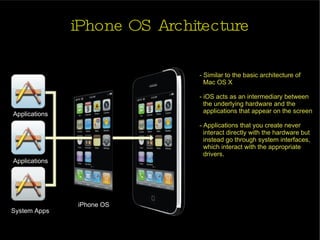
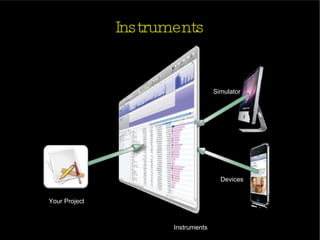
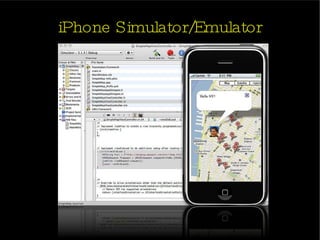
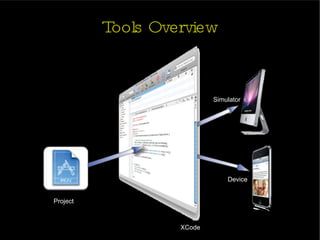
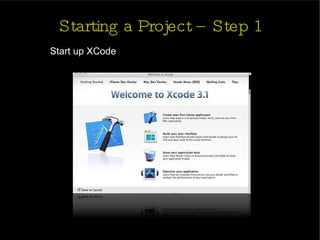
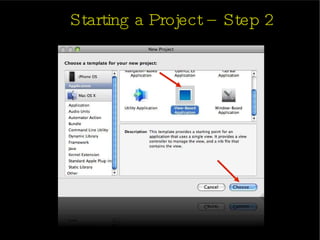
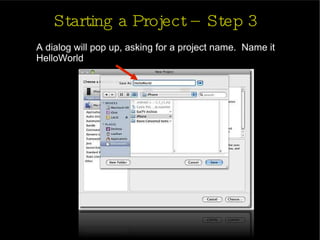
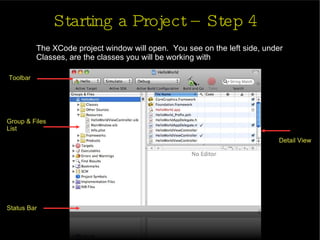
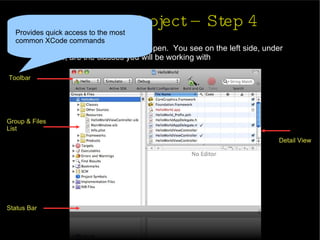
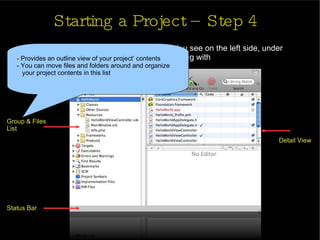
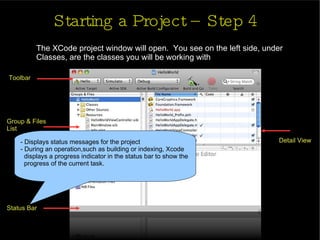
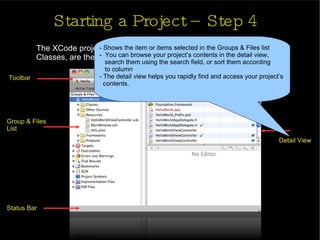
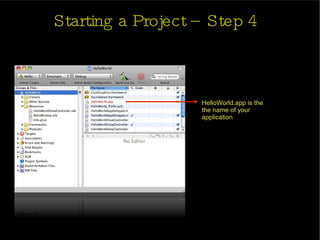
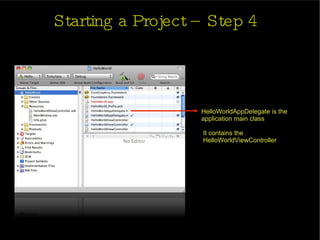
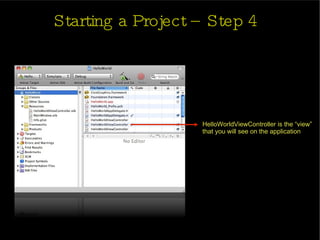
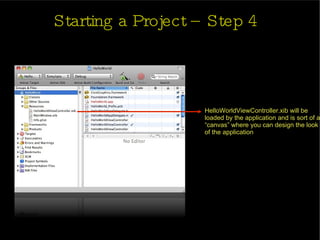
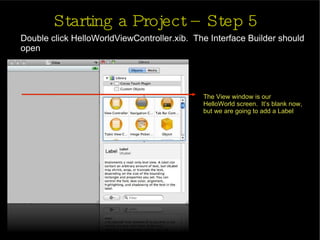
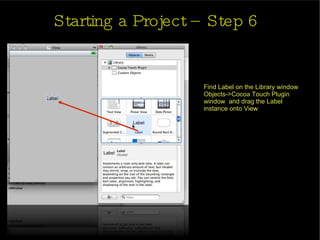
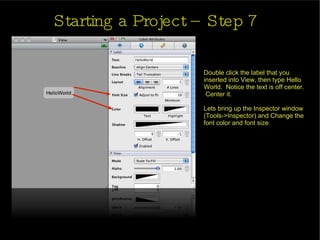
The document provides an introduction and agenda for a two-day iPhone development training. Day 1 covers iPhone architecture, development tools like Xcode and Interface Builder, and how to create a basic "Hello World" iPhone app. Day 2 will focus on adding more UI elements and an Objective-C overview.