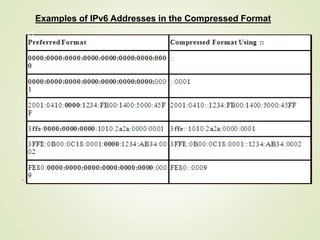
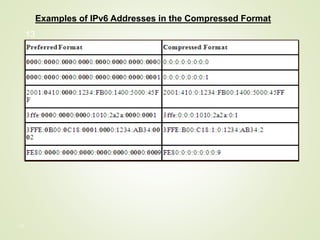
This document discusses IPv4 and IPv6 addressing. It begins by explaining IPv4 addressing, including that IPv4 addresses have 32 bits and can be represented in binary or dotted decimal notation. It then discusses the two methods of IPv4 addressing: classful and classless addressing. Classful addressing divides the address space into five classes (A, B, C, D, E) while classless addressing grants address blocks based on requirements. The document notes the need for IPv6 due to the limited address space of IPv4 and explains key aspects of IPv6 including that IPv6 addresses have 128 bits and various formats for representing IPv6 addresses. It provides examples of compressing IPv6 addresses and embedding IPv4 addresses within IPv6 addresses