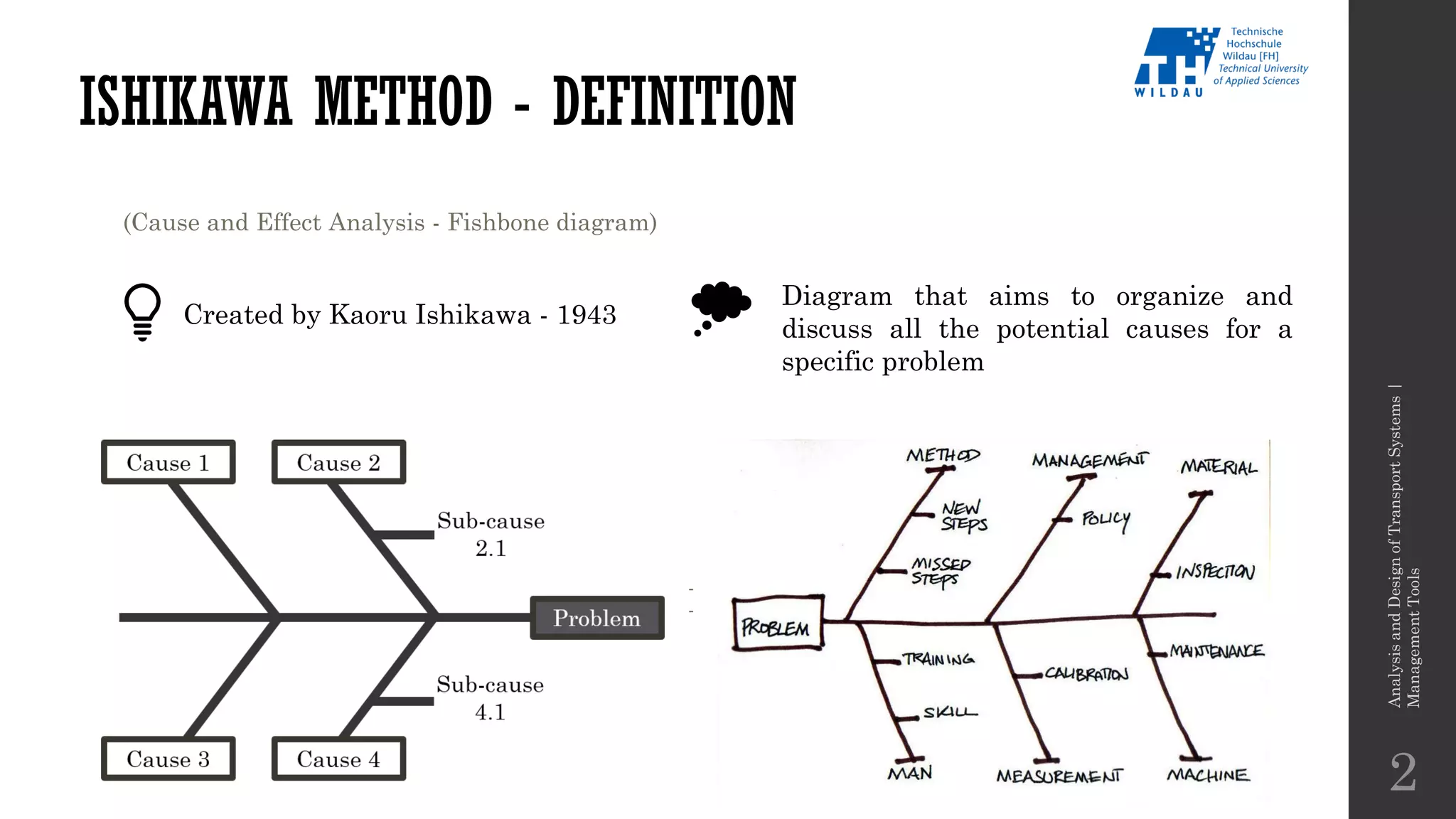
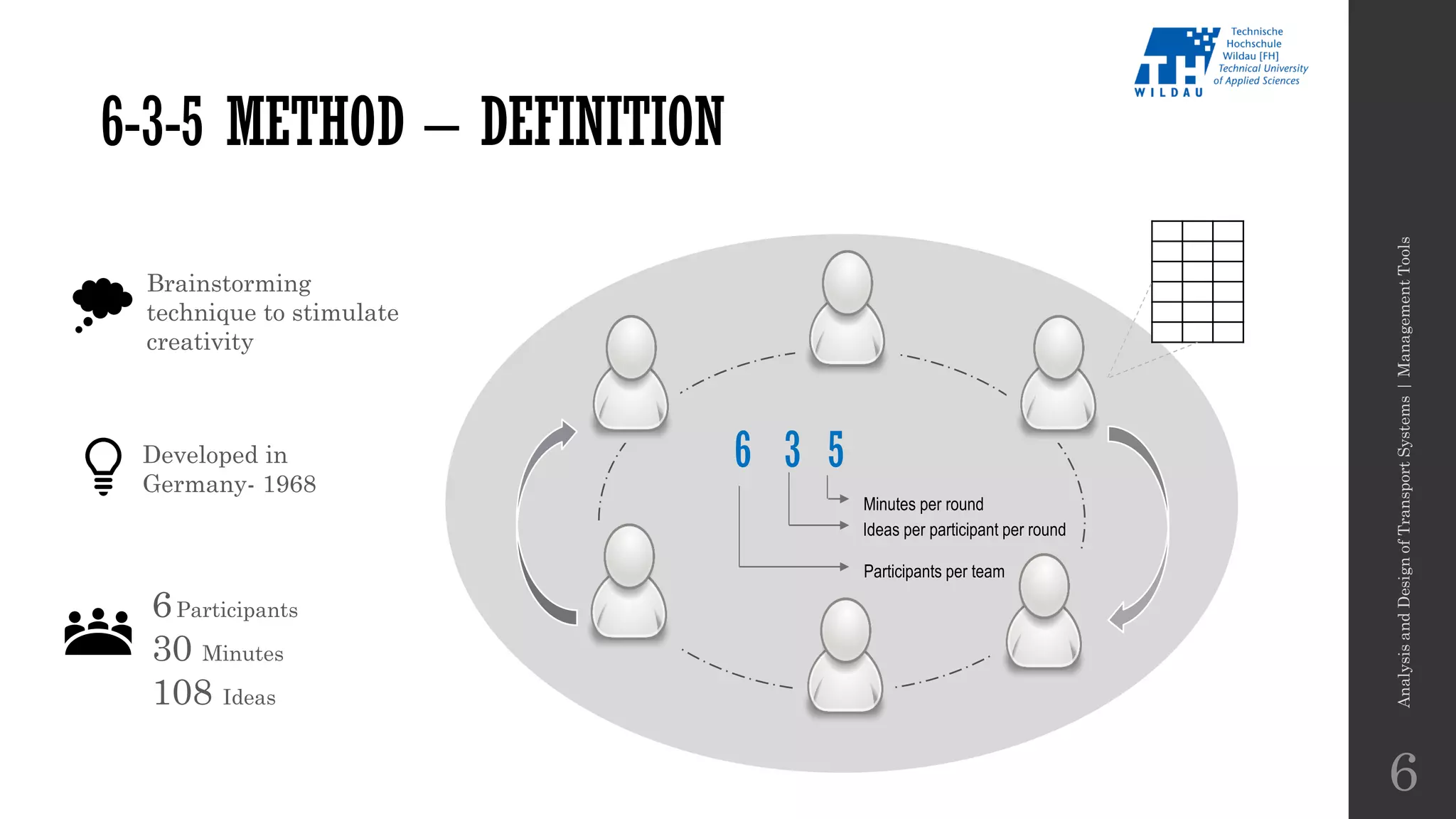
The document discusses various management tools including the Ishikawa method, the 6-3-5 method, and Six Thinking Hats for problem-solving in transport systems. It outlines definitions, advantages, and disadvantages of these techniques, providing examples and applications for improving processes and decision-making. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of collaborative brainstorming in identifying root causes and generating innovative solutions.