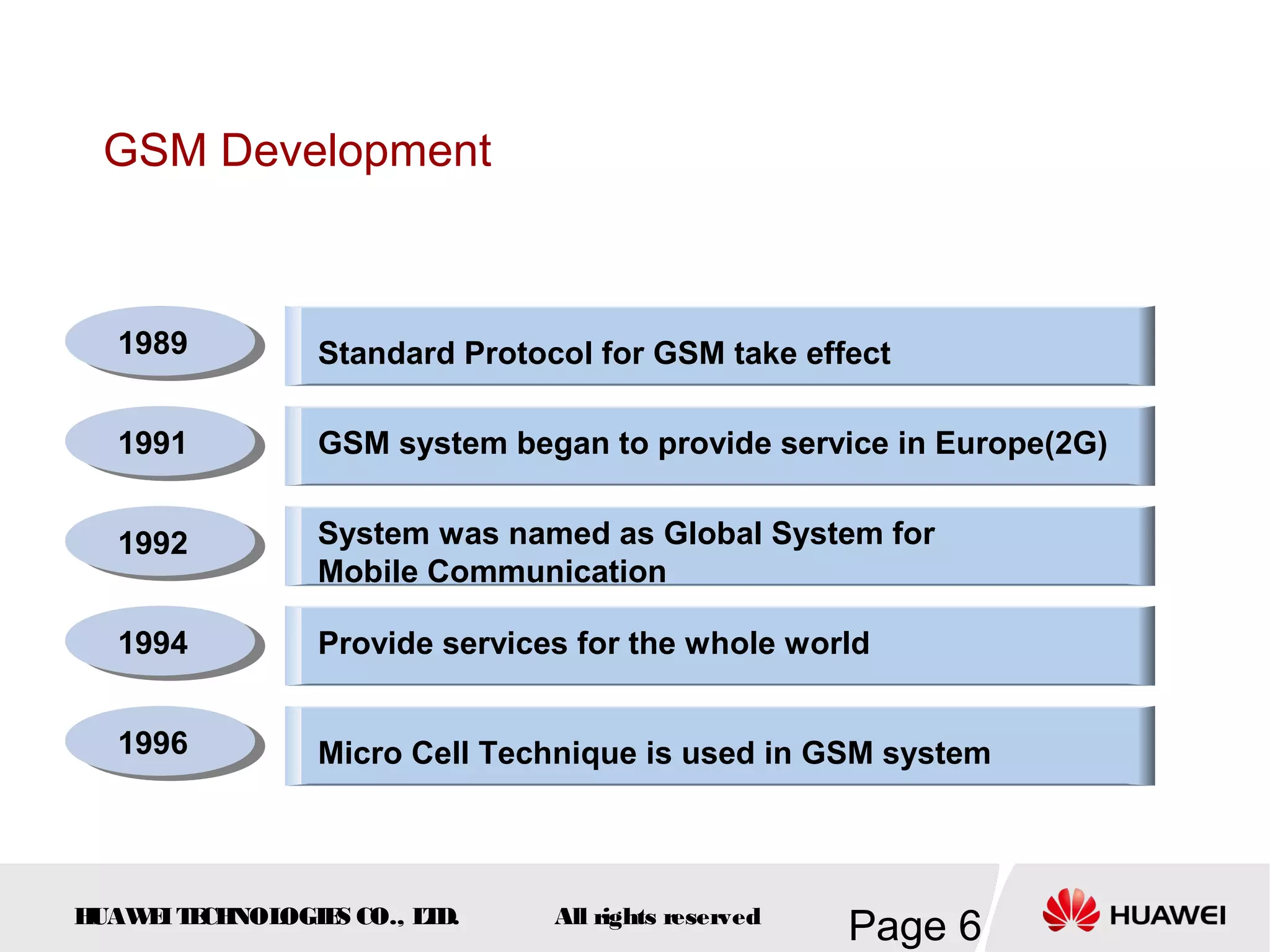
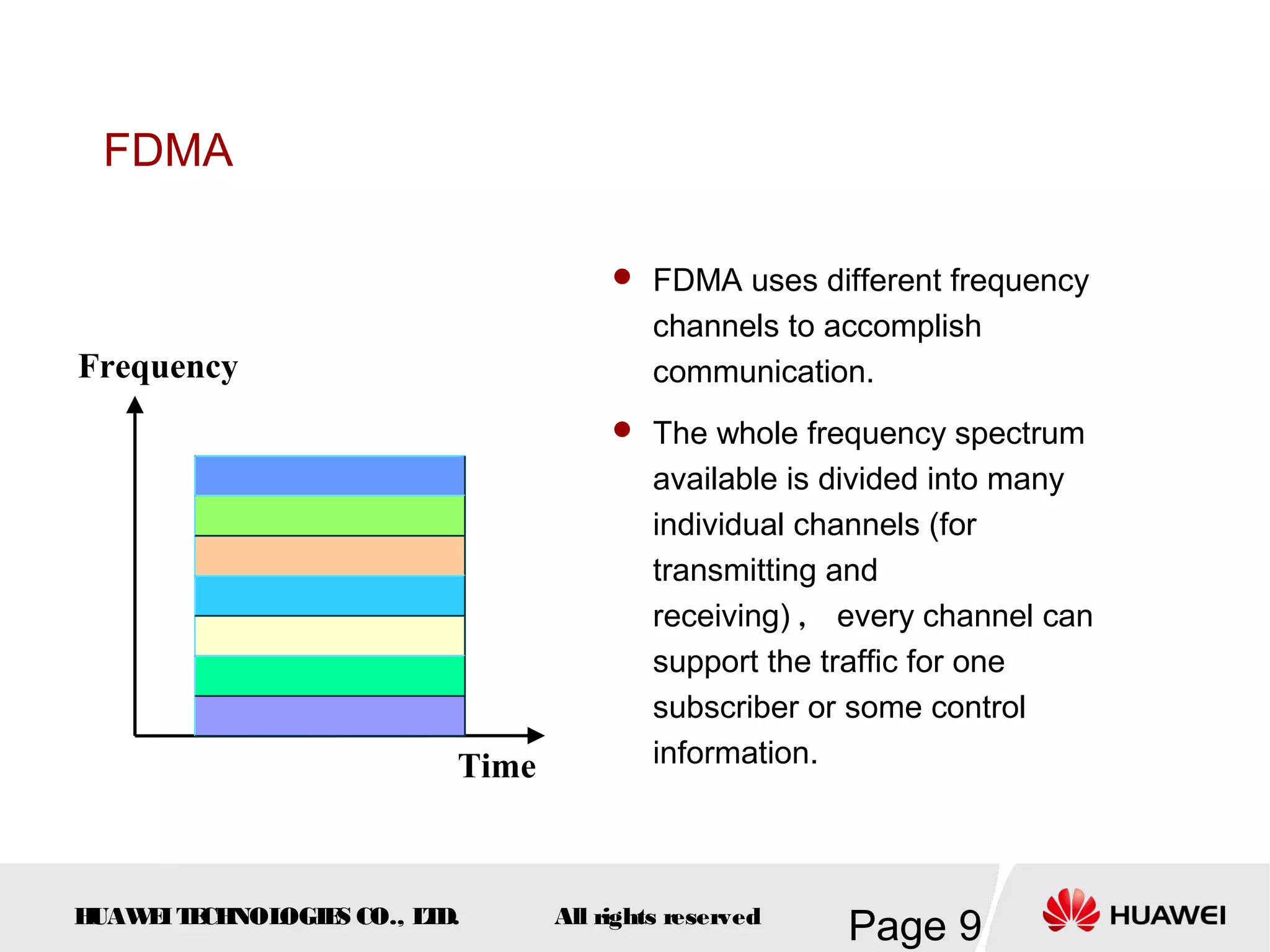
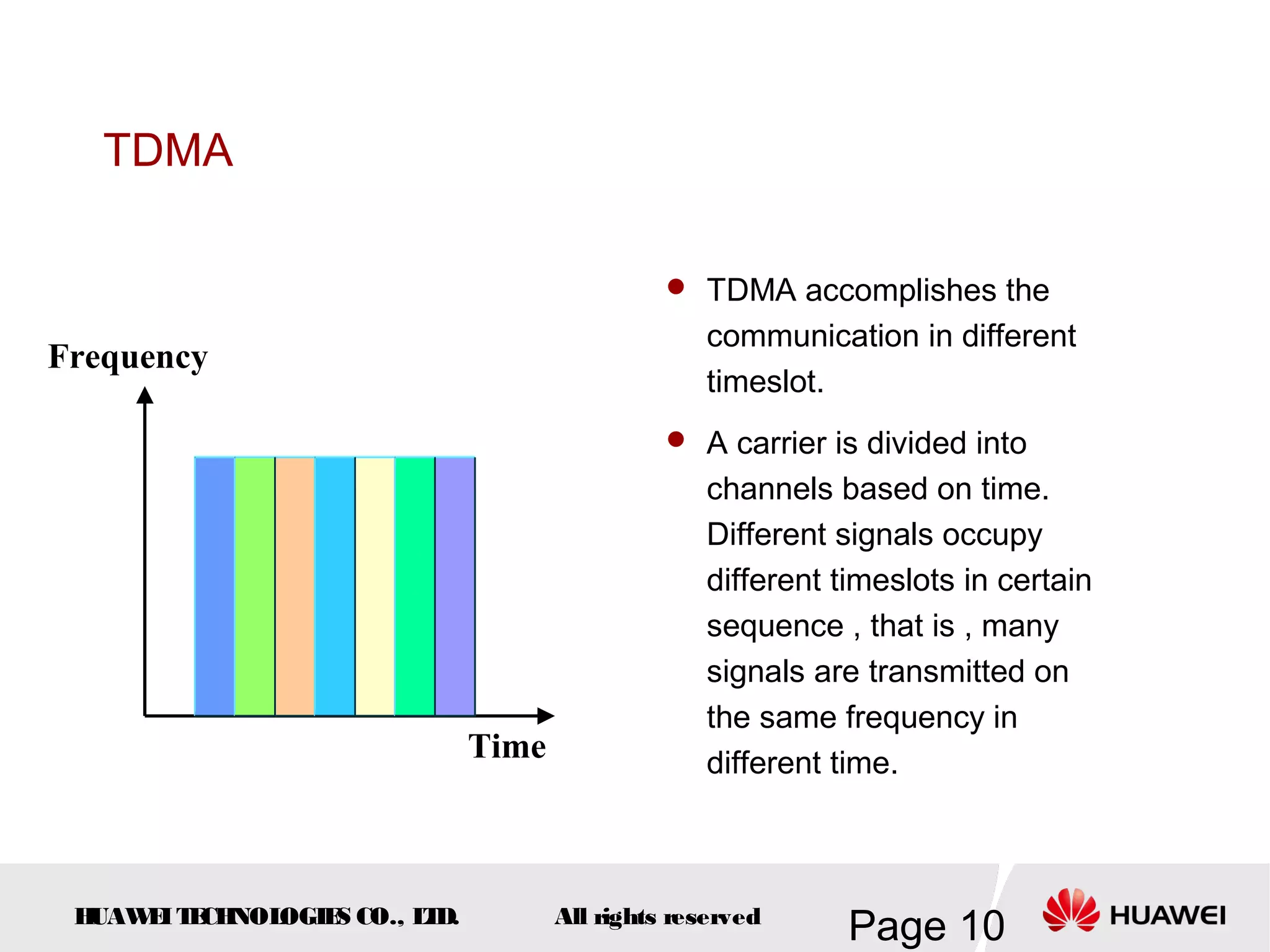
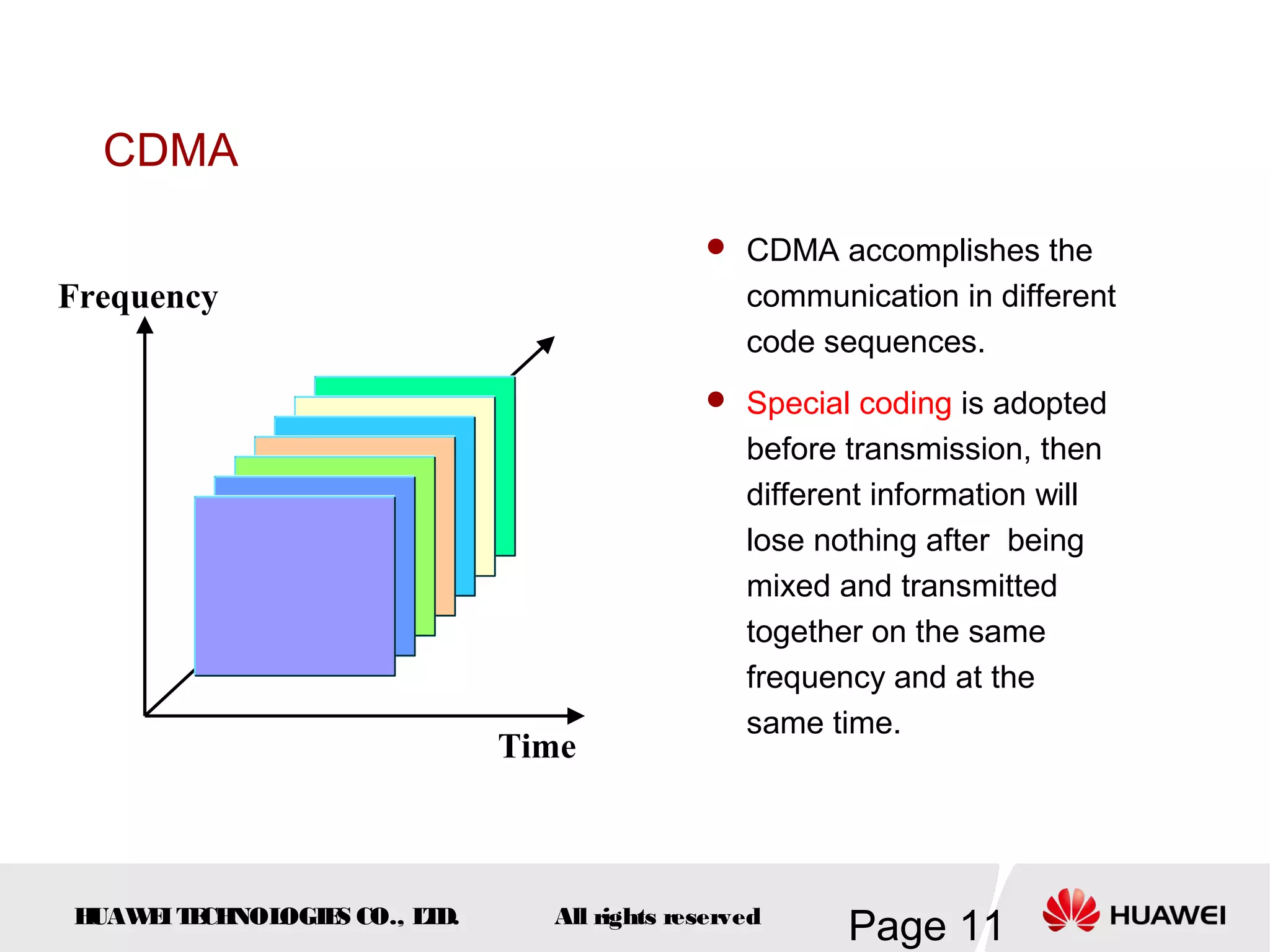
