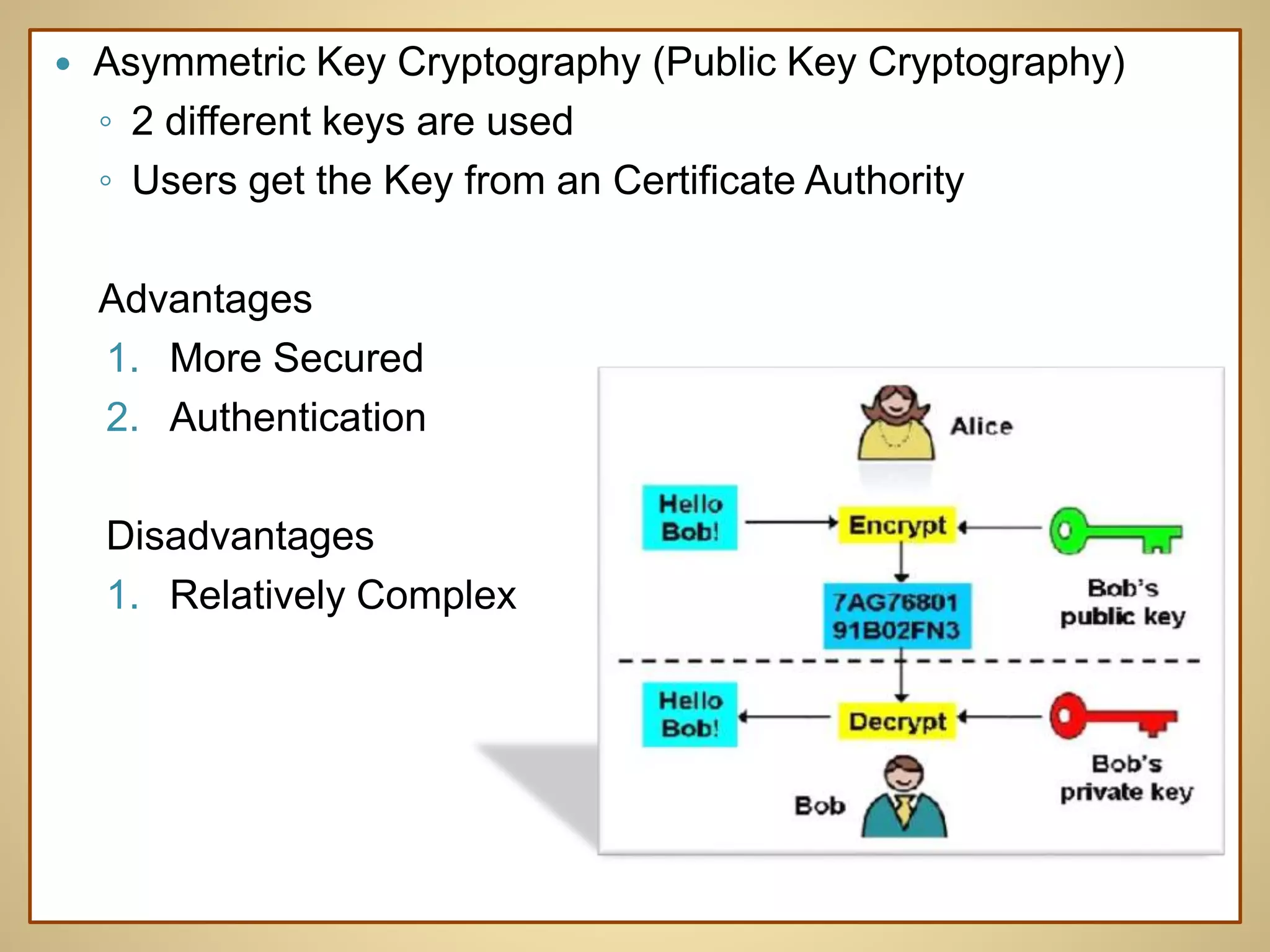
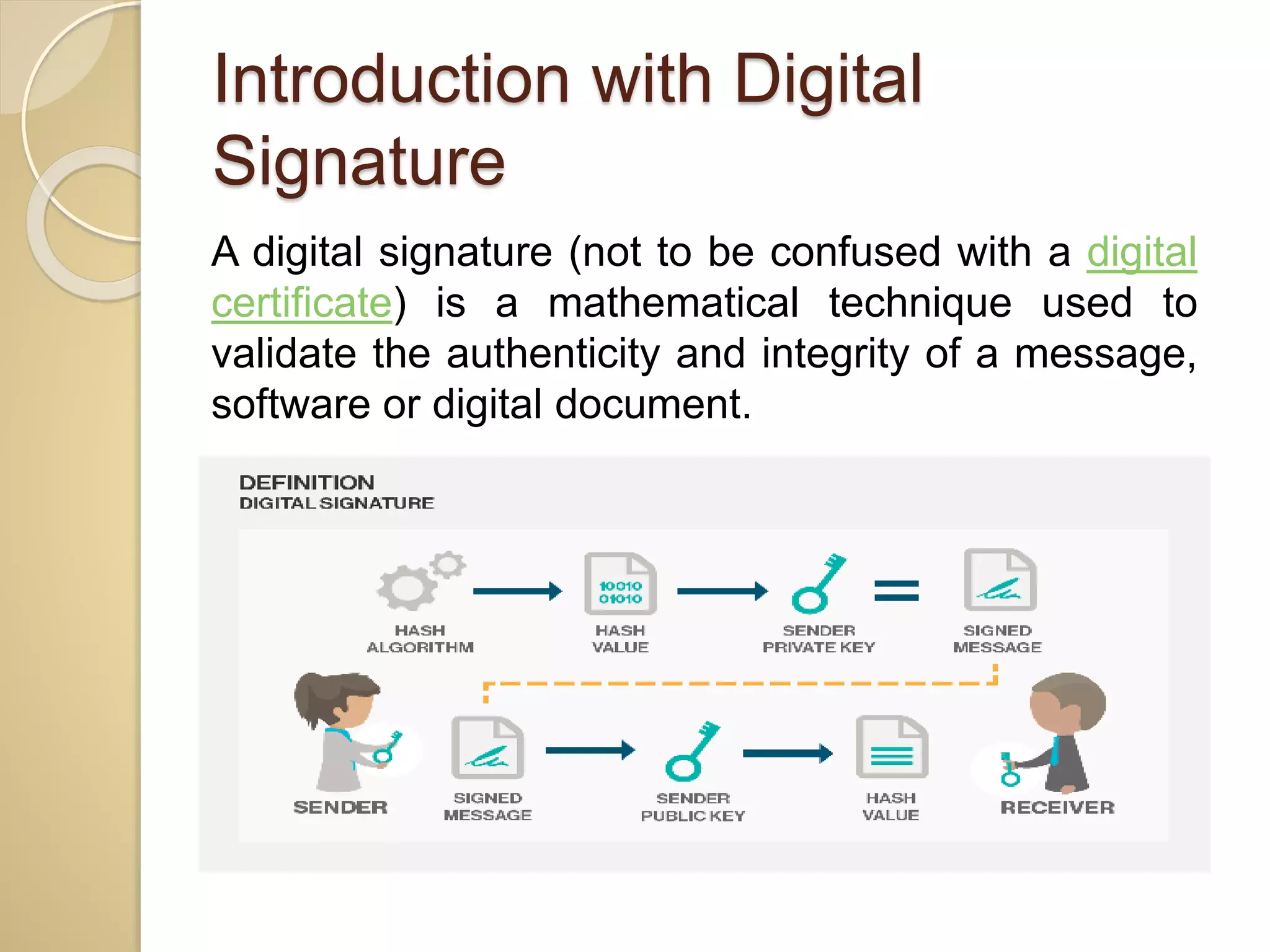
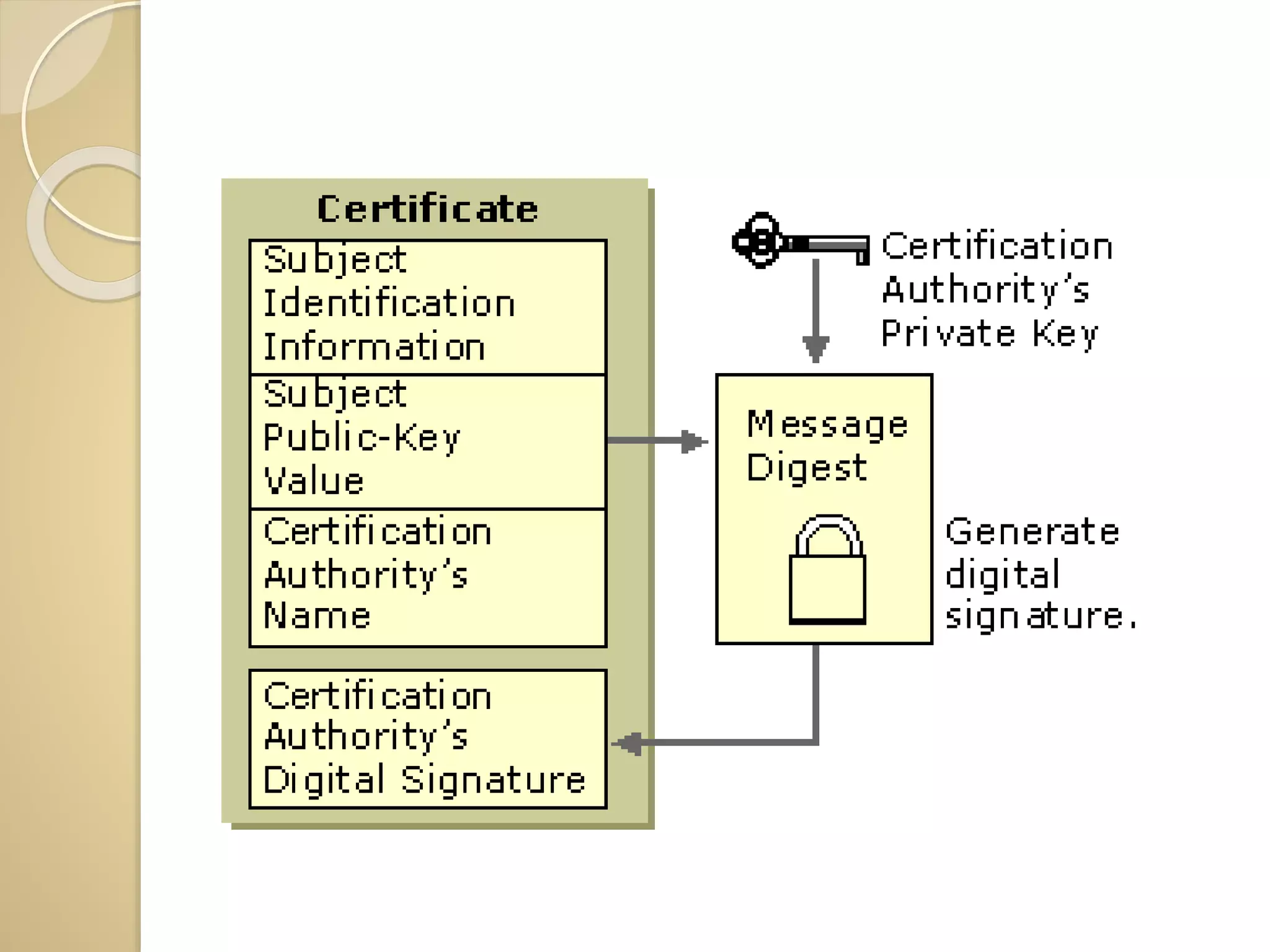
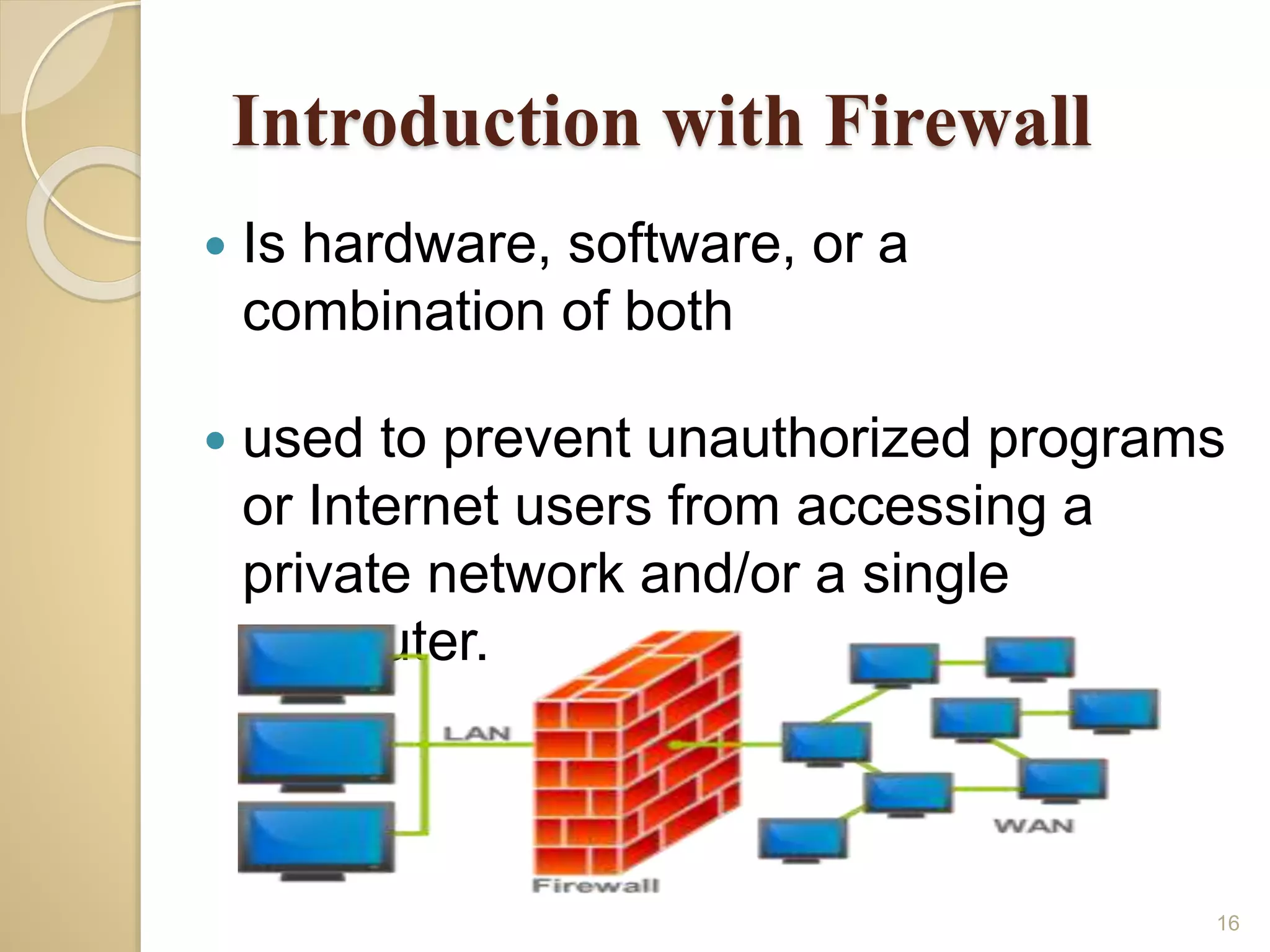
