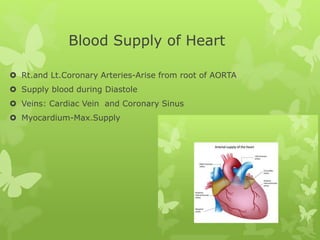
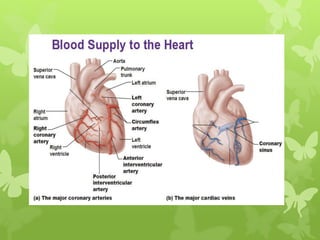
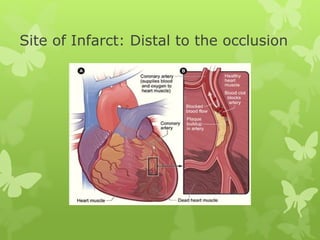
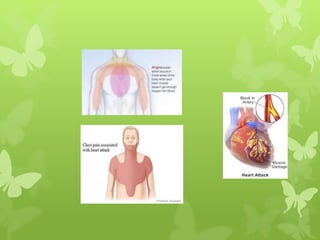
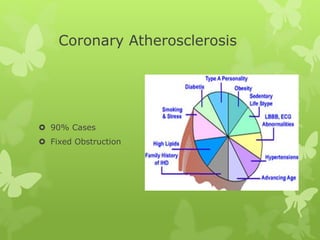
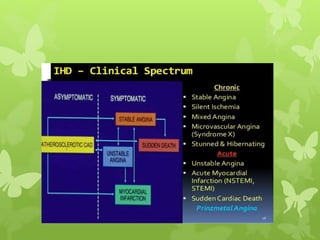
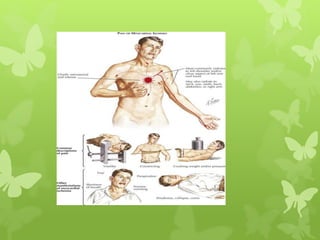
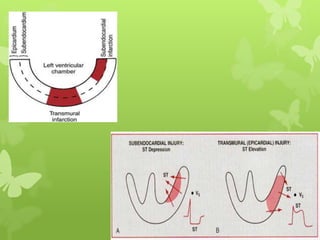
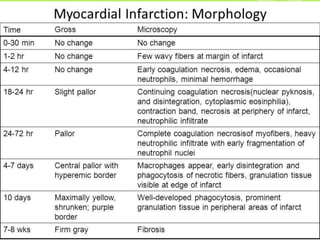
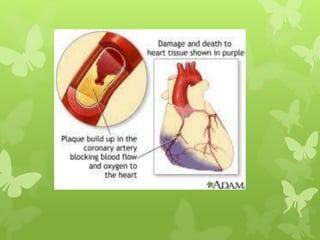
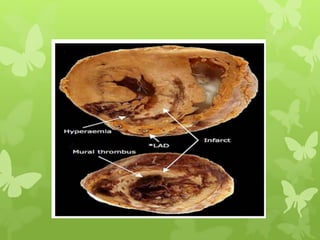
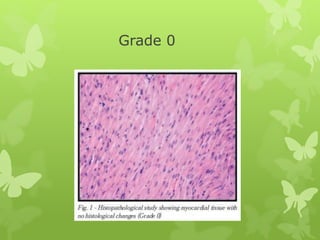
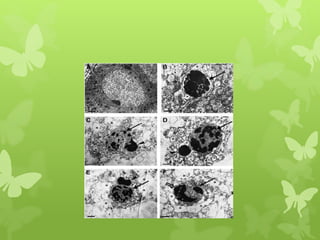
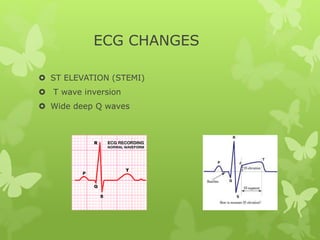
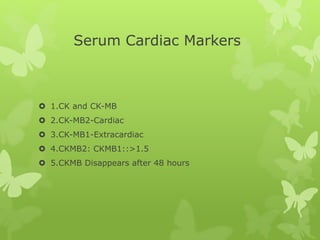
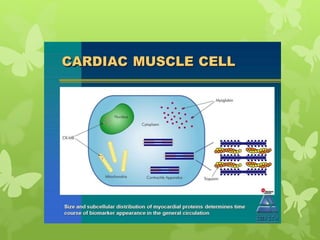
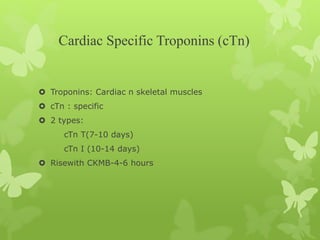
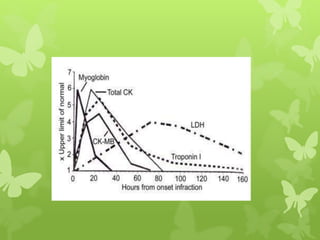
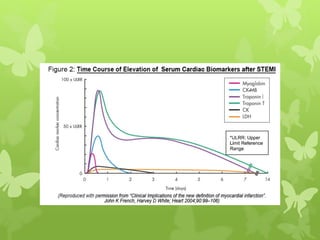
Ischaemic heart disease (IHD), also known as coronary artery disease (CAD), is caused by an imbalance between the heart muscle's supply and demand for oxygenated blood. IHD is commonly caused by coronary atherosclerosis which leads to the narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries and reduces blood flow. This can result in ischemia, infarction, and complications such as angina, myocardial infarction (MI), heart failure, and sudden cardiac death. MI occurs when an atherosclerotic plaque ruptures, causing a blood clot that blocks one of the coronary arteries and leads to cell death in the heart muscle. Diagnosis of MI involves clinical features, electrocardiogram changes, and elevated cardiac enzyme markers in the