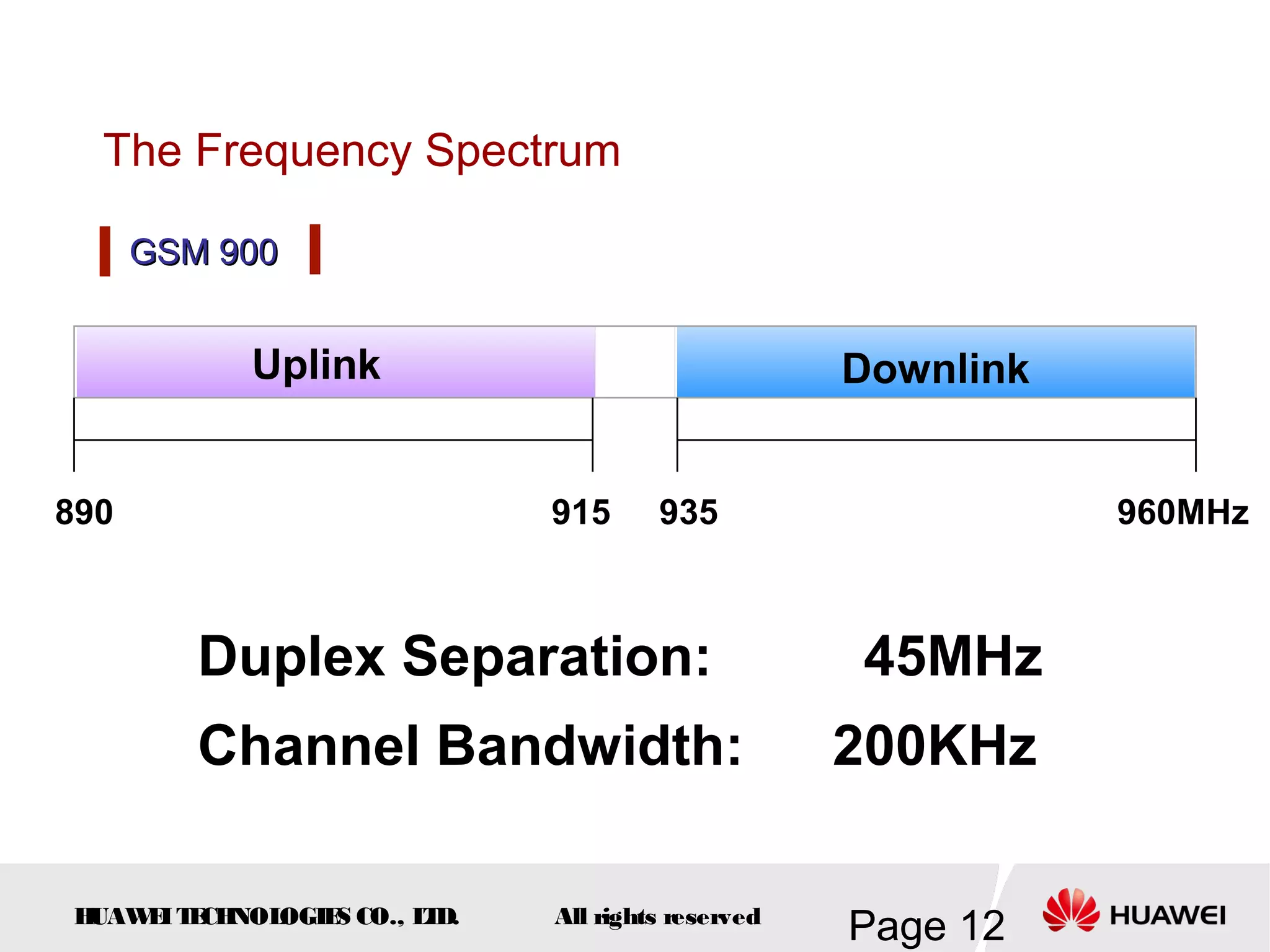
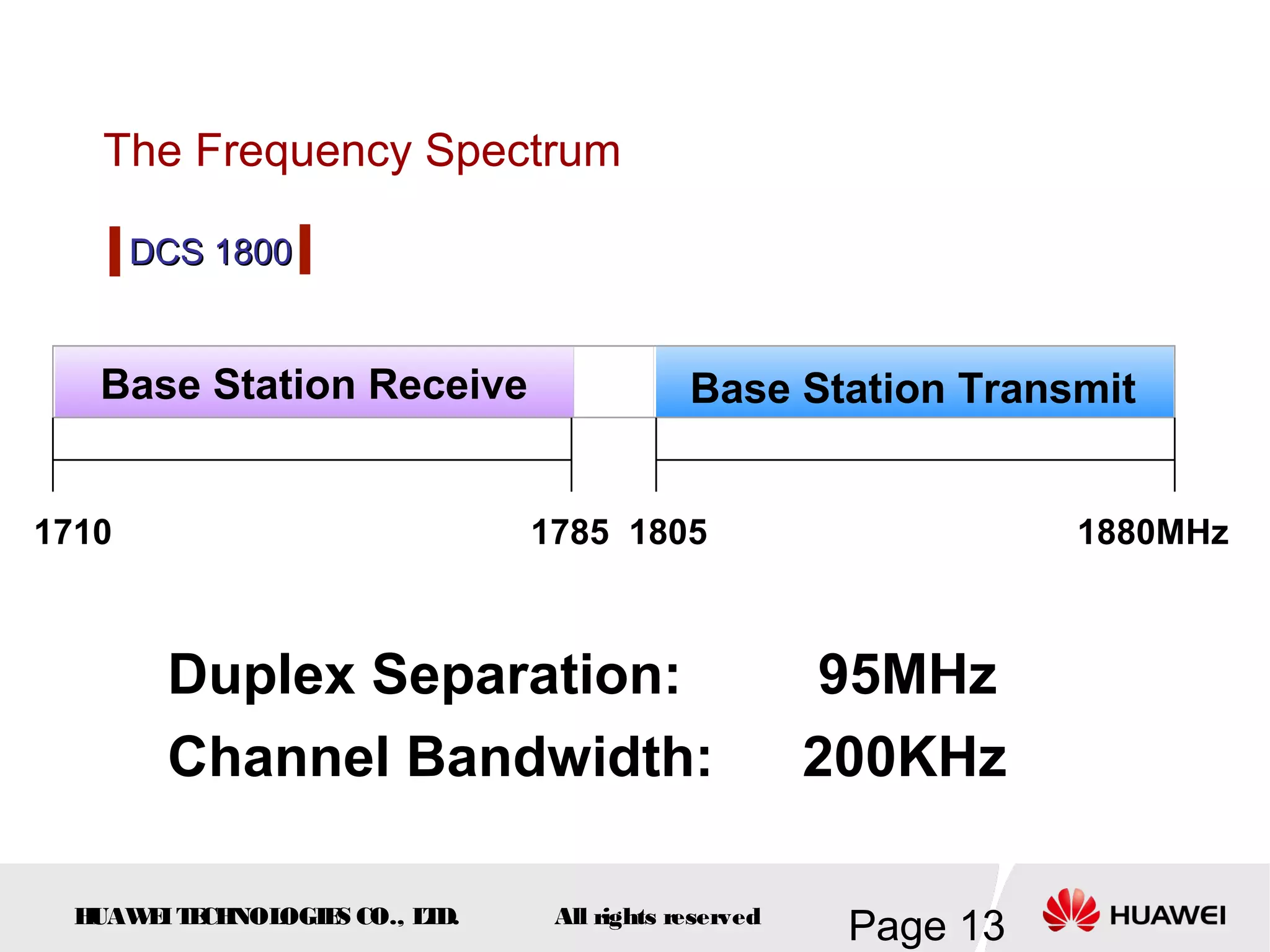
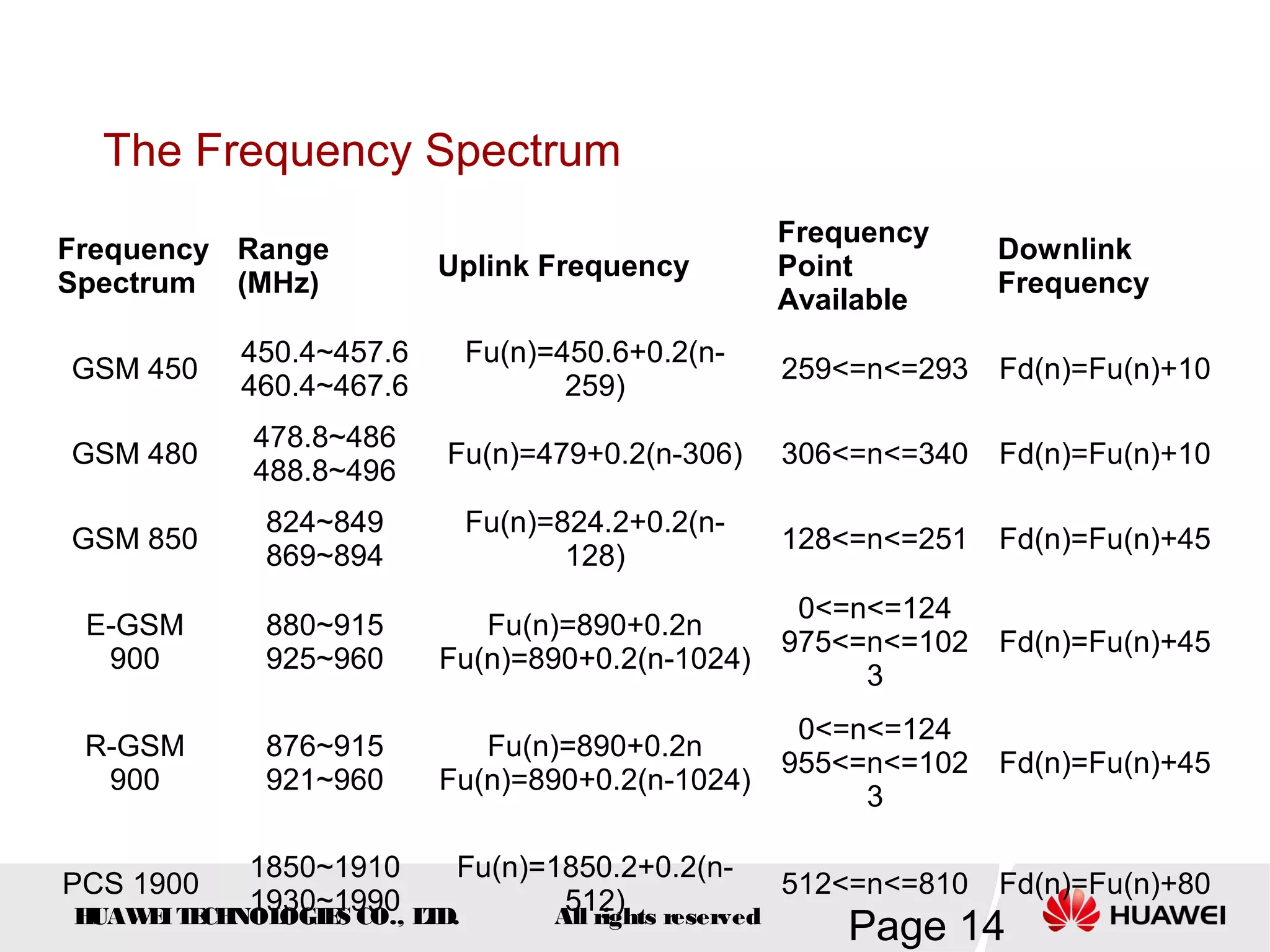
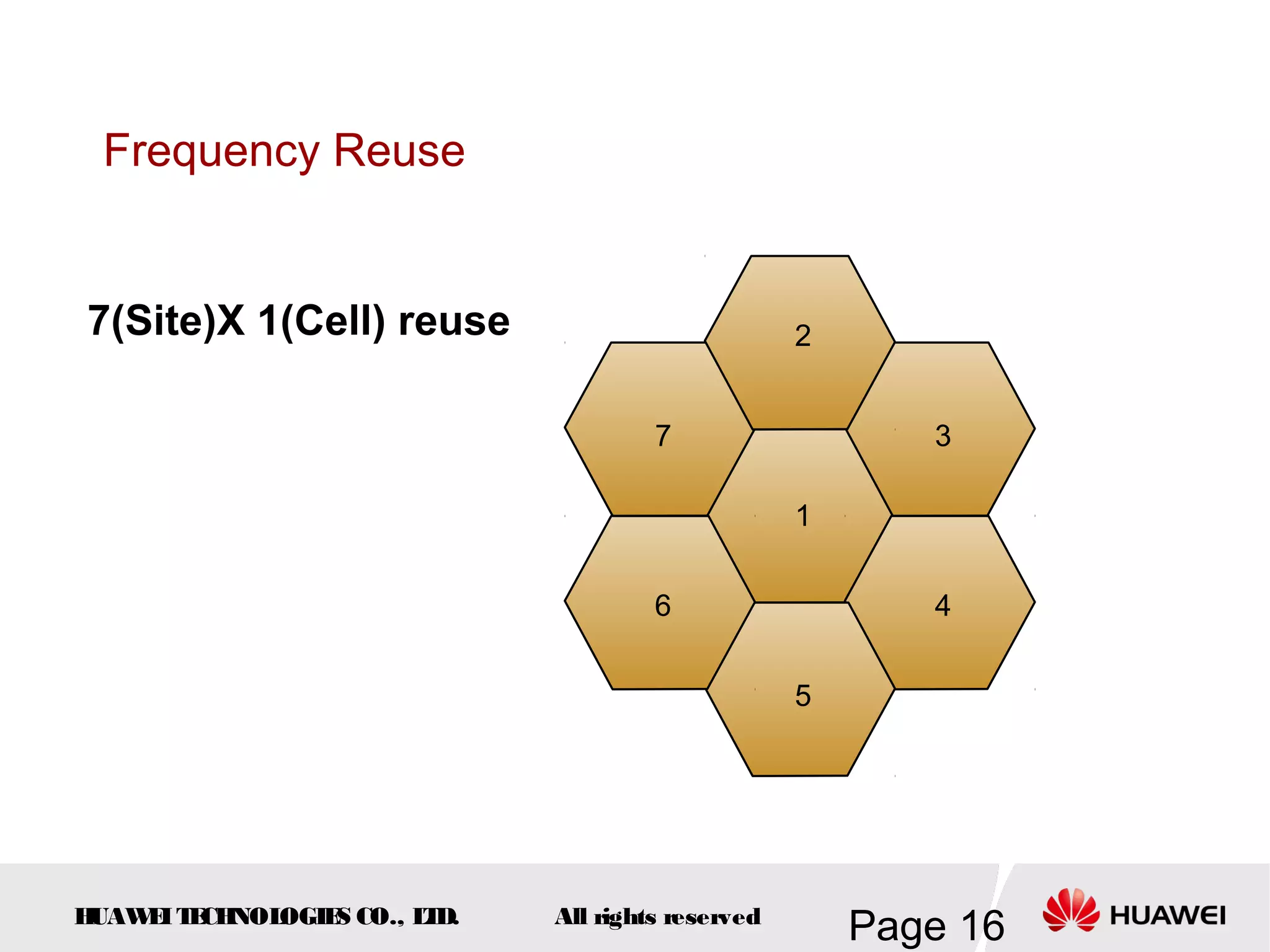