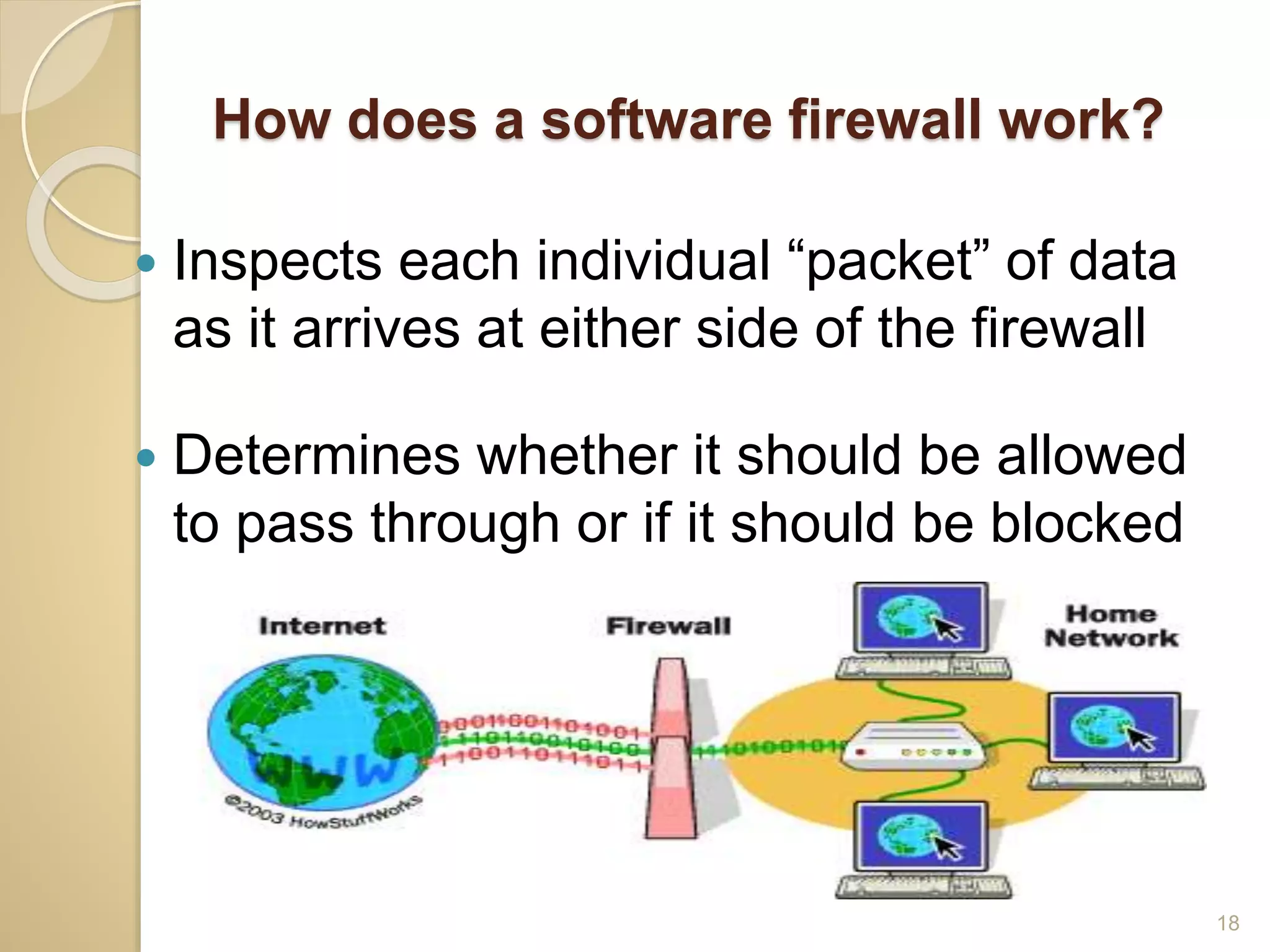
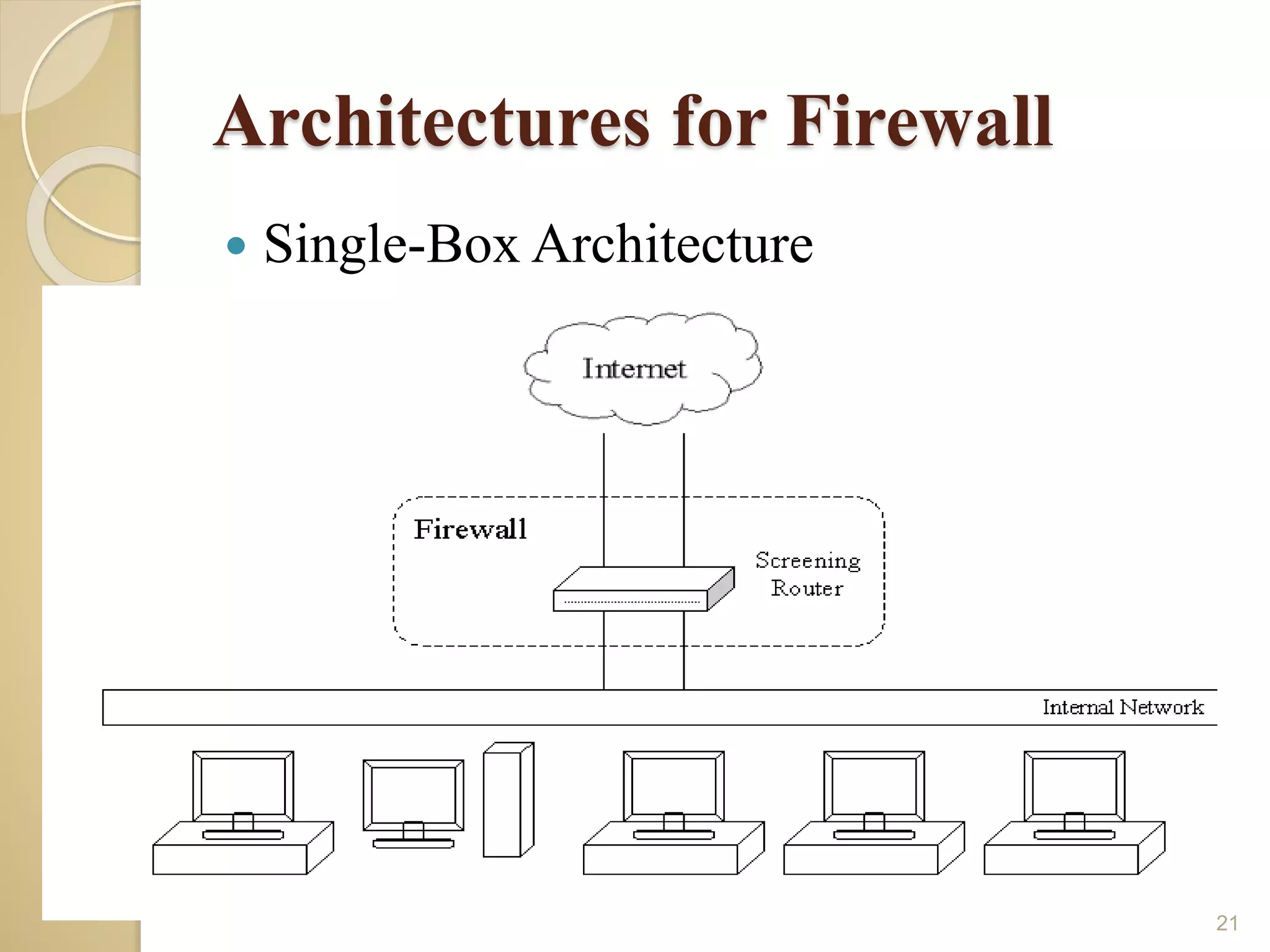
This document discusses various topics related to computer security, including data encryption, digital signatures, digital certificates, firewalls, and threats to client computers. It provides information on cryptography and the different types of encryption methods. Digital signatures are explained as a way to validate the authenticity and integrity of electronic documents. Digital certificates are described as electronic passports issued by certification authorities to allow secure internet exchanges. The roles of hardware and software firewalls in preventing unauthorized access are outlined. Common threats to client computers like cookies, Java applets, and malware are also mentioned. Security measures for client computers including anti-malware software and secure connection protocols are recommended.