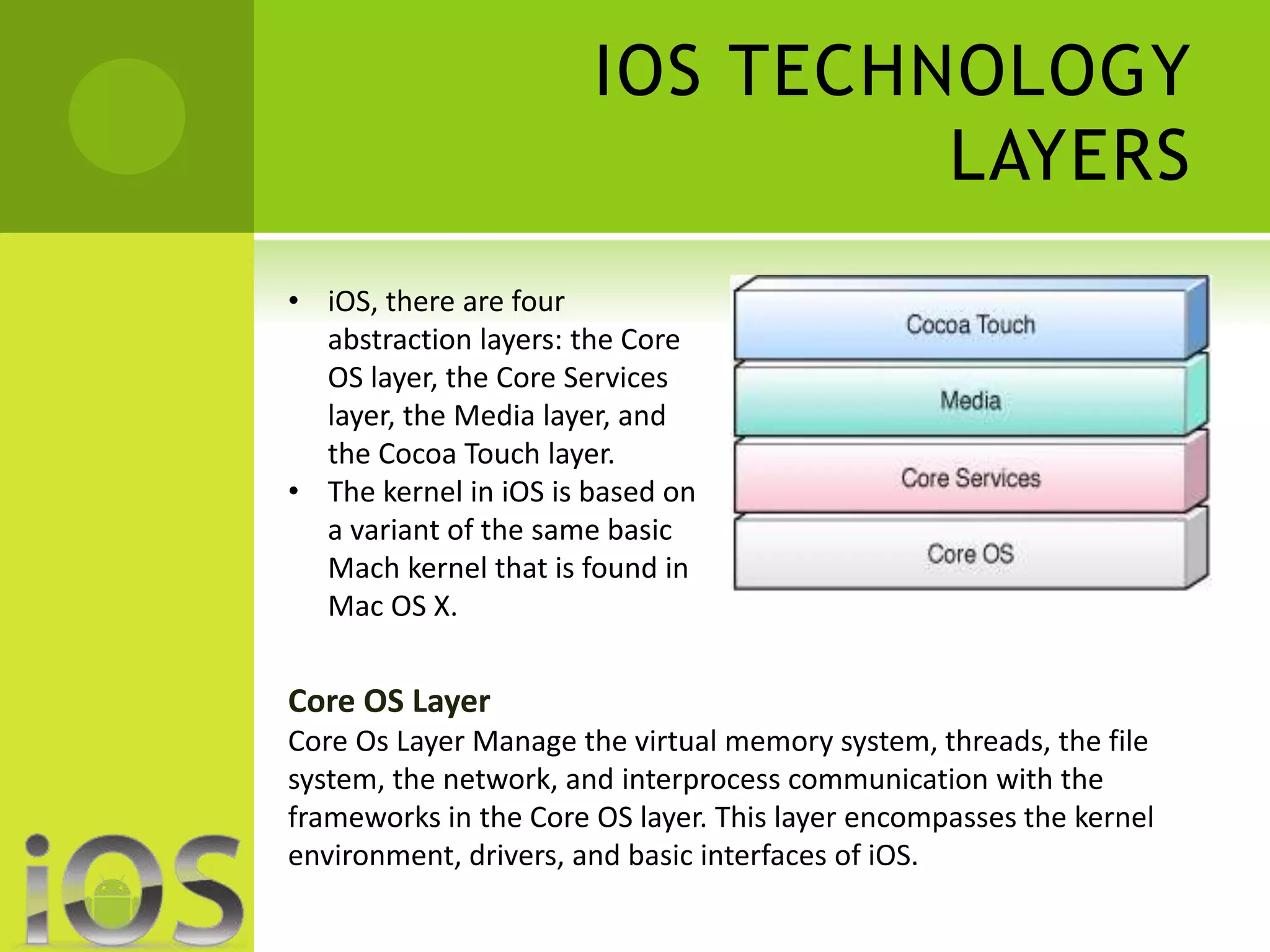
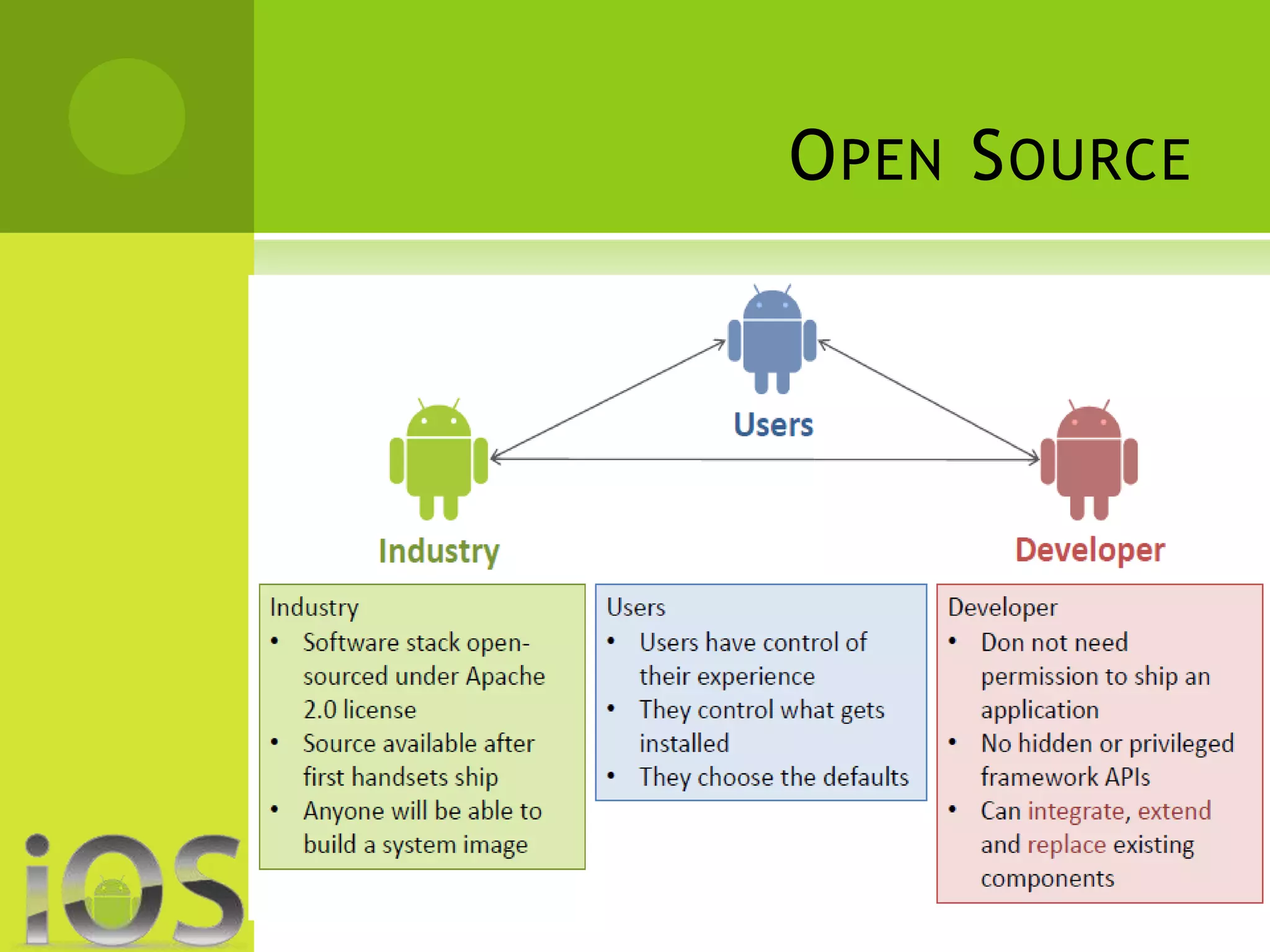
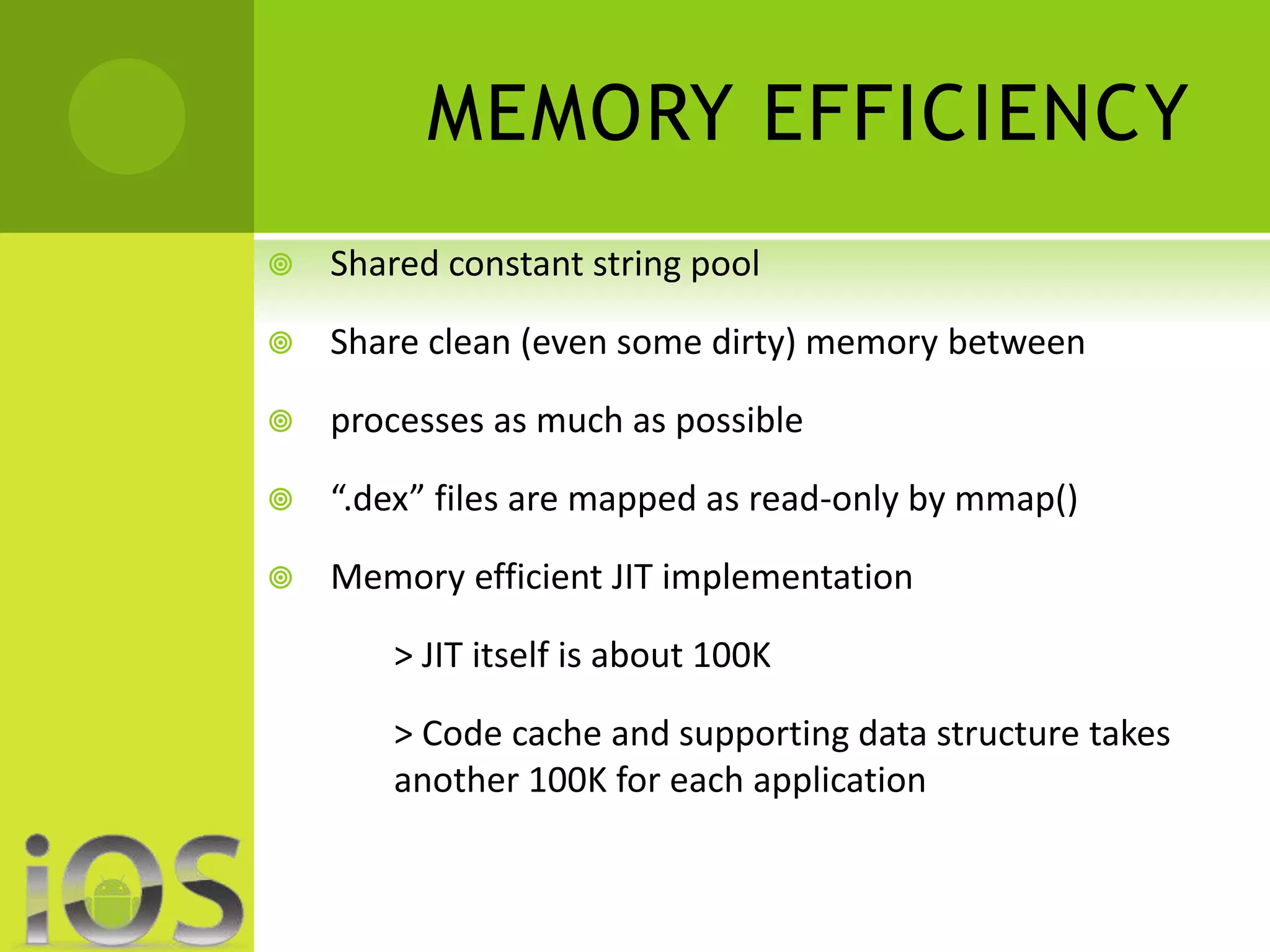
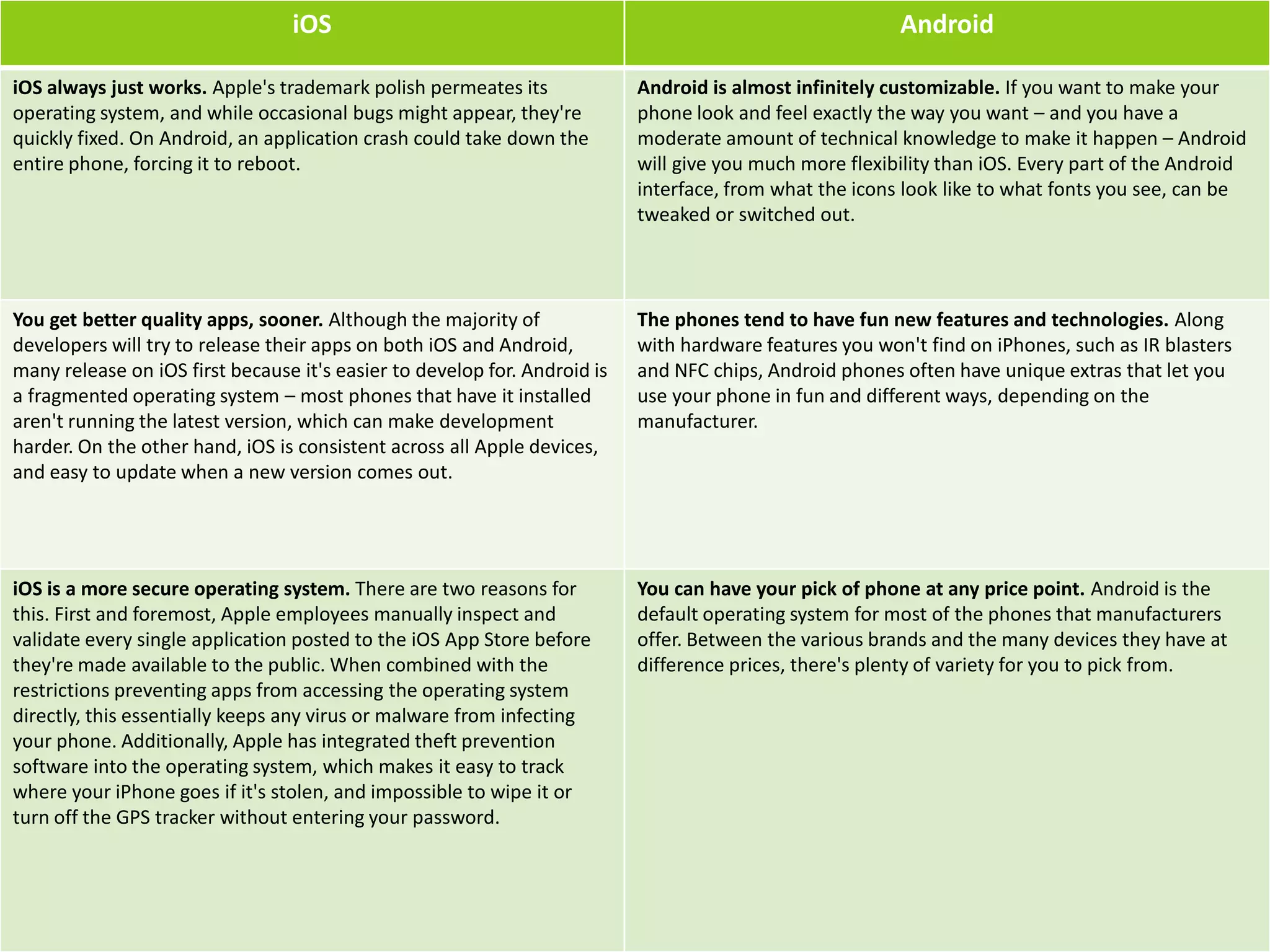
iOS provides a polished, consistent experience across Apple devices where apps generally work smoothly and bugs are quickly fixed. However, it offers less customization than Android. Android allows for high levels of customization but can be less stable due to its fragmentation across devices and versions. While Android offers more options and unique features from manufacturers, iOS typically receives higher quality apps sooner and has more secure app validation processes.