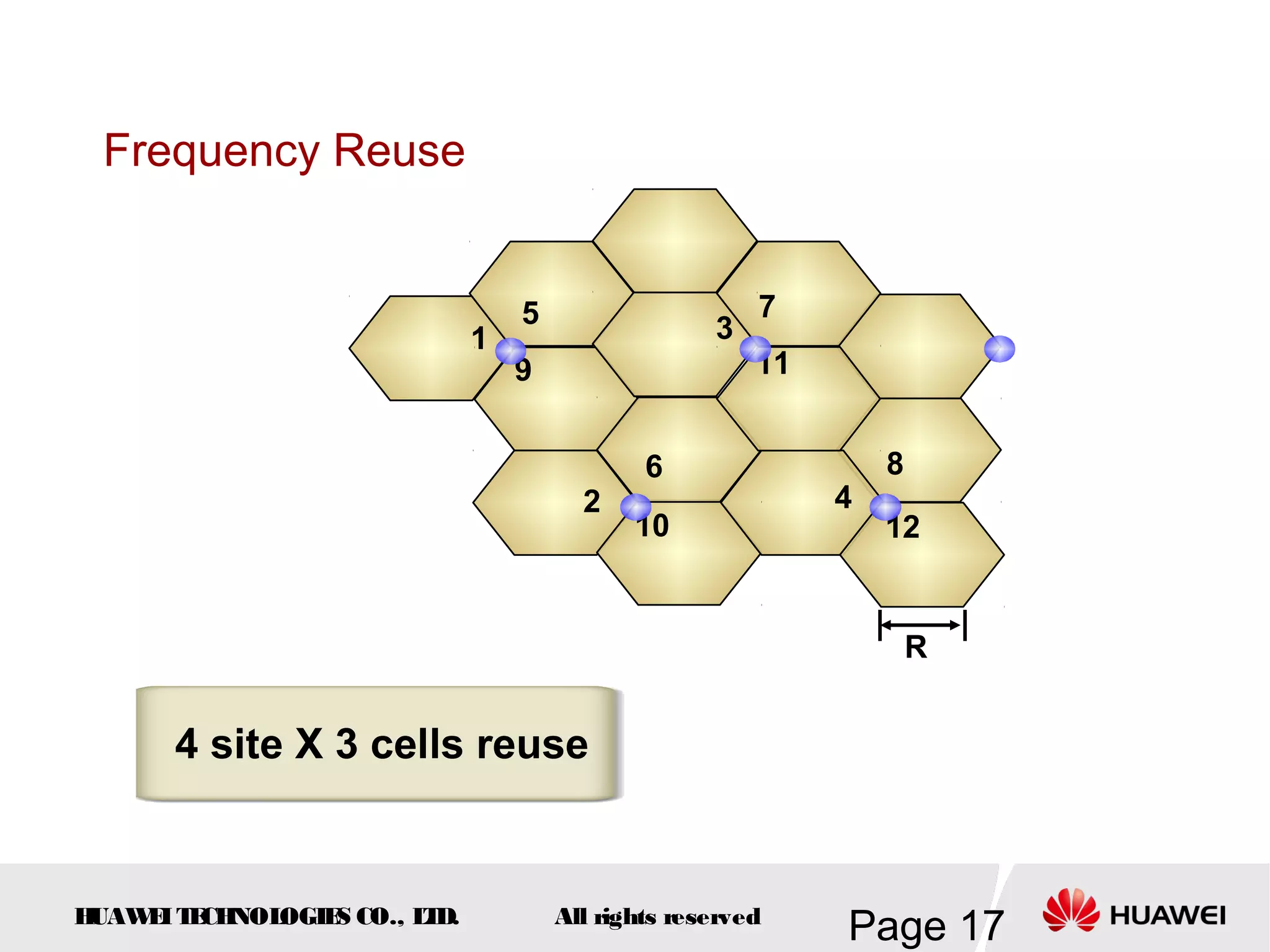
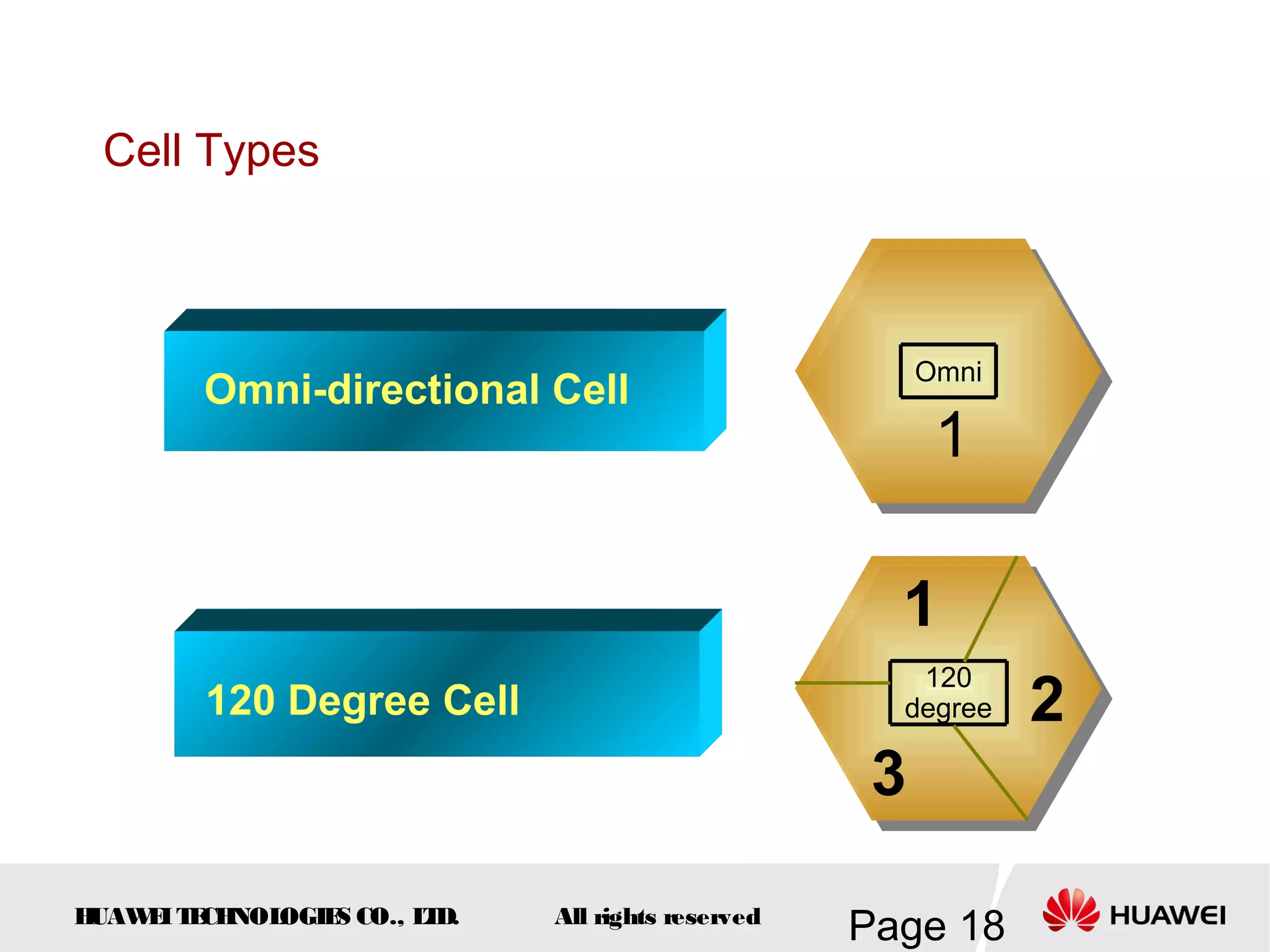
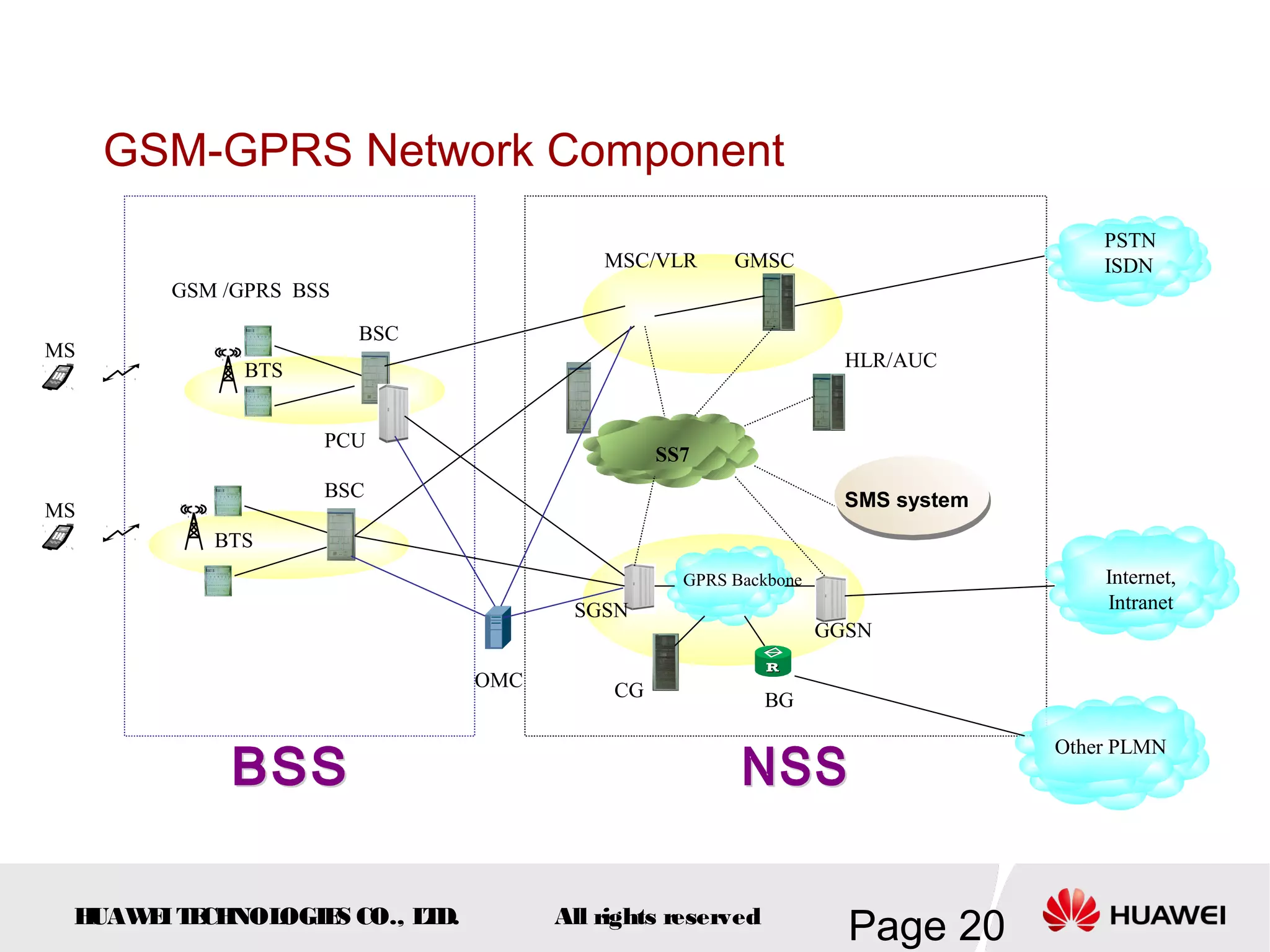
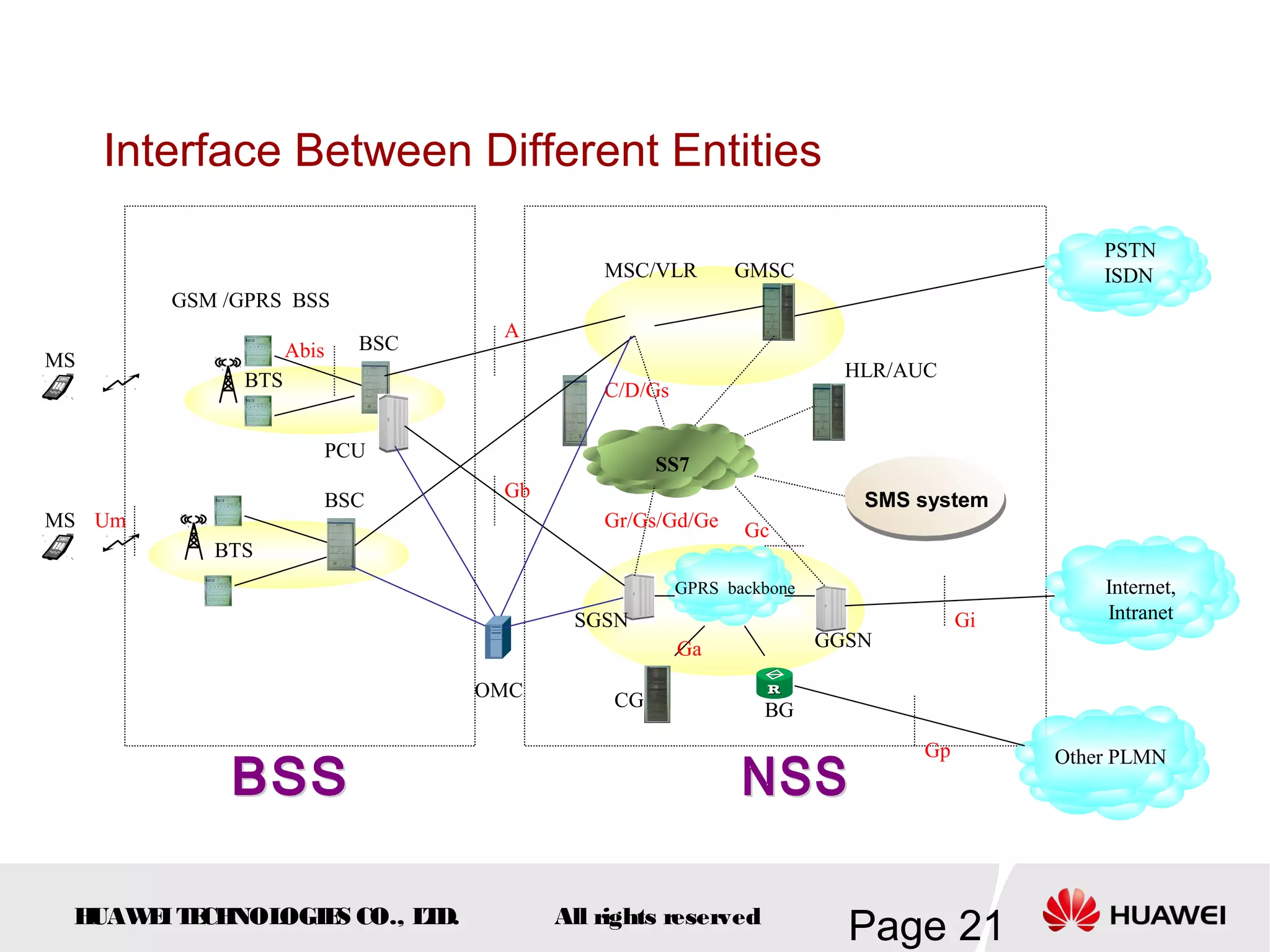
