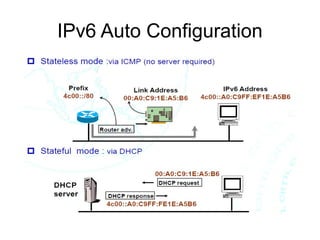
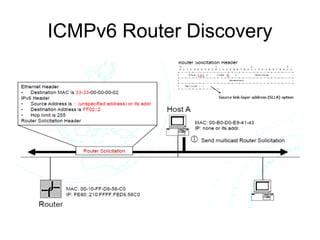
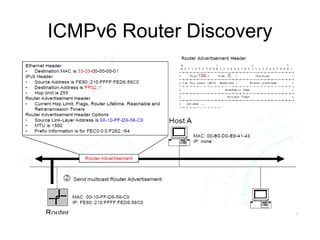
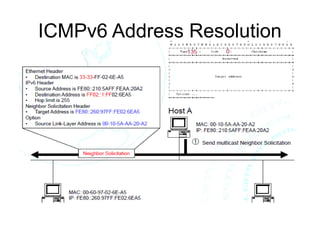
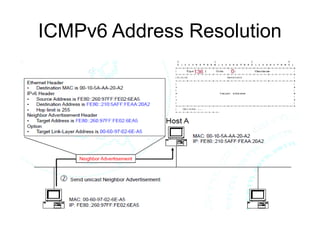
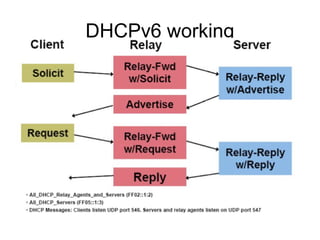
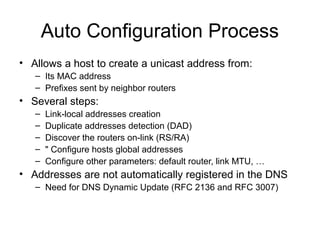
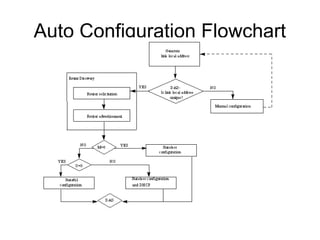
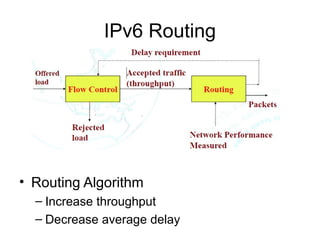
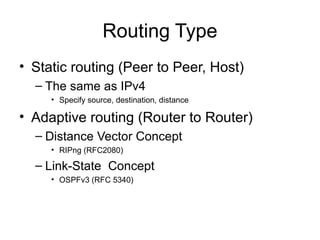
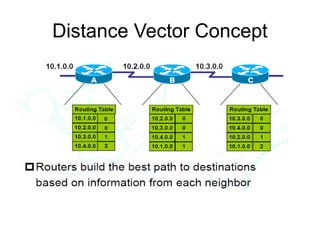
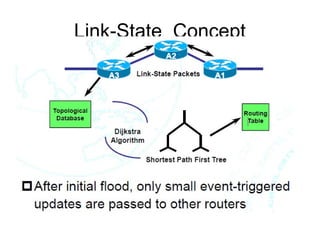
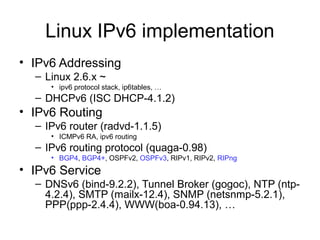
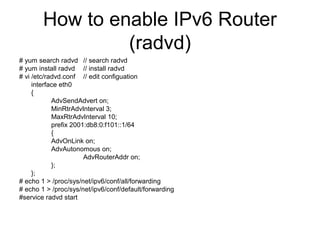
This document provides an overview of IPv6 including addressing, routing, autoconfiguration, transition technologies, and Linux implementation. Key points covered include IPv6 address formats and types, stateless and stateful autoconfiguration using ICMPv6 and DHCPv6, static and adaptive routing protocols like RIPng and OSPFv3, DNS record formats, and dual stack and tunneling transition technologies. It also reviews how to configure an IPv6 router using the radvd daemon on Linux systems.


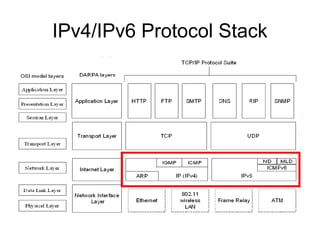
![What is IPv6
• IPv4 (32bits) → IPv6 (128 bits)
– 2001:0db8:1a2b:0015:0000:0000:1a2f:0000
• 2001:db8:1a2b:15:0:0:1a2f:0
– (0 can ignore)
• 2001:db8:1a2b:15::1a2f:0
– multiple “0” block can combine to :: (only once)
• Prefix is network address
– 2001:0:0:b3::1234/64
• Address type
– Unicast
– Multicast [Multicast Listener Disscovery]
– Anycast (router only)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ipv6introduction-130601090341-phpapp02/85/IPv6-introduction-4-320.jpg)