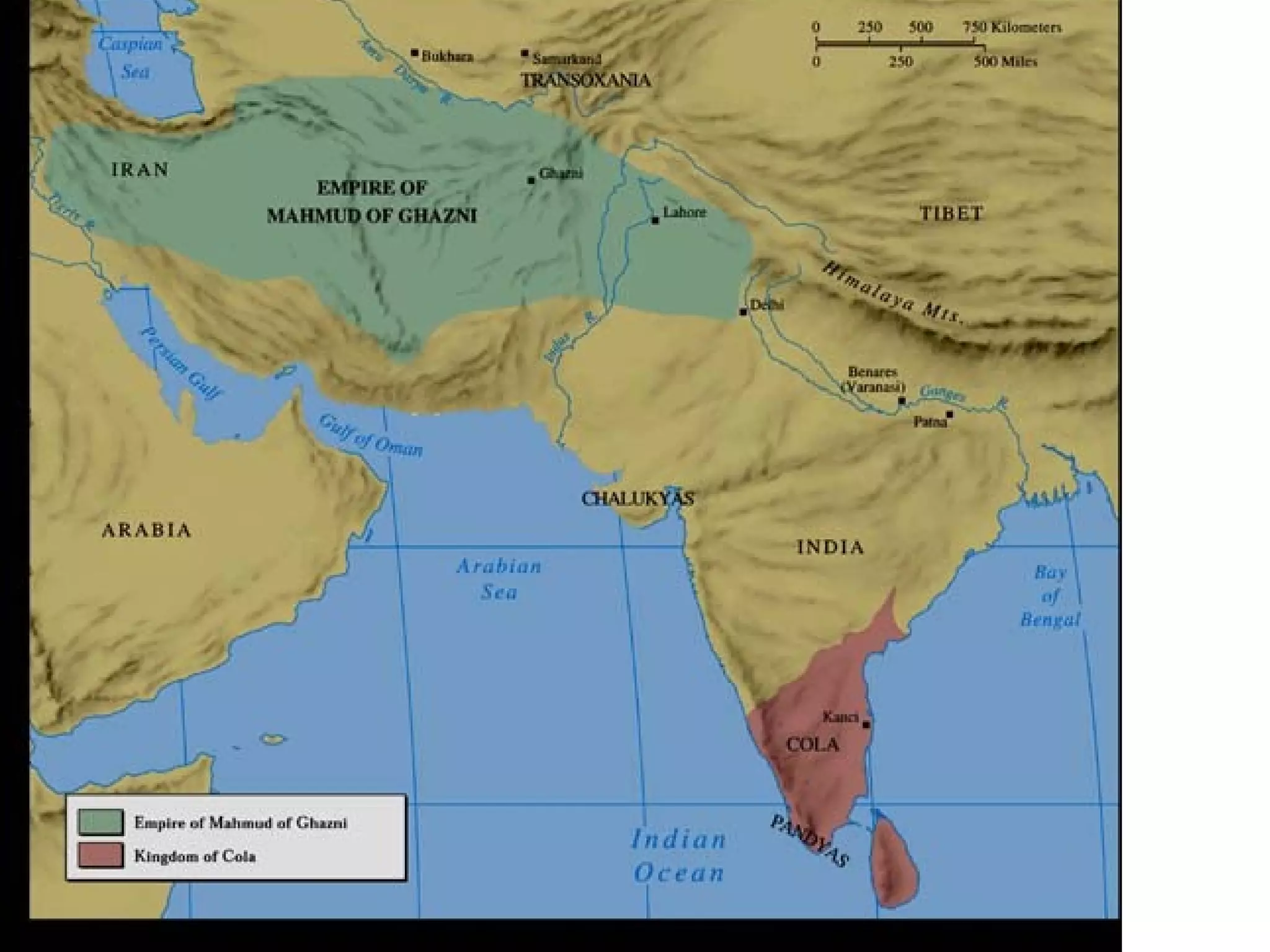
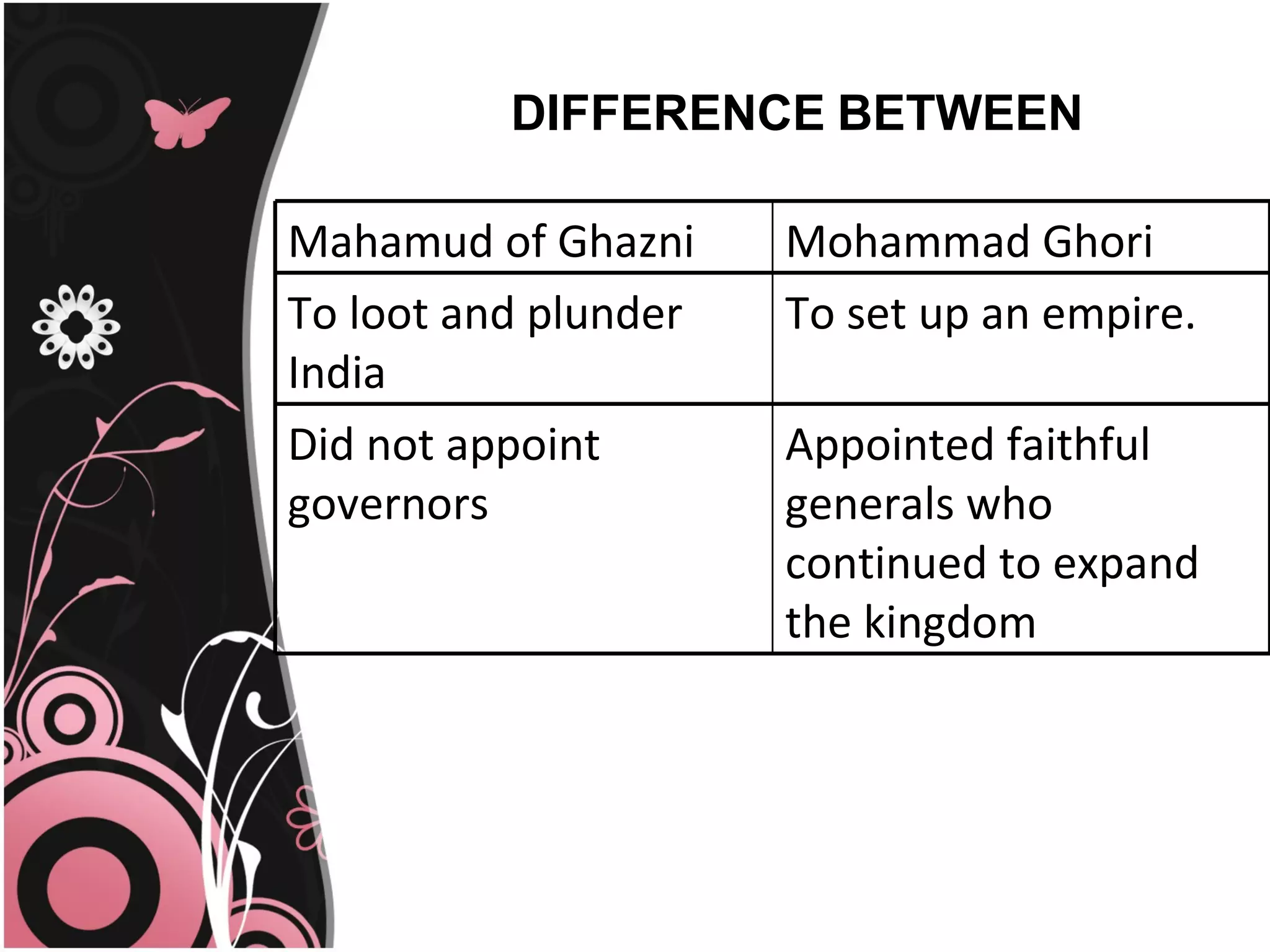
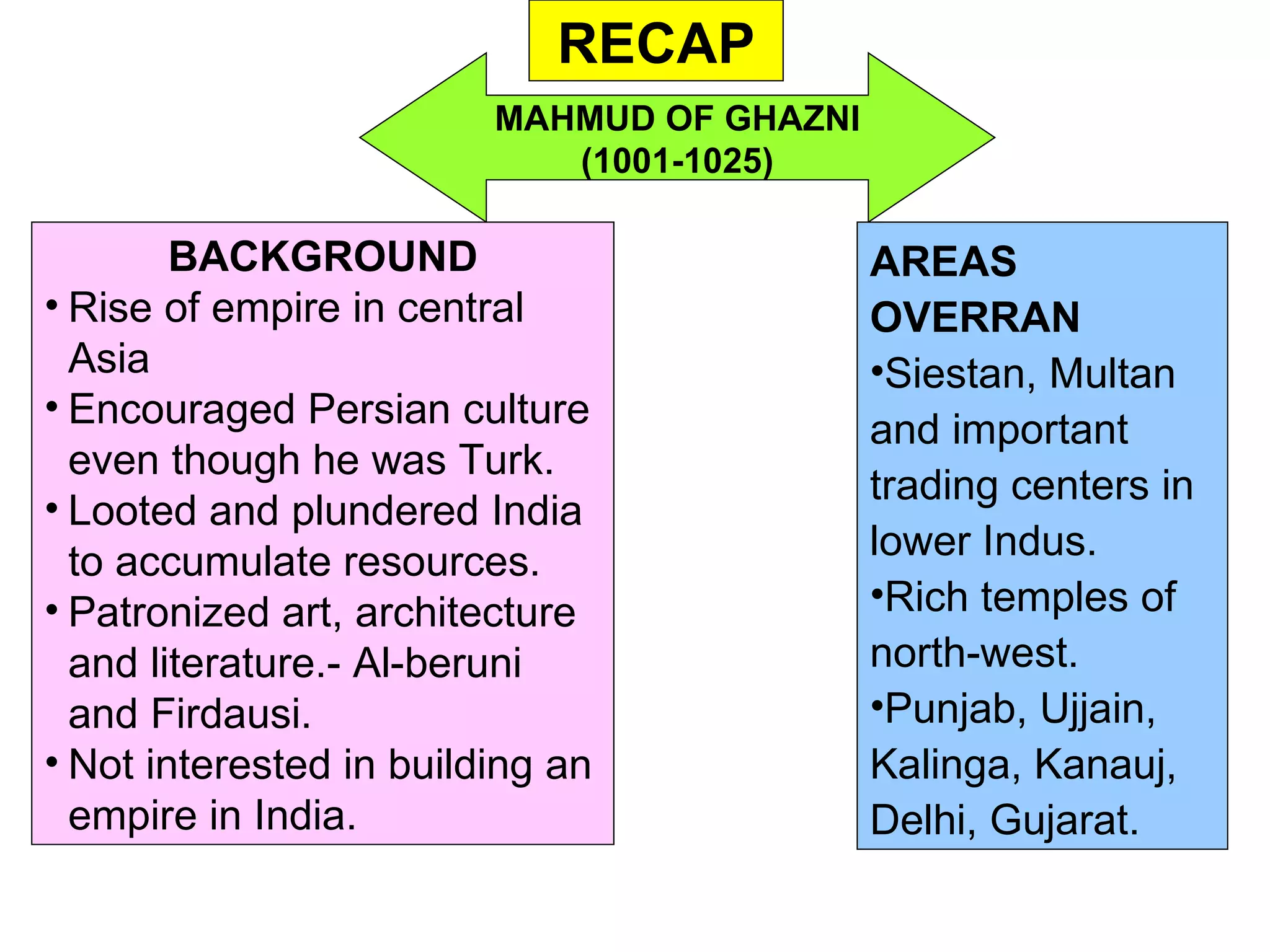
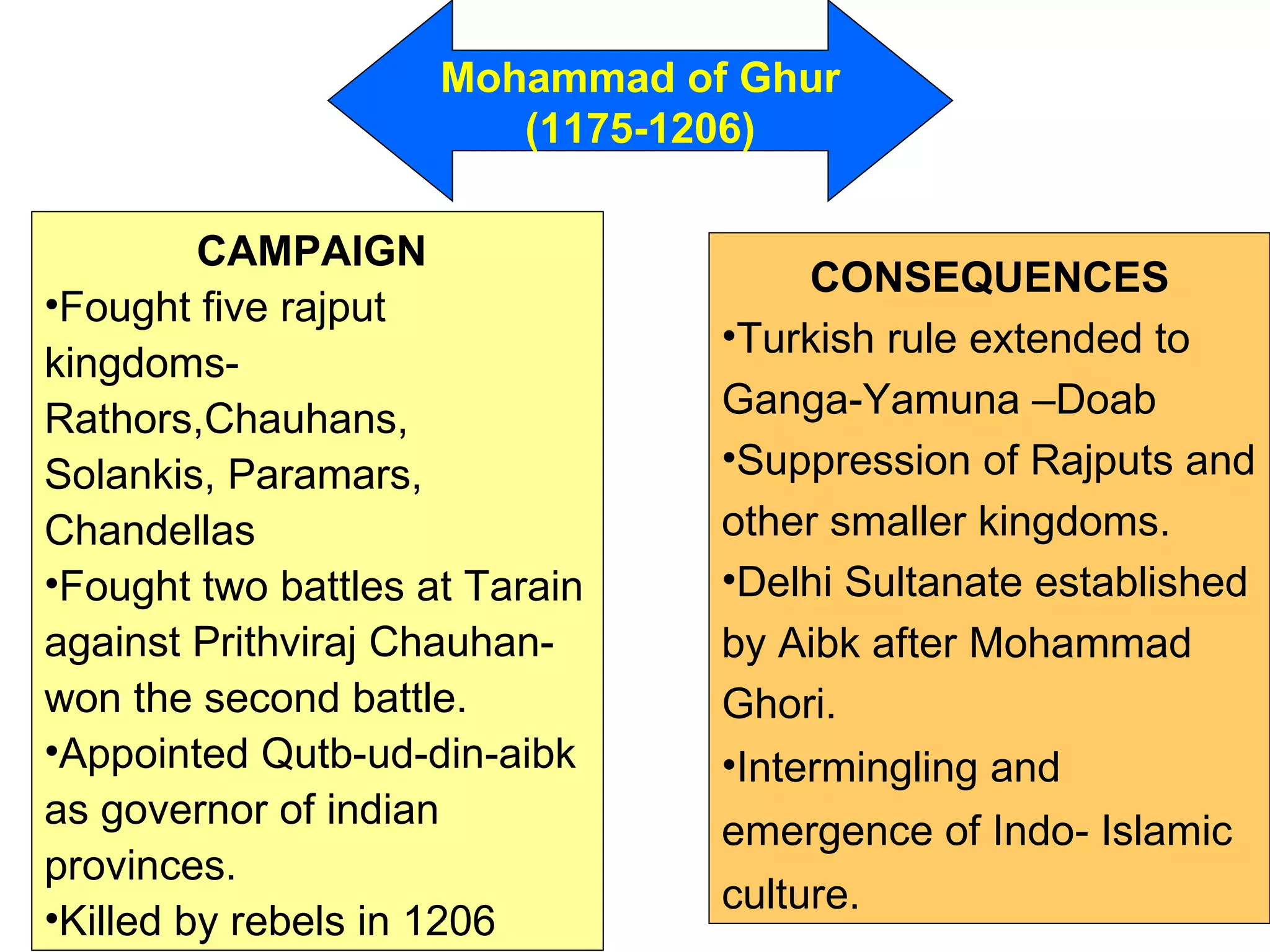
Mahmud of Ghazni and Mohammad of Ghur were rulers from the 11th-12th century who invaded northern India from their power bases in Ghazni and Ghur, located in modern day Afghanistan. Mahmud raided India 17 times between 1001-1025, plundering wealthy temples and cities to fund his empire. Mohammad of Ghur conquered the Rajput kingdoms in the late 12th century and established the Delhi Sultanate under his general Qutb al-Din Aibak, laying the foundations for Turkic rule in northern India.