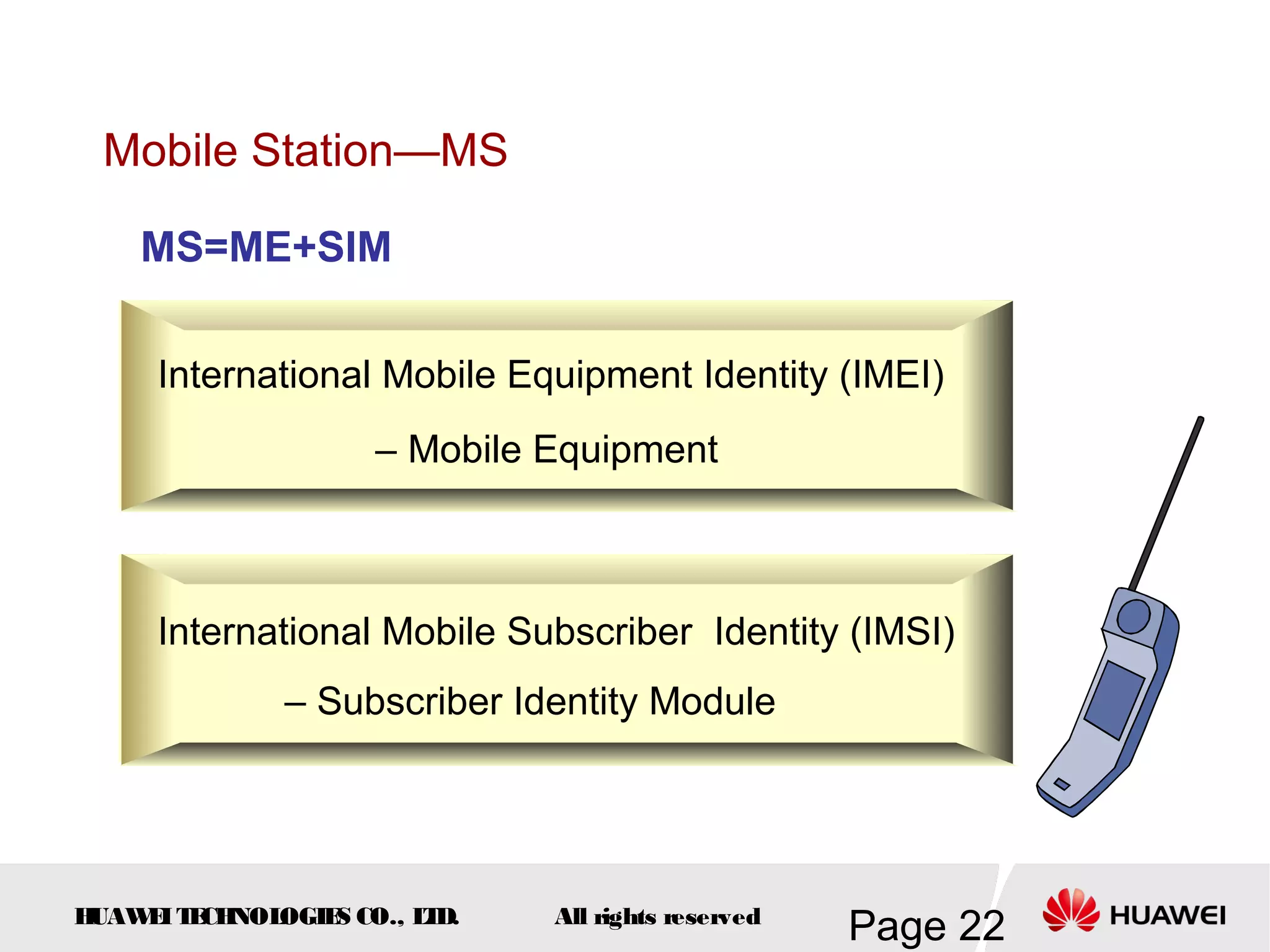
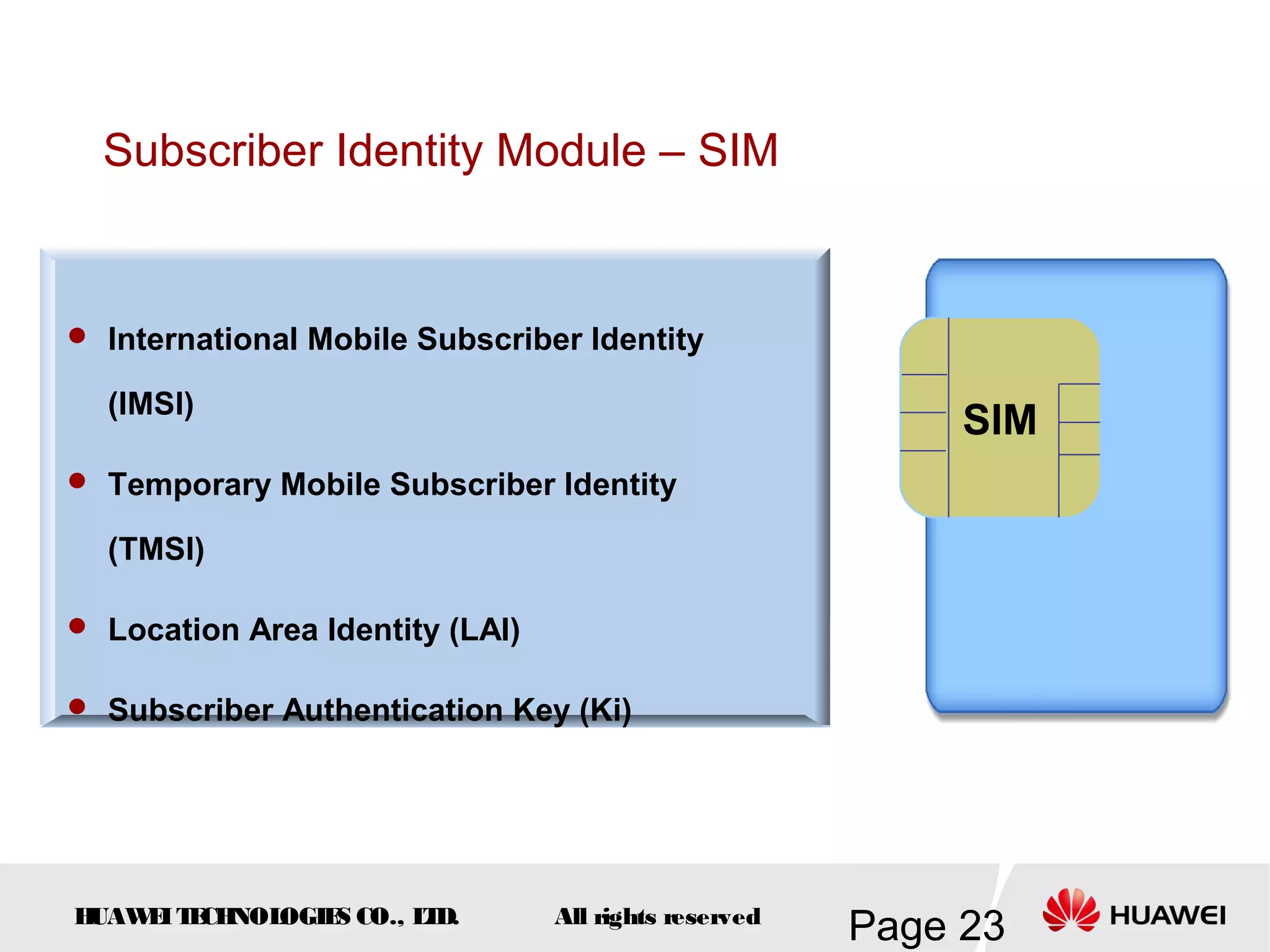
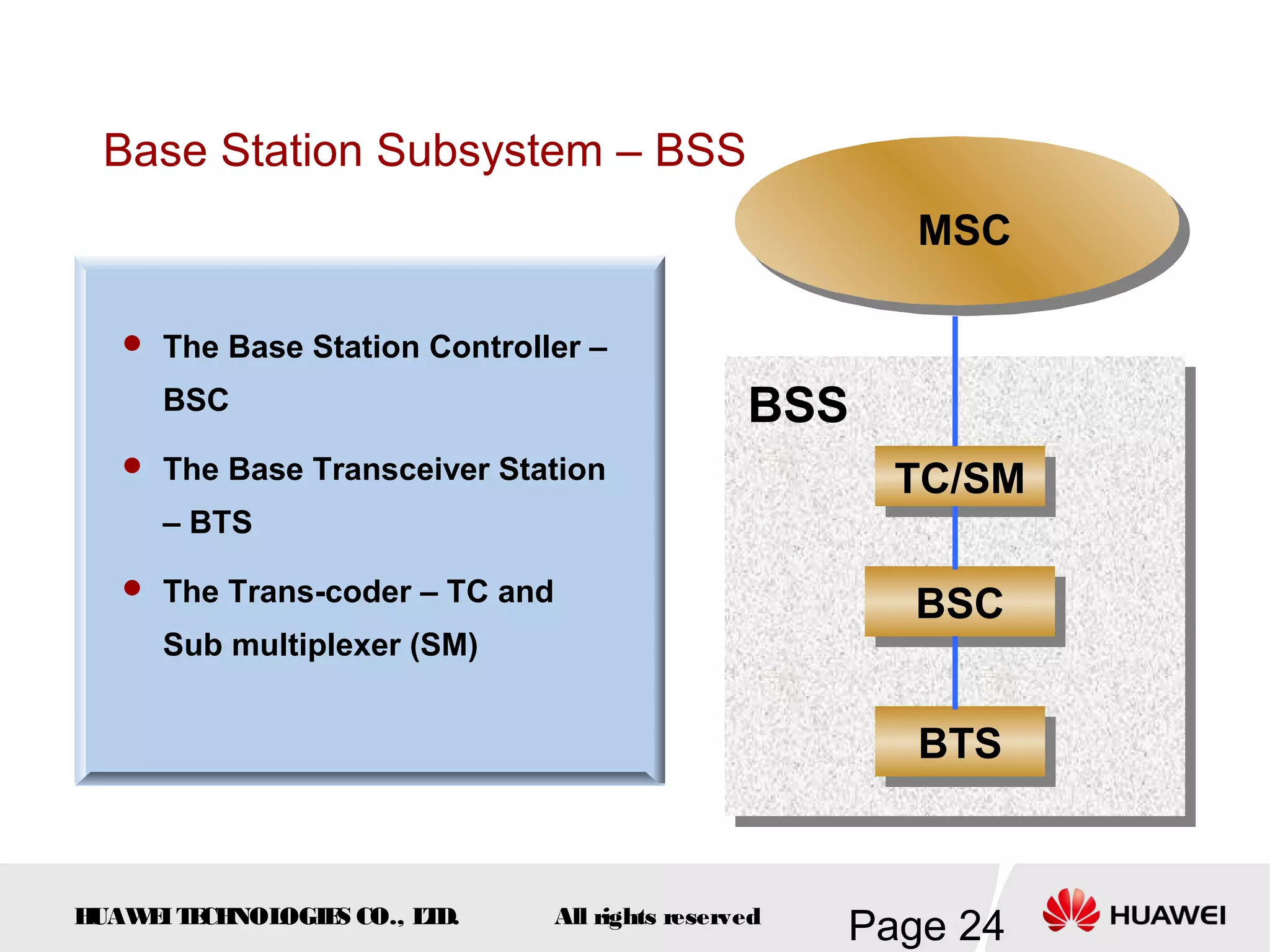
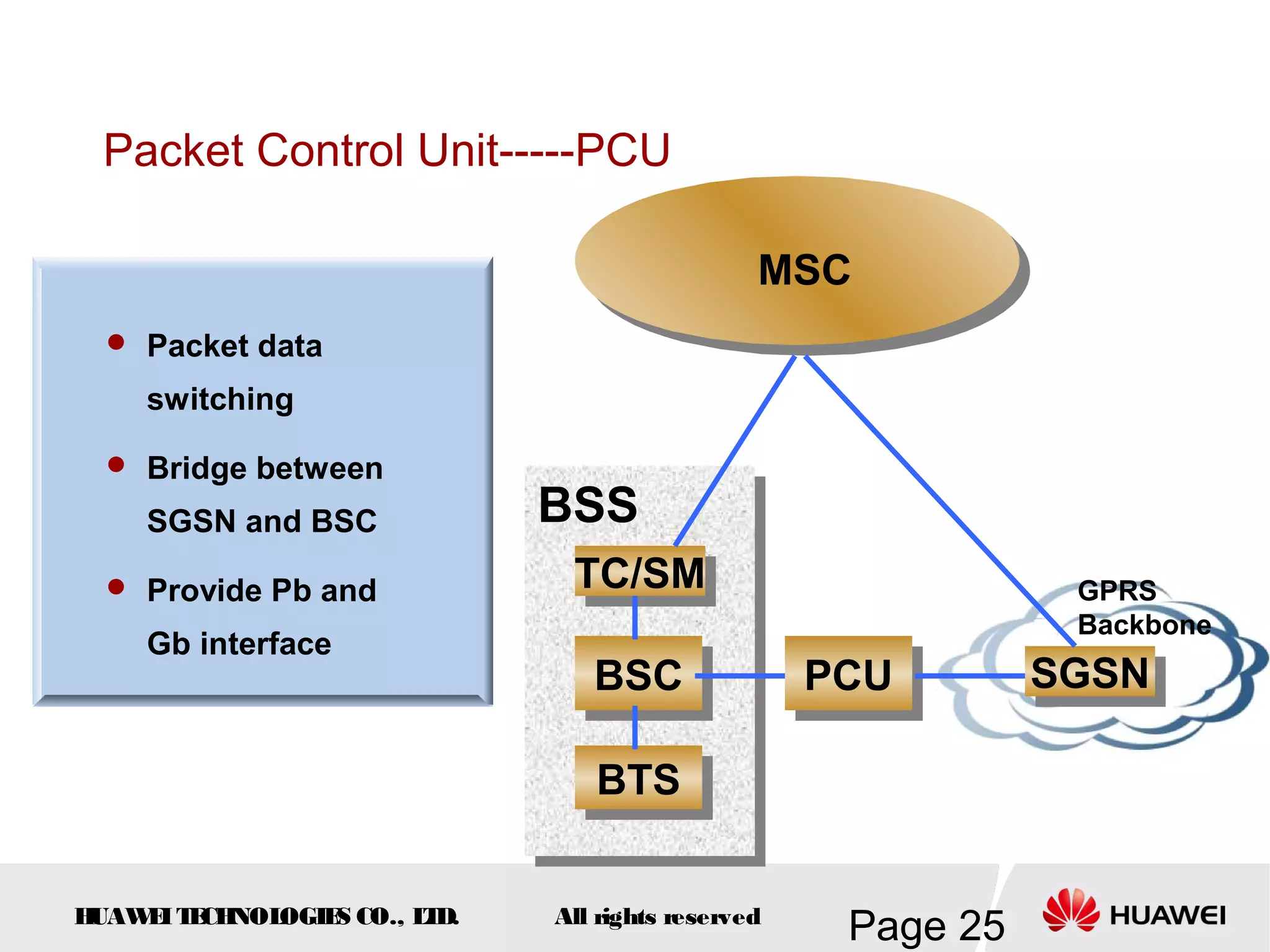
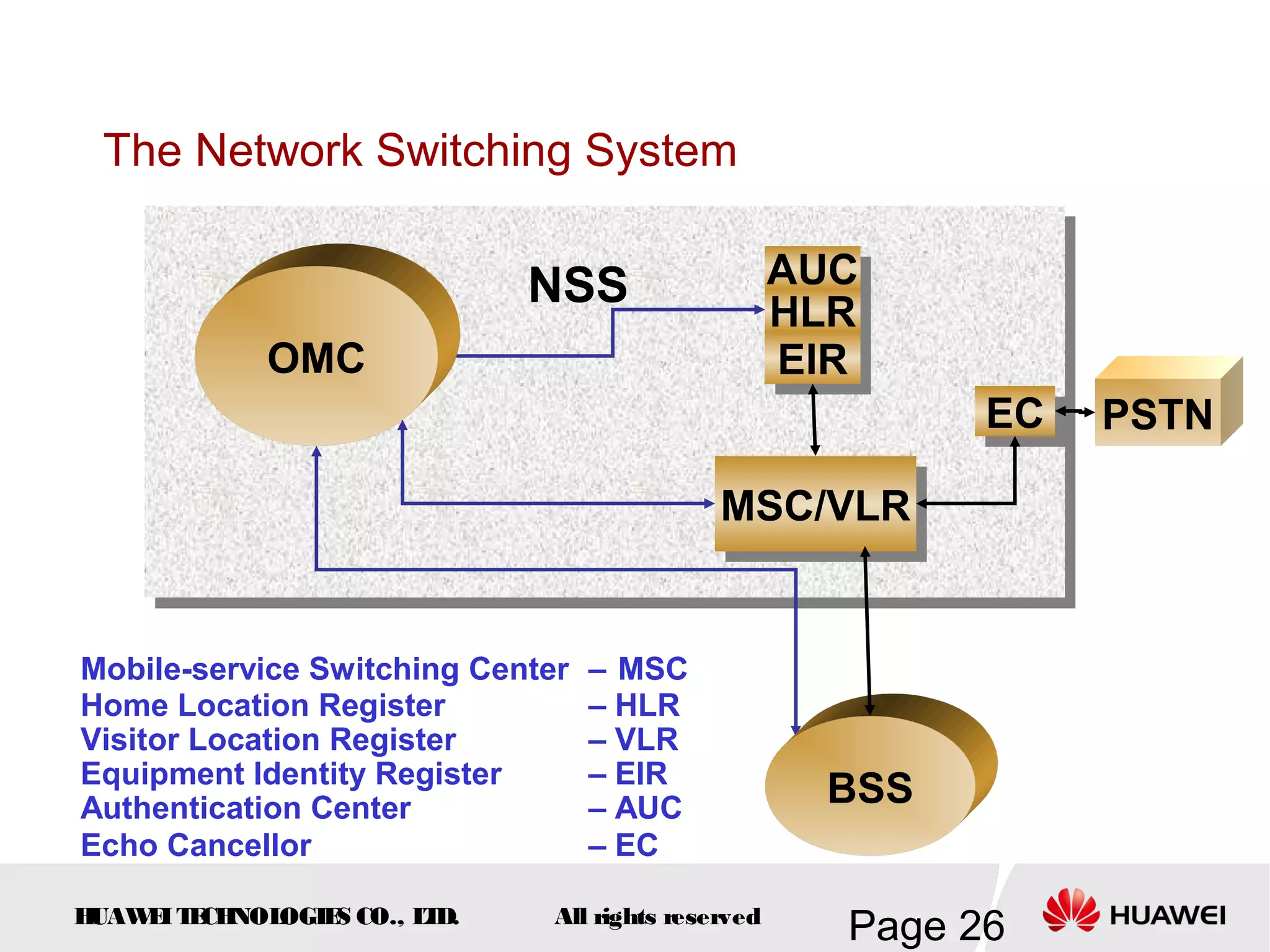
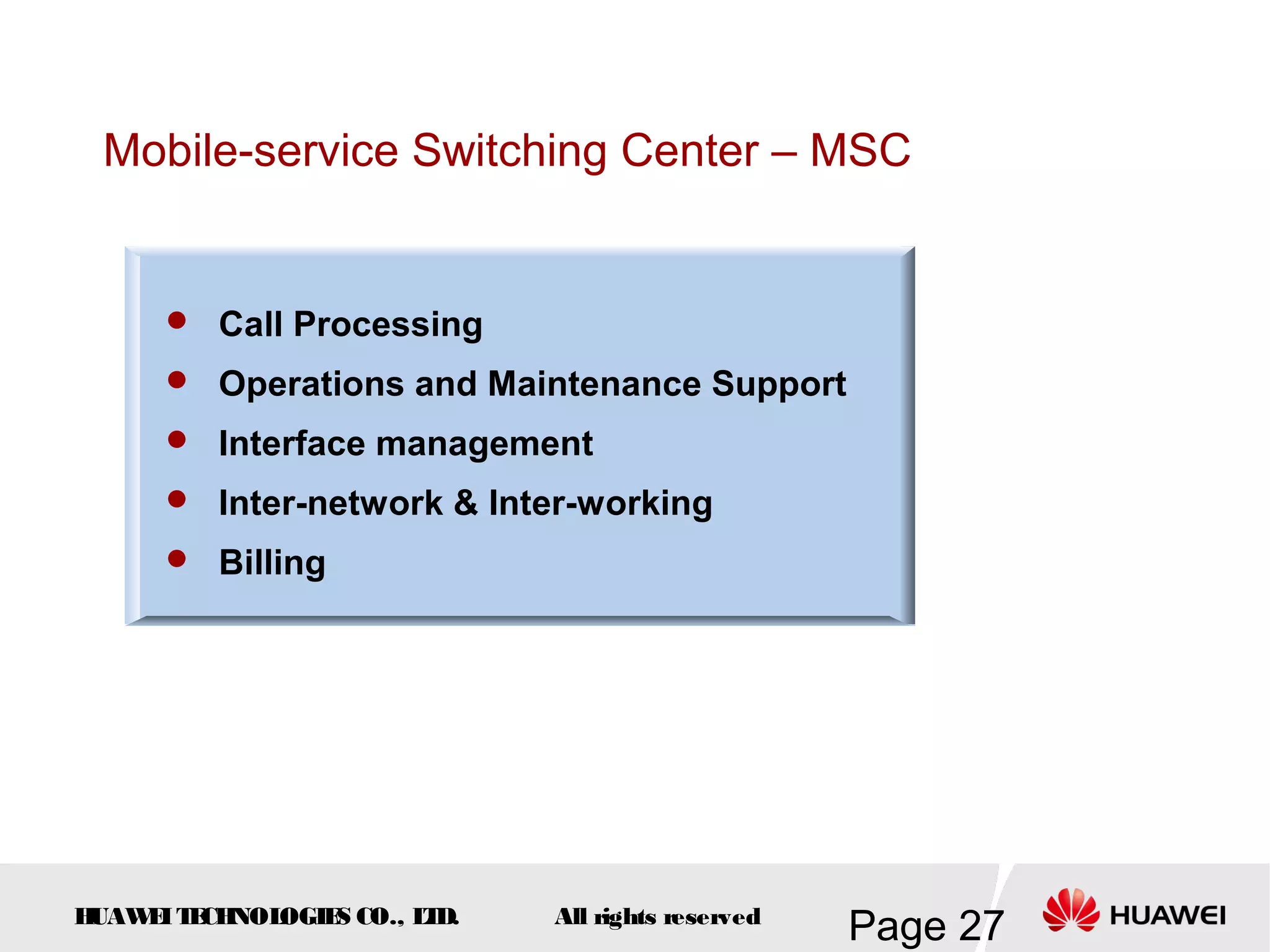
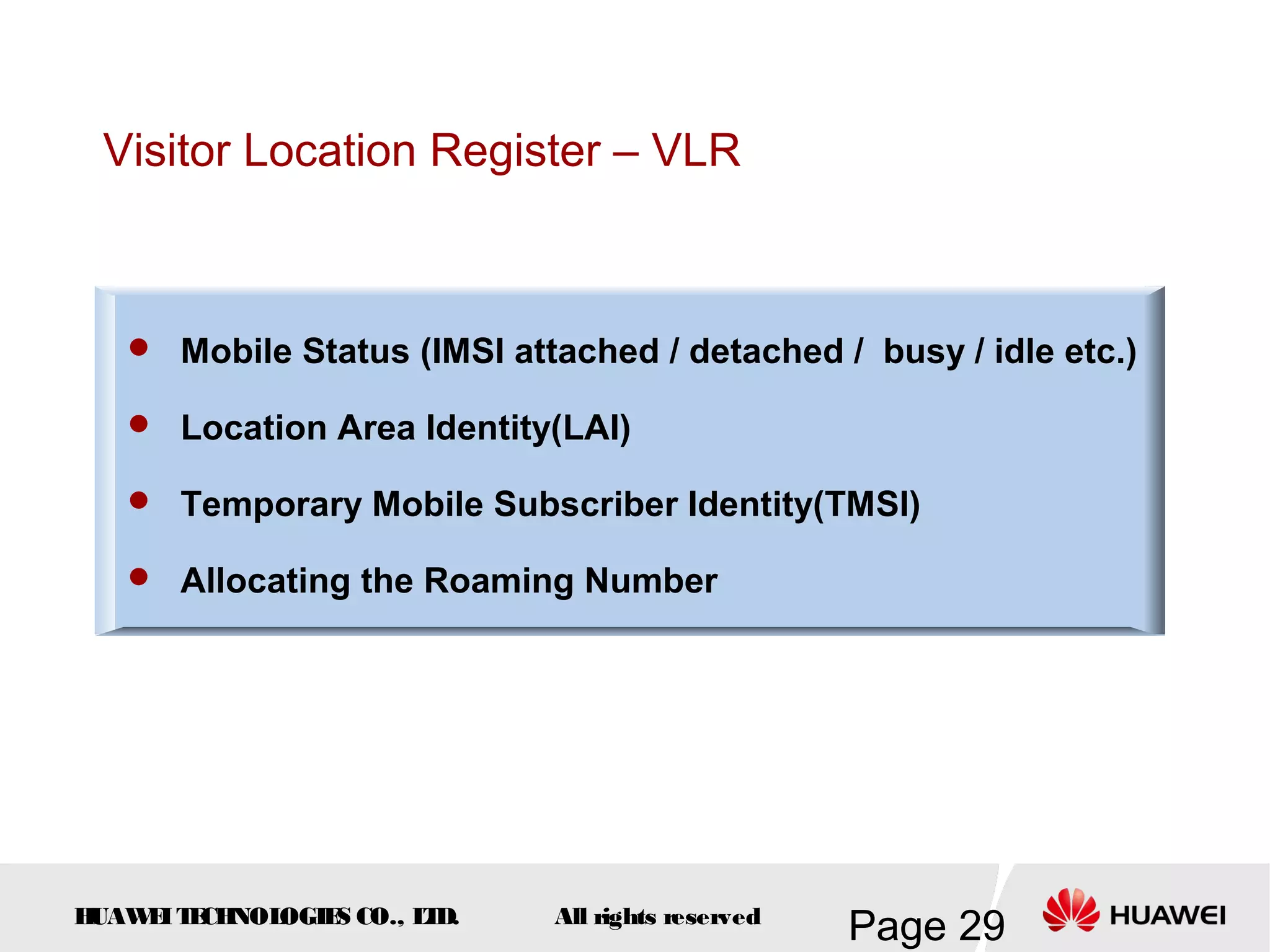
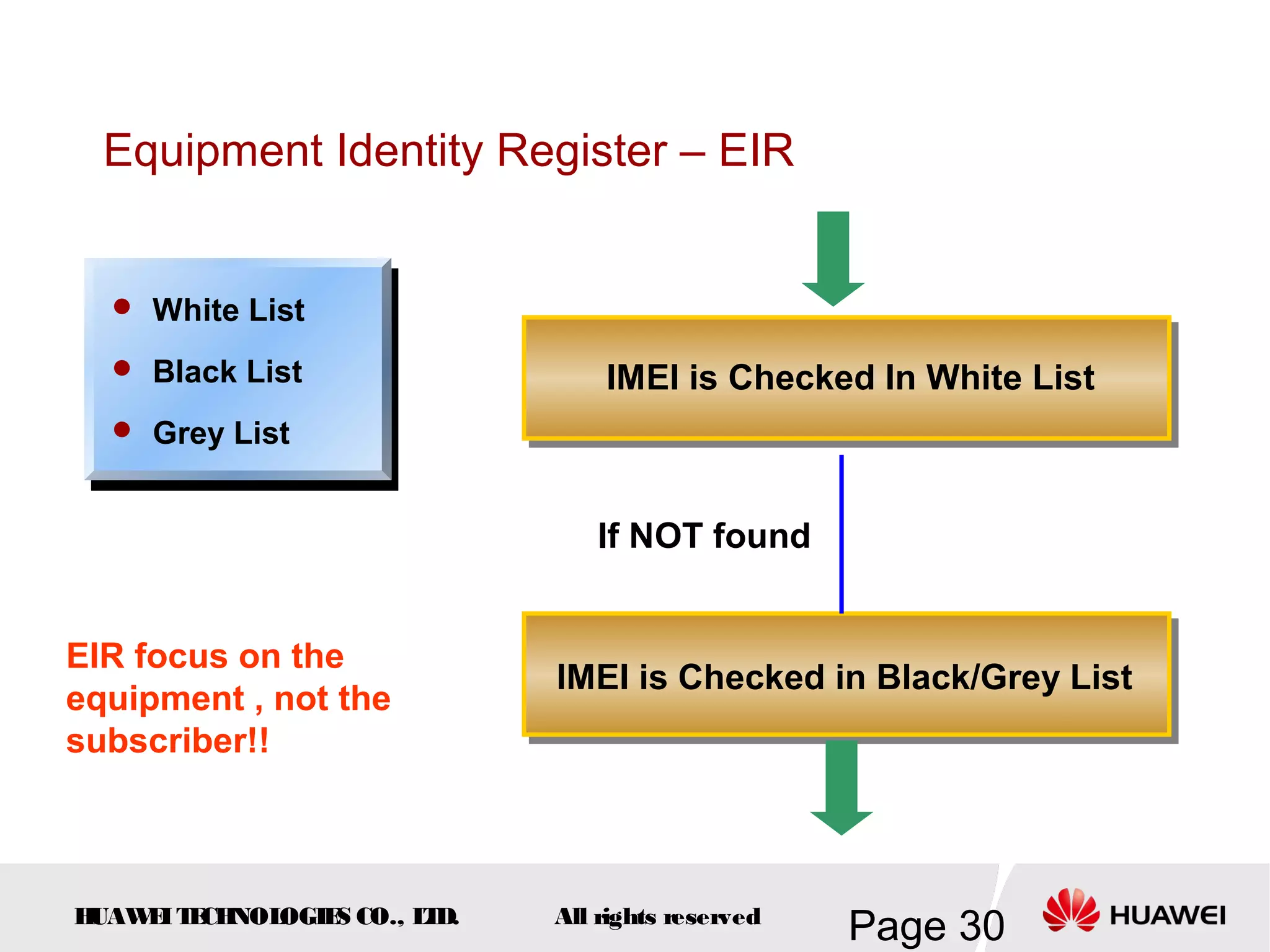
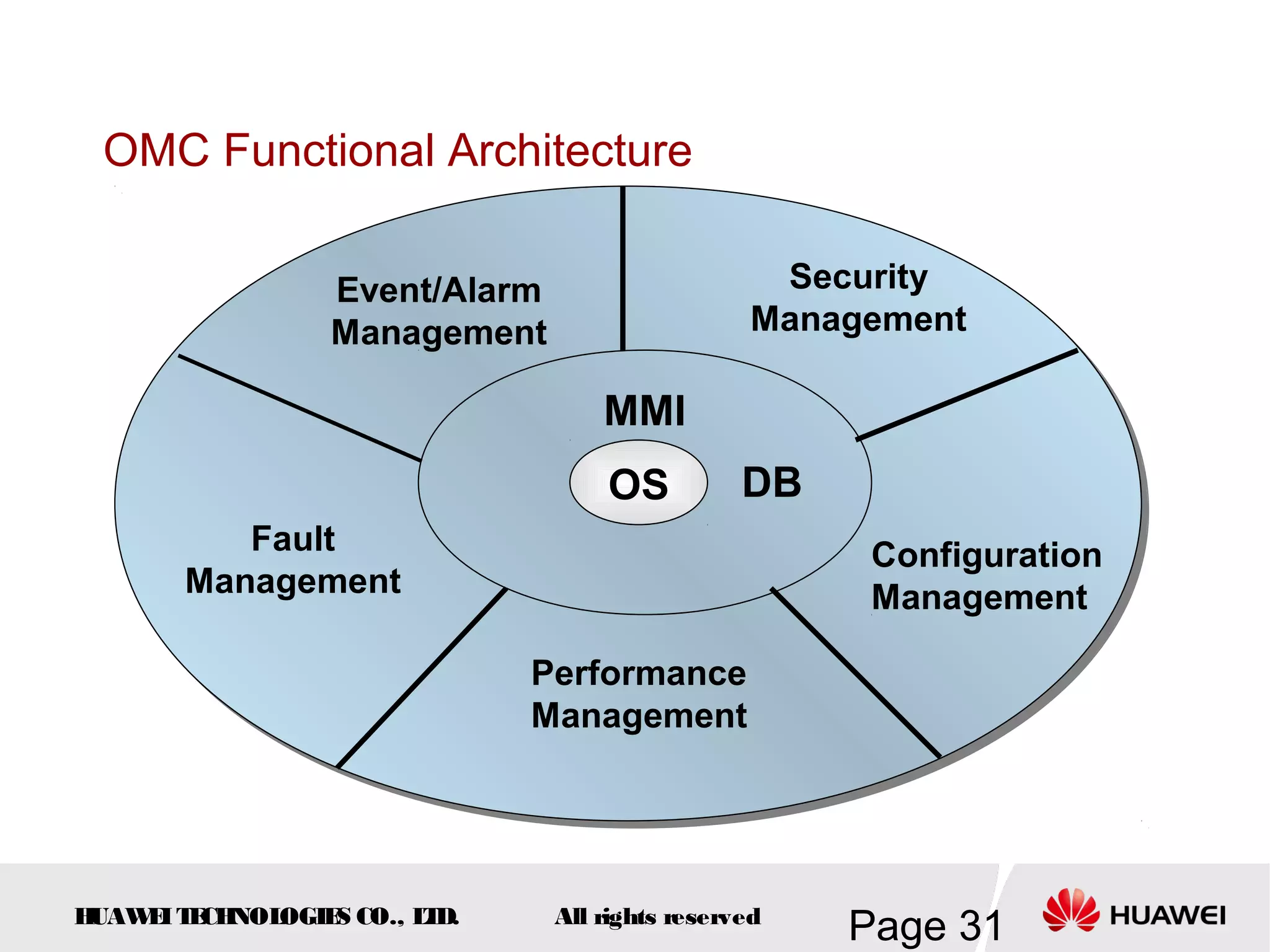
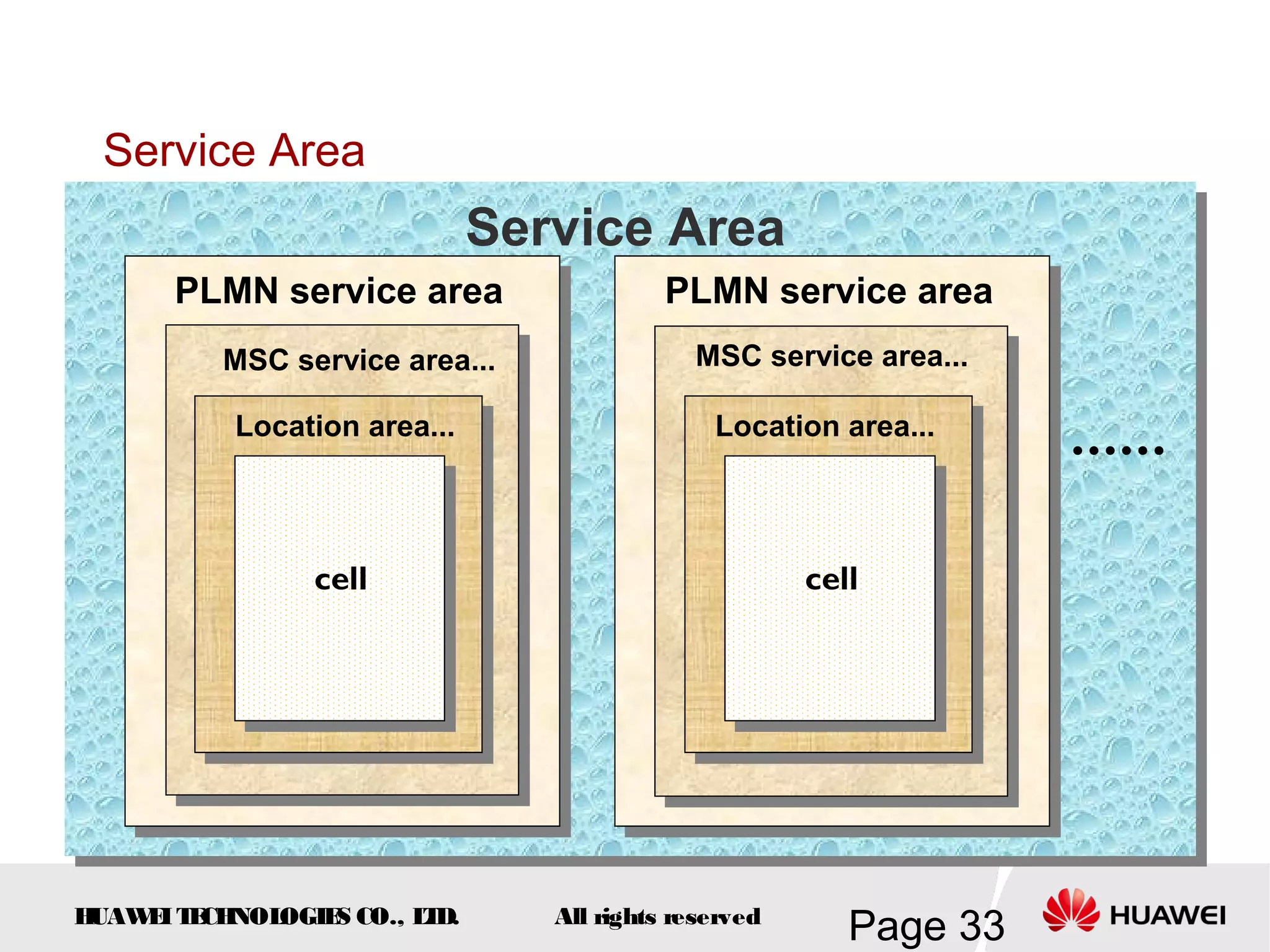
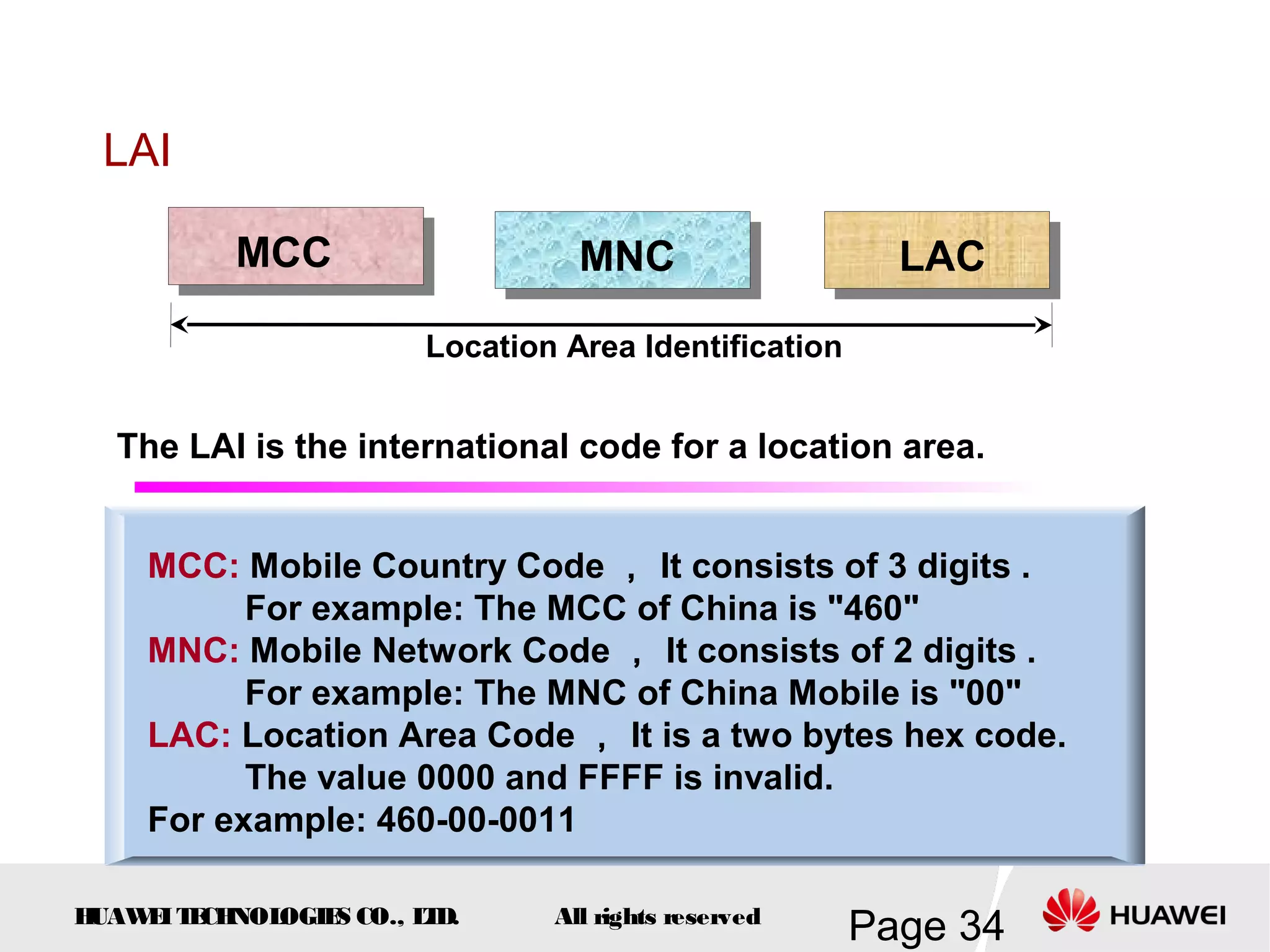
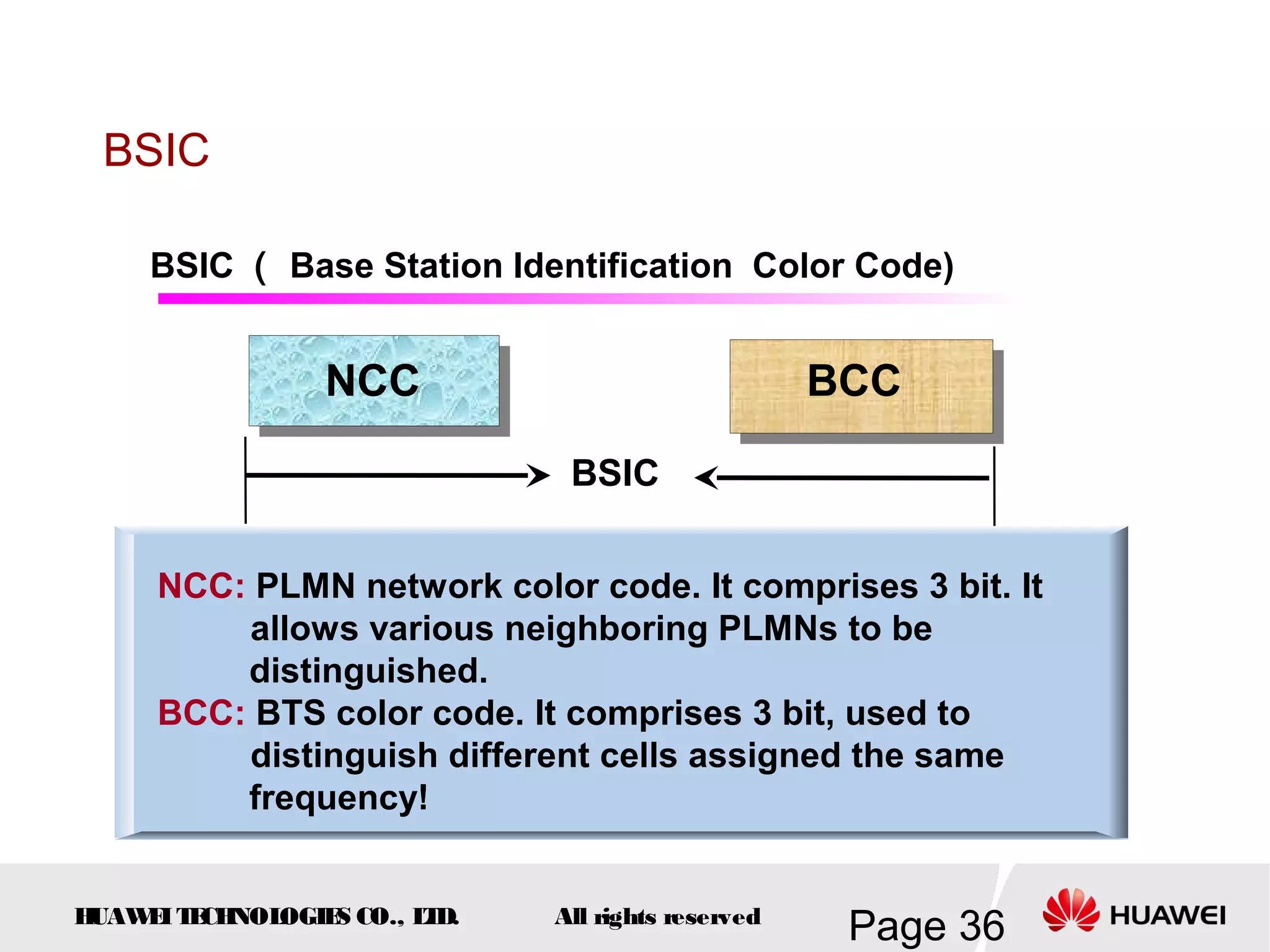
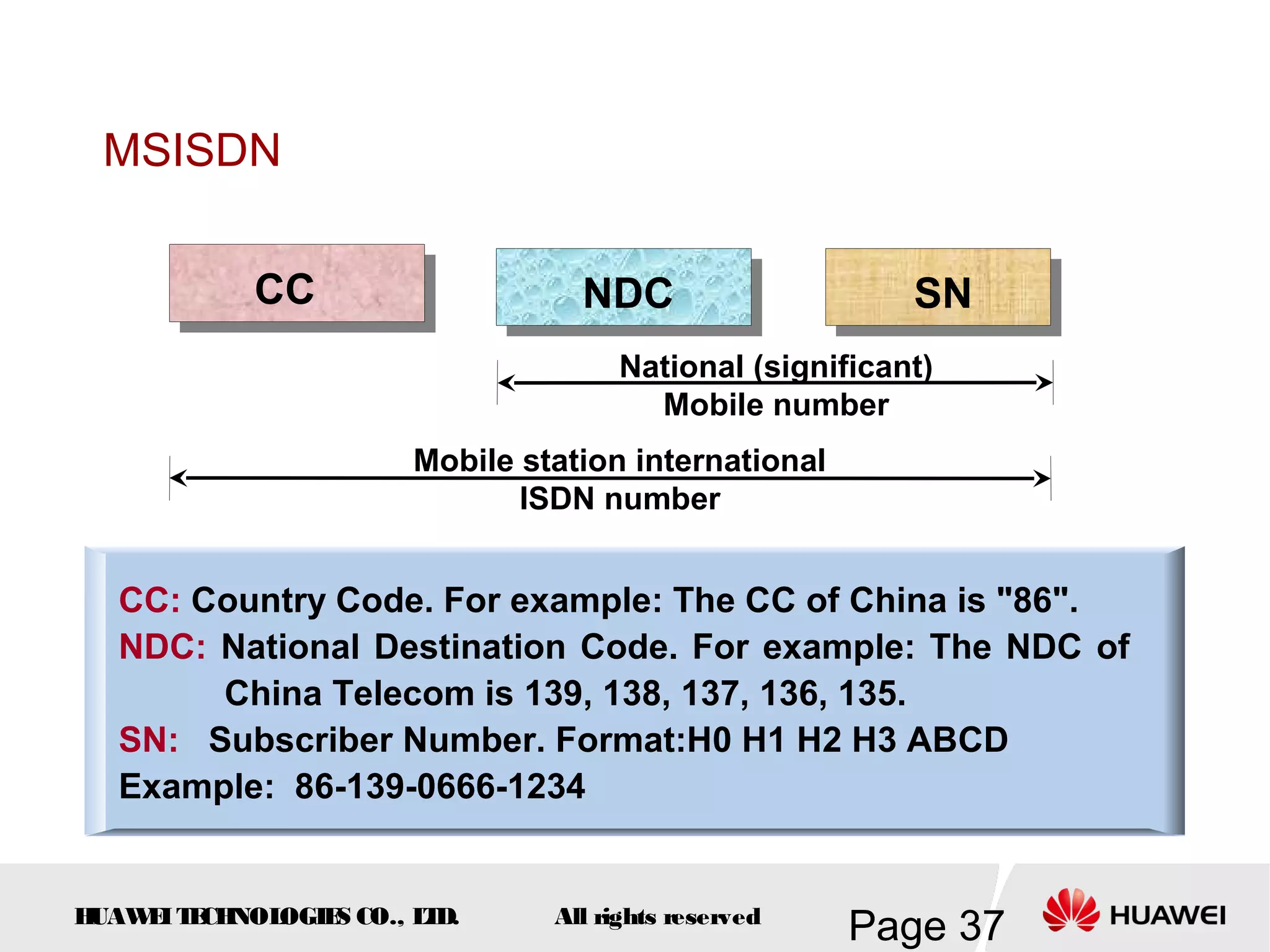
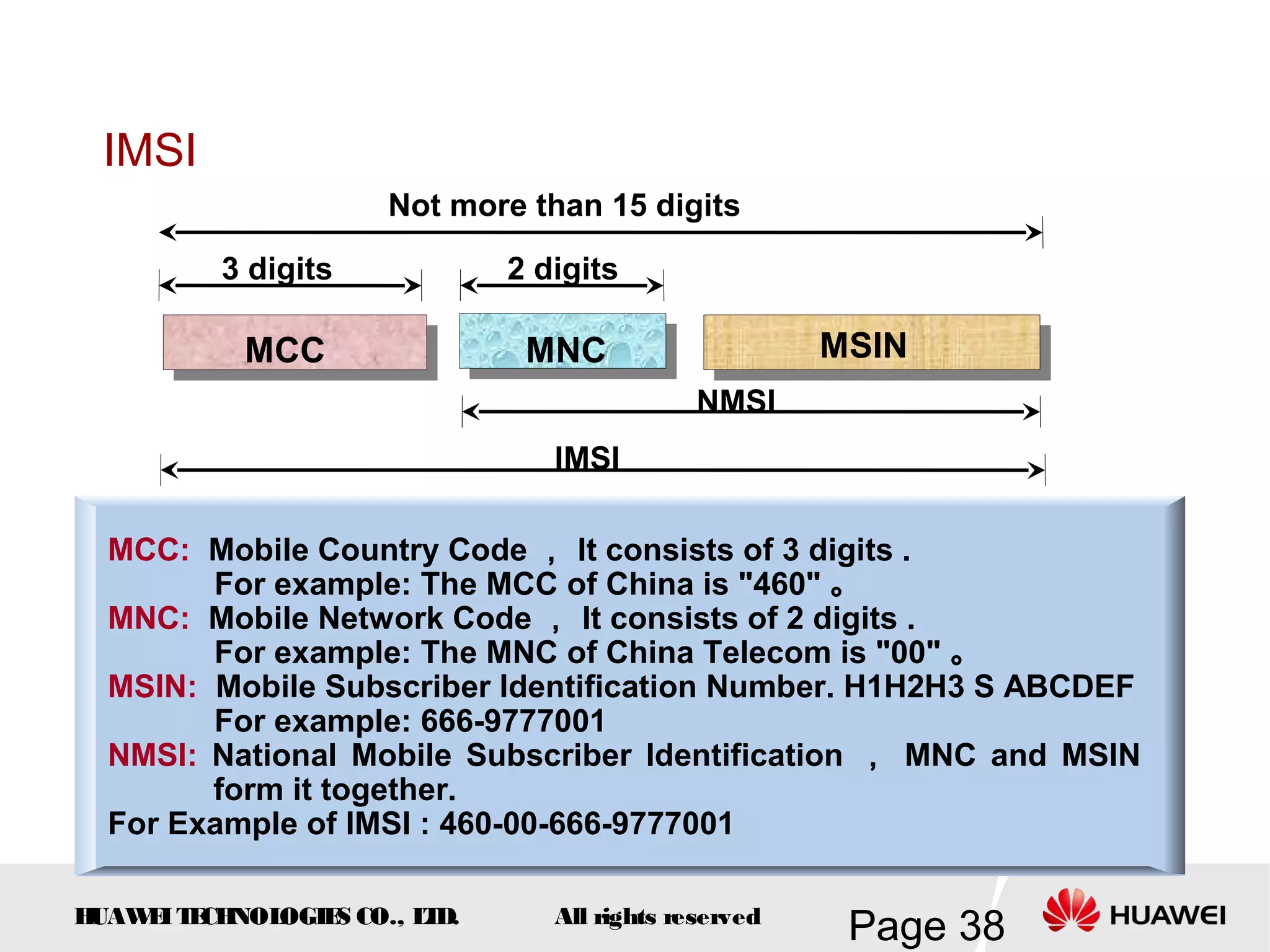
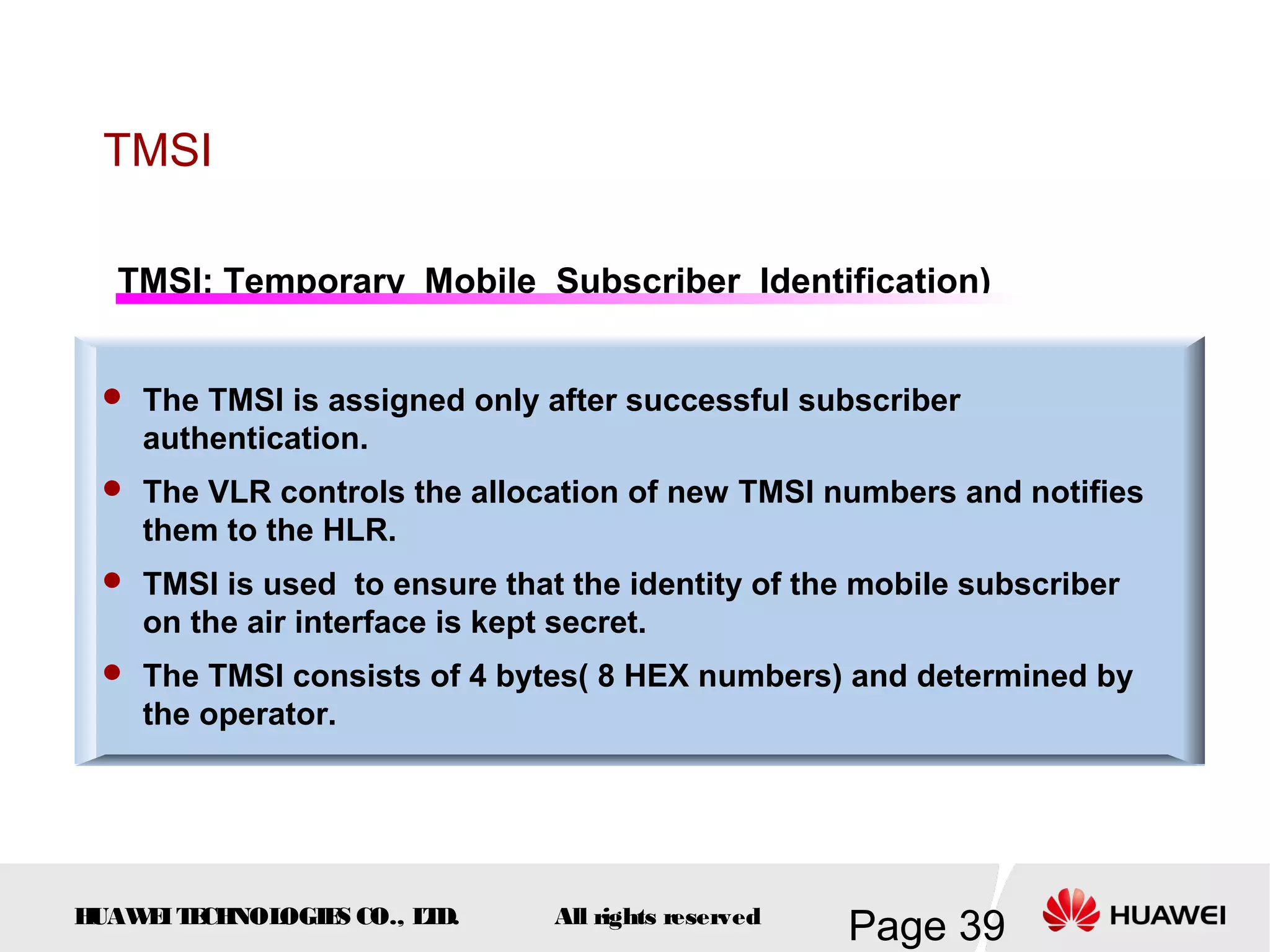
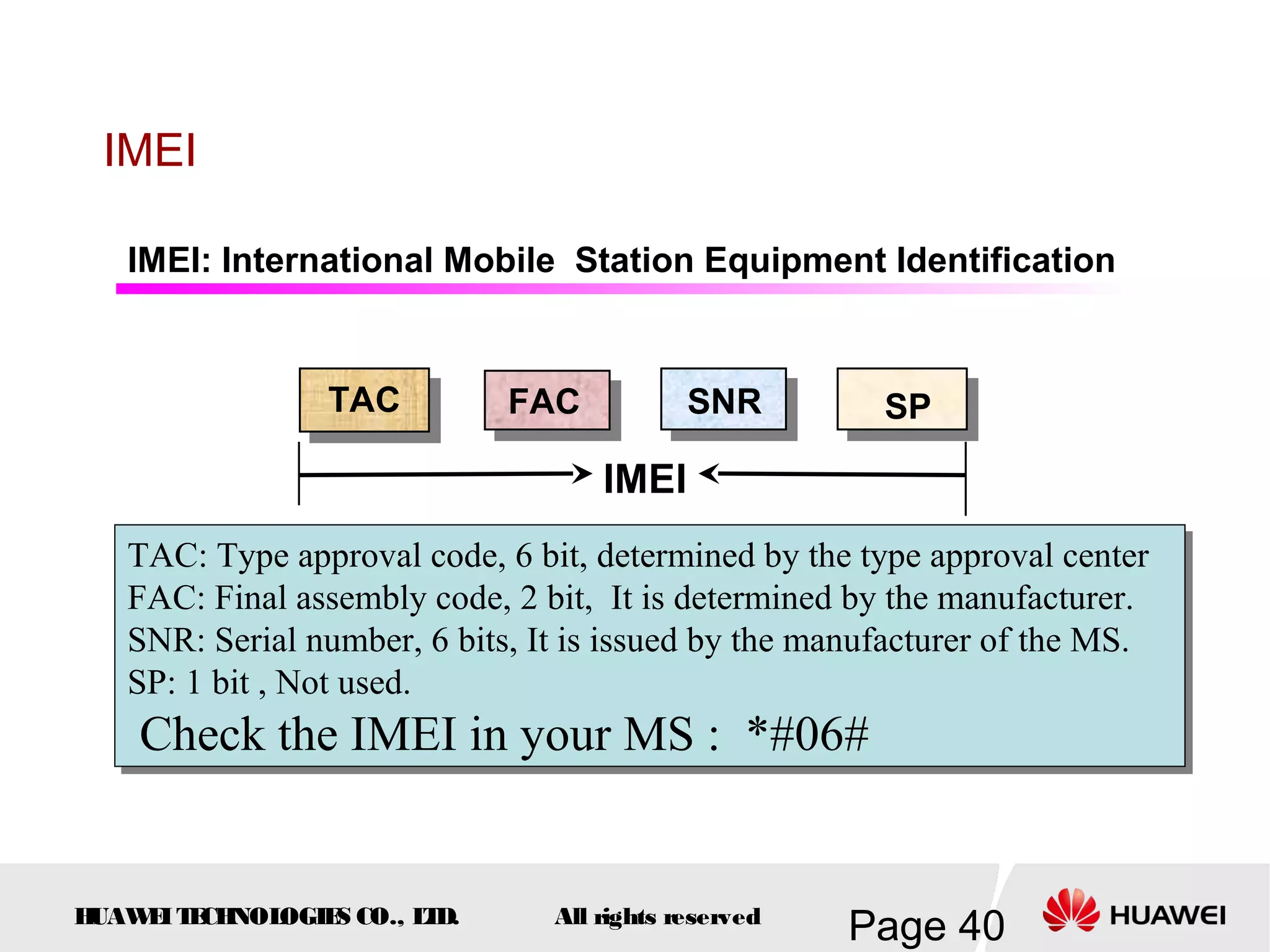
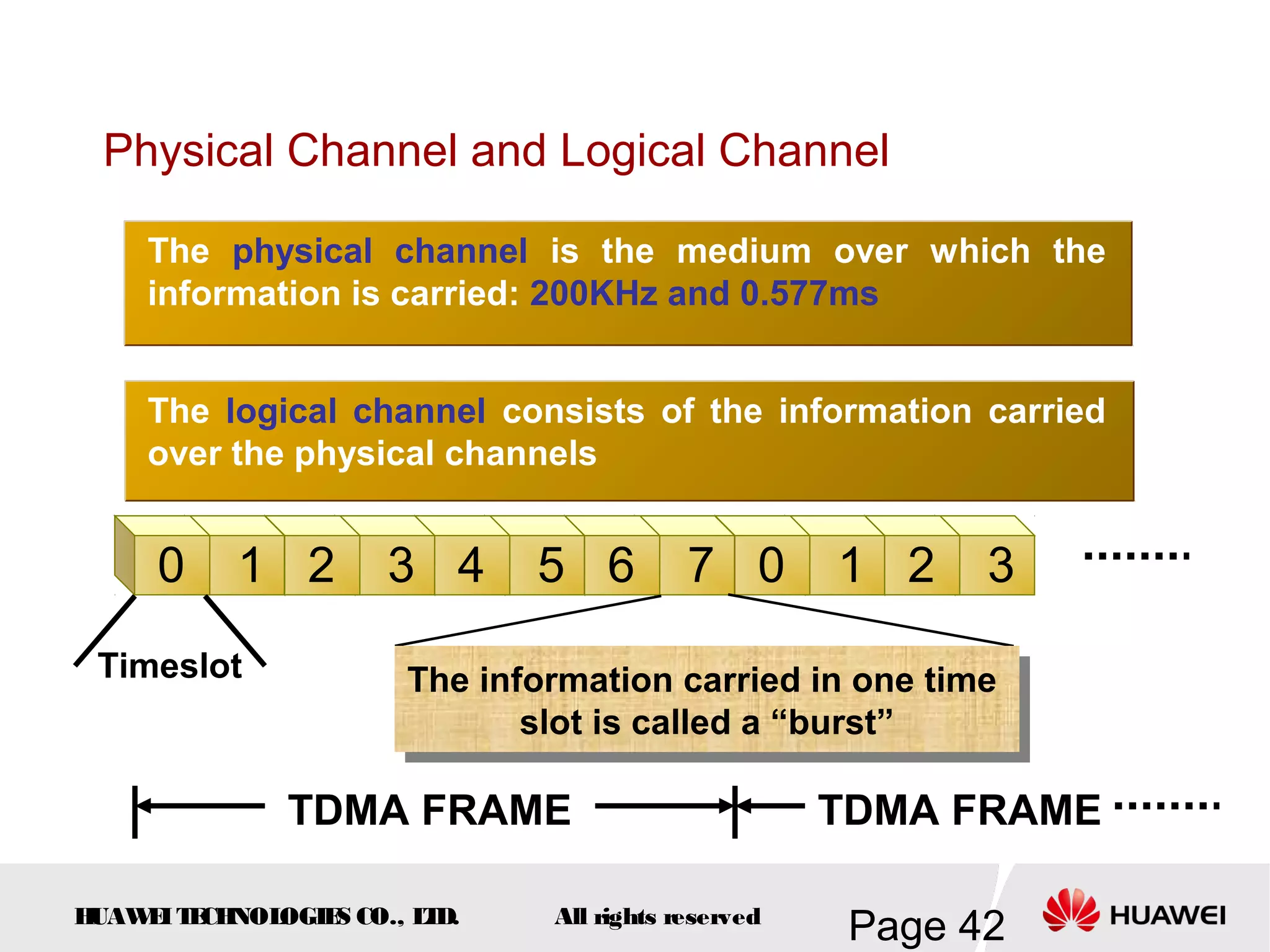
