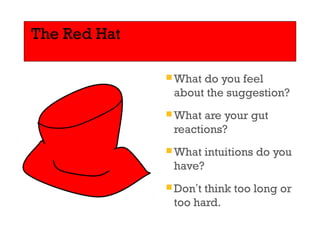
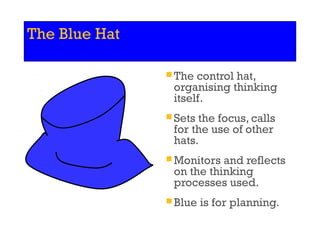
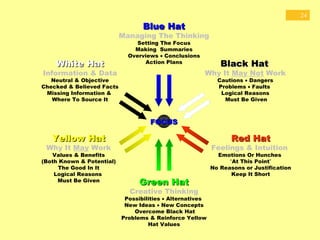
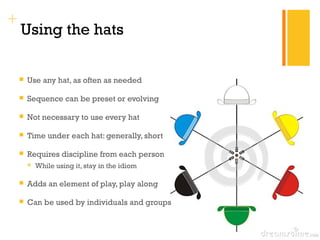
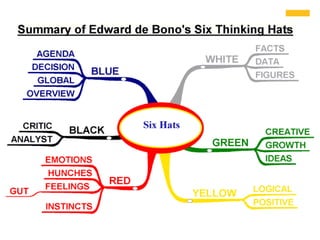
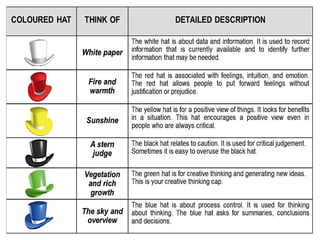
Edward de Bono's Six Thinking Hats is a structured tool for decision making and problem solving that utilizes six distinct modes of thinking, represented by different colored hats. Each hat symbolizes a specific approach, such as emotional (red), analytical (black), optimistic (yellow), creative (green), factual (white), and organizational (blue), encouraging parallel thinking among individuals. This method aims to improve creativity, collaboration, and efficiency in diverse settings and has been widely adopted since its inception.