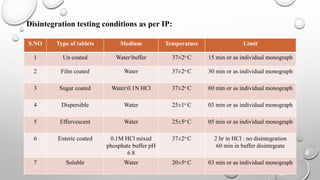
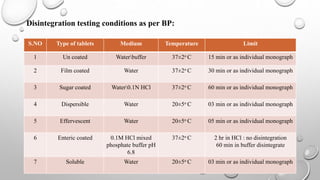
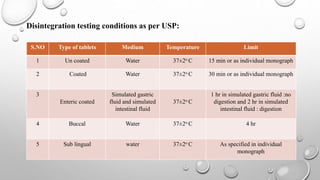
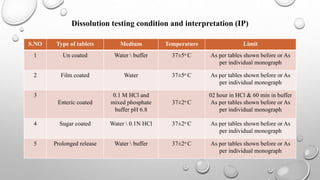
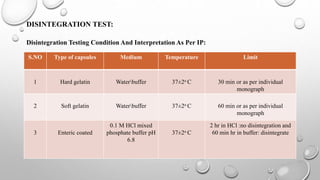
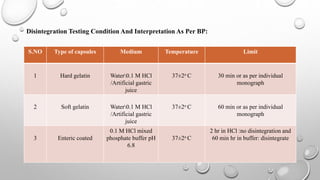
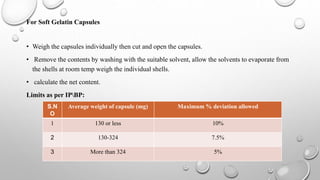
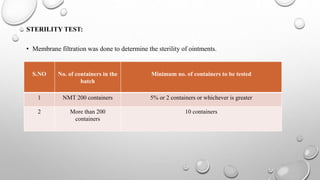
IPQC tests are important quality control checks performed during the manufacturing of tablets, capsules, and ointments. For tablets, key tests include weight variation, disintegration, dissolution, drug content, hardness, and friability. Tests for capsules include uniformity of content, disintegration, weight variation, and dissolution. Common tests for ointments are not described. IPQC aims to detect errors, minimize human error, and ensure quality at each stage of production according to established procedures.


![IPQC:
• In process quality control [IPQC] is concerned with providing accurate, specific and definite
description of procedures to be employed from the receipt of raw materials to the release of
finished dosage forms.
• IPQC procedures are generally quick, simple and rapid tests that carried out at on going
manufacturing.
• It is a planned system to identify the materials, equipment, process and operations.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ipqcfortabletscapsulesandointments-230807070606-2ff7c1d7/85/IPQC-for-tablets-capsules-and-ointments-pptx-3-320.jpg)