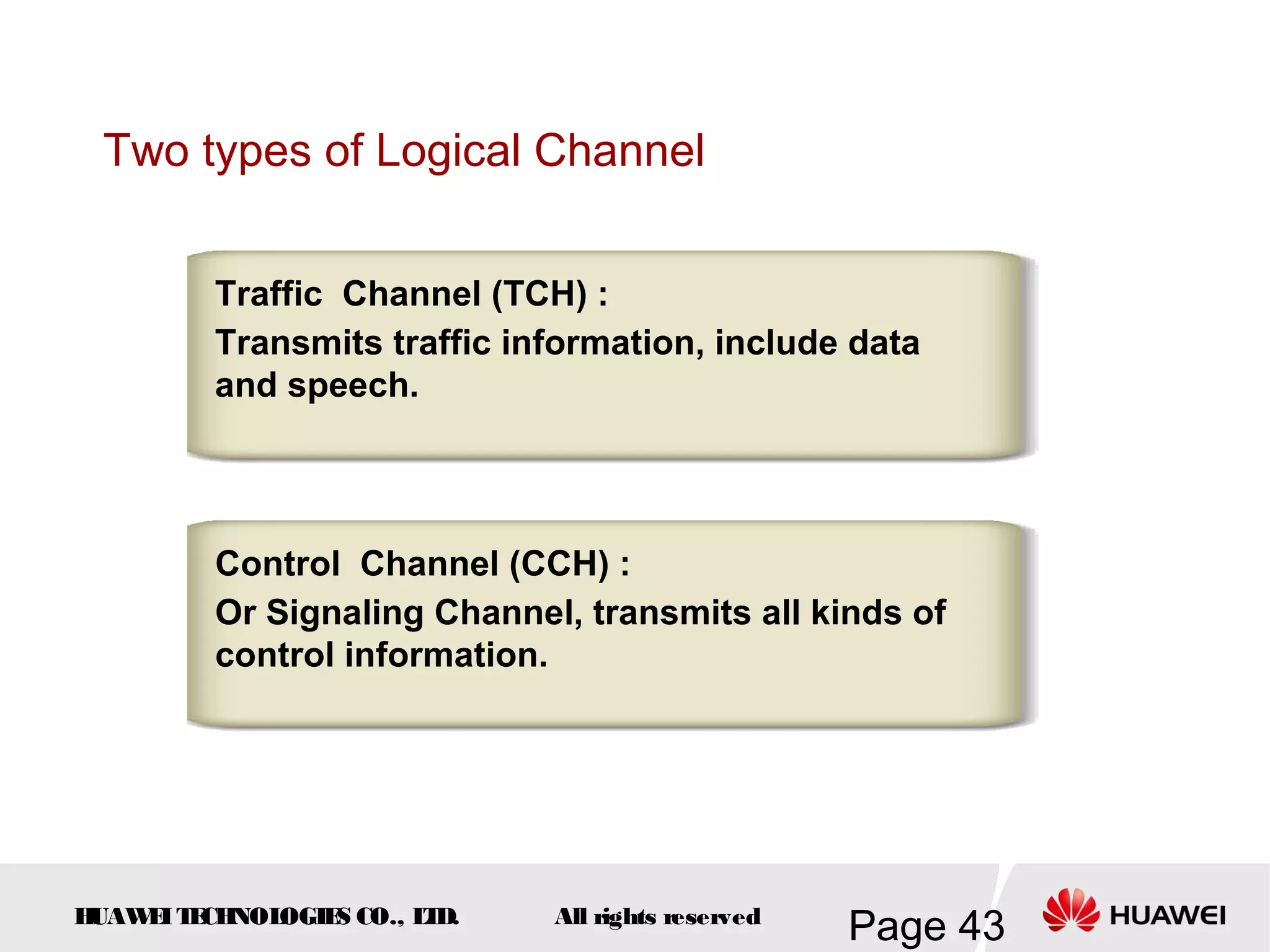
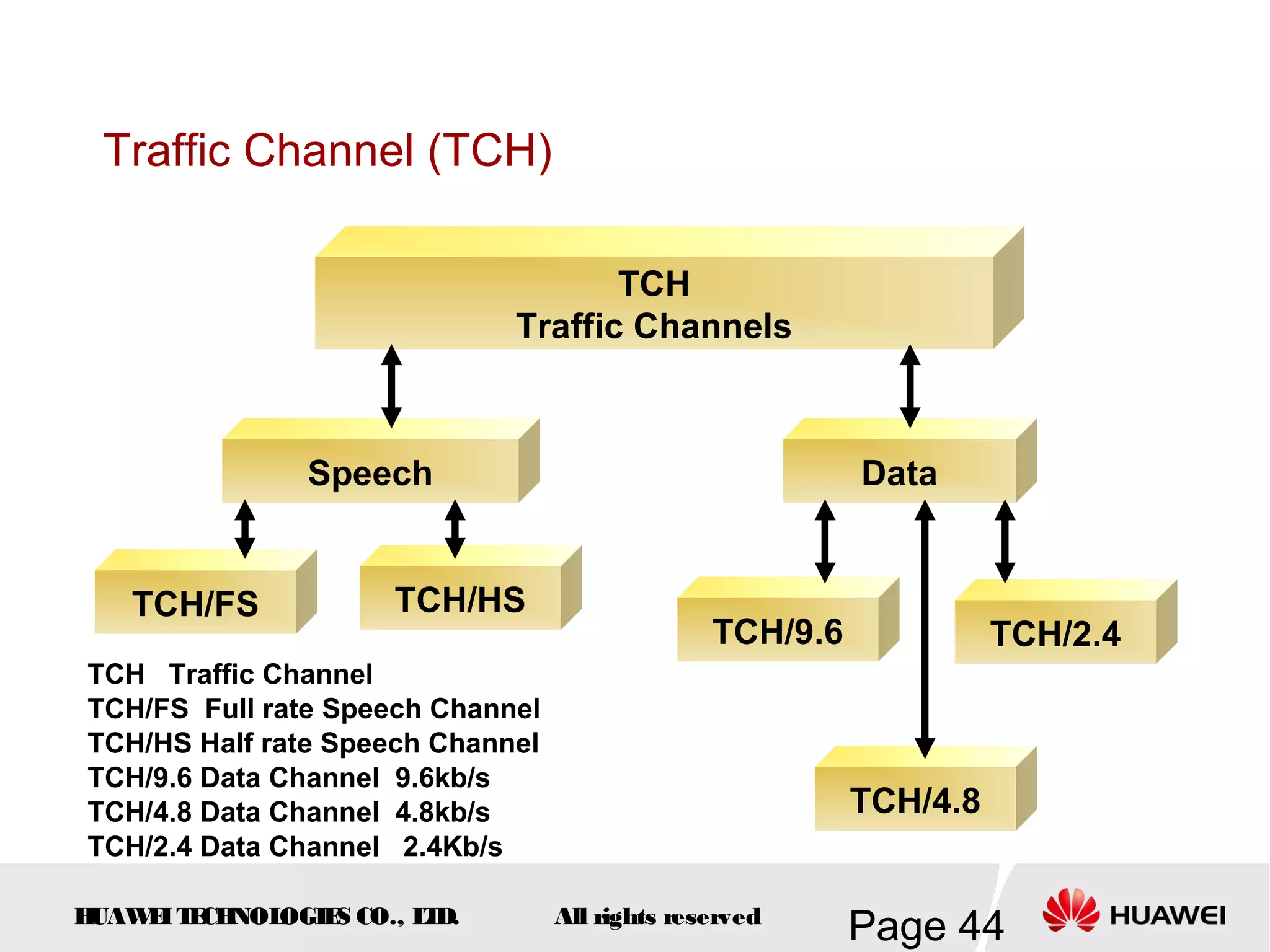
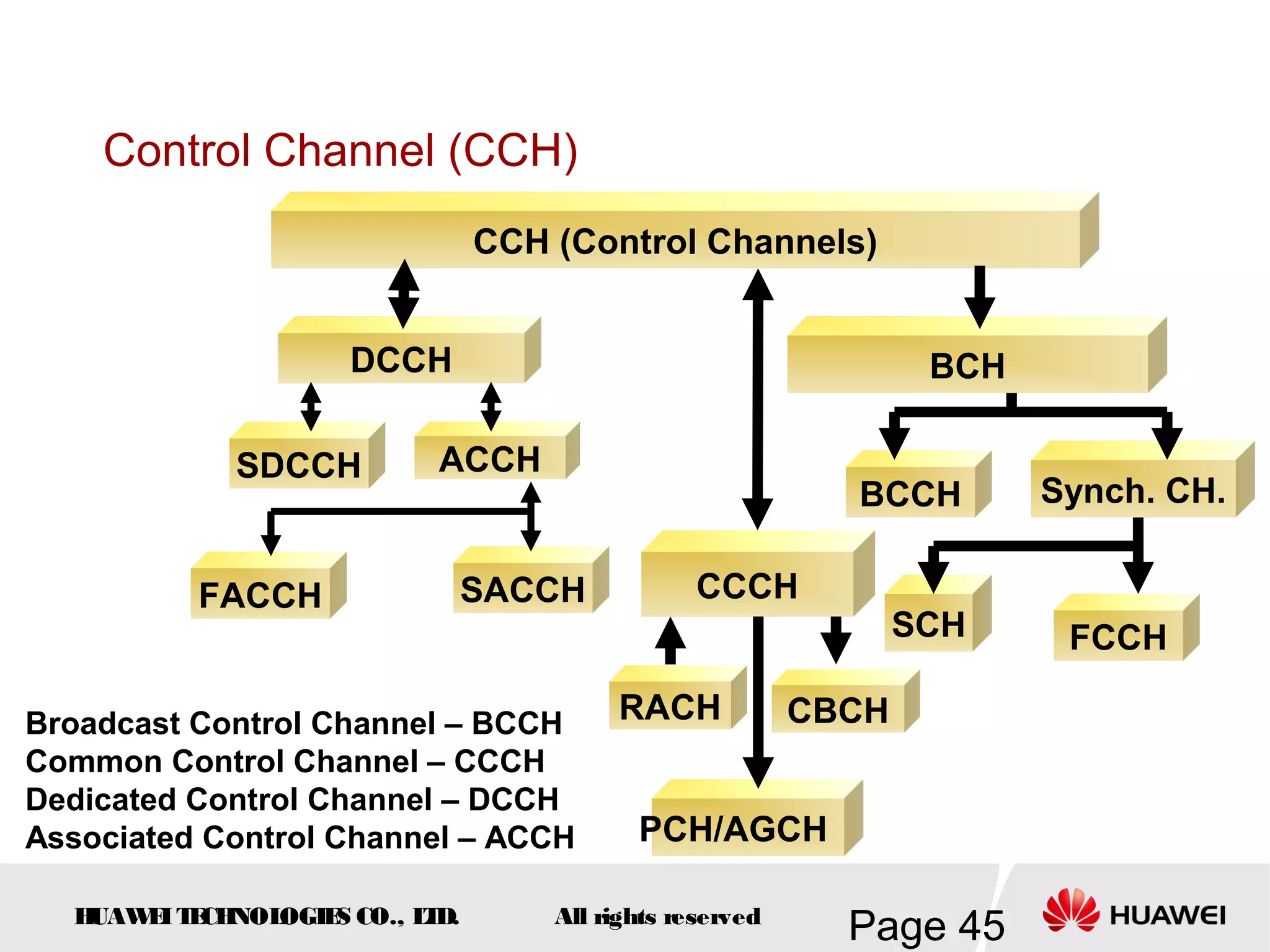
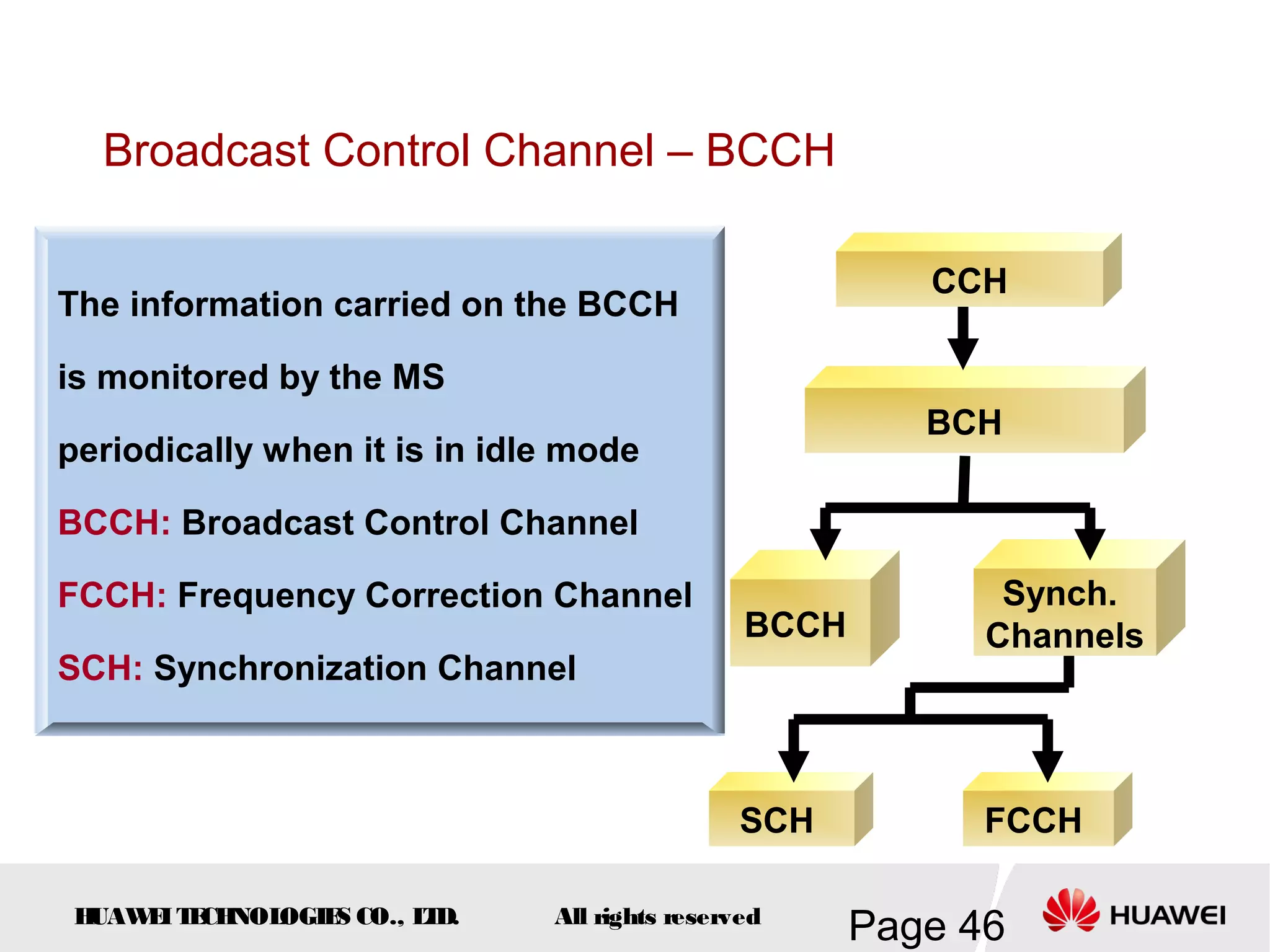
