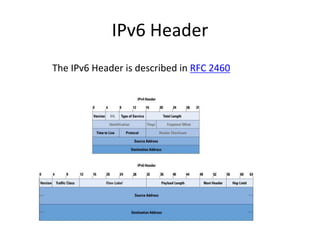
IPv6 is the next generation Internet Protocol that increases the address space to 128 bits from 32 bits in IPv4. It was developed by the IETF and specified in RFC 1883. IPv6 addresses are written as 8 groups of 4 hexadecimal digits separated by colons. Consecutive sections of zeros can be represented by double colons. The document discusses the basic address and header structure of IPv6 and plans to set up IPv6 in virtual machines and routers to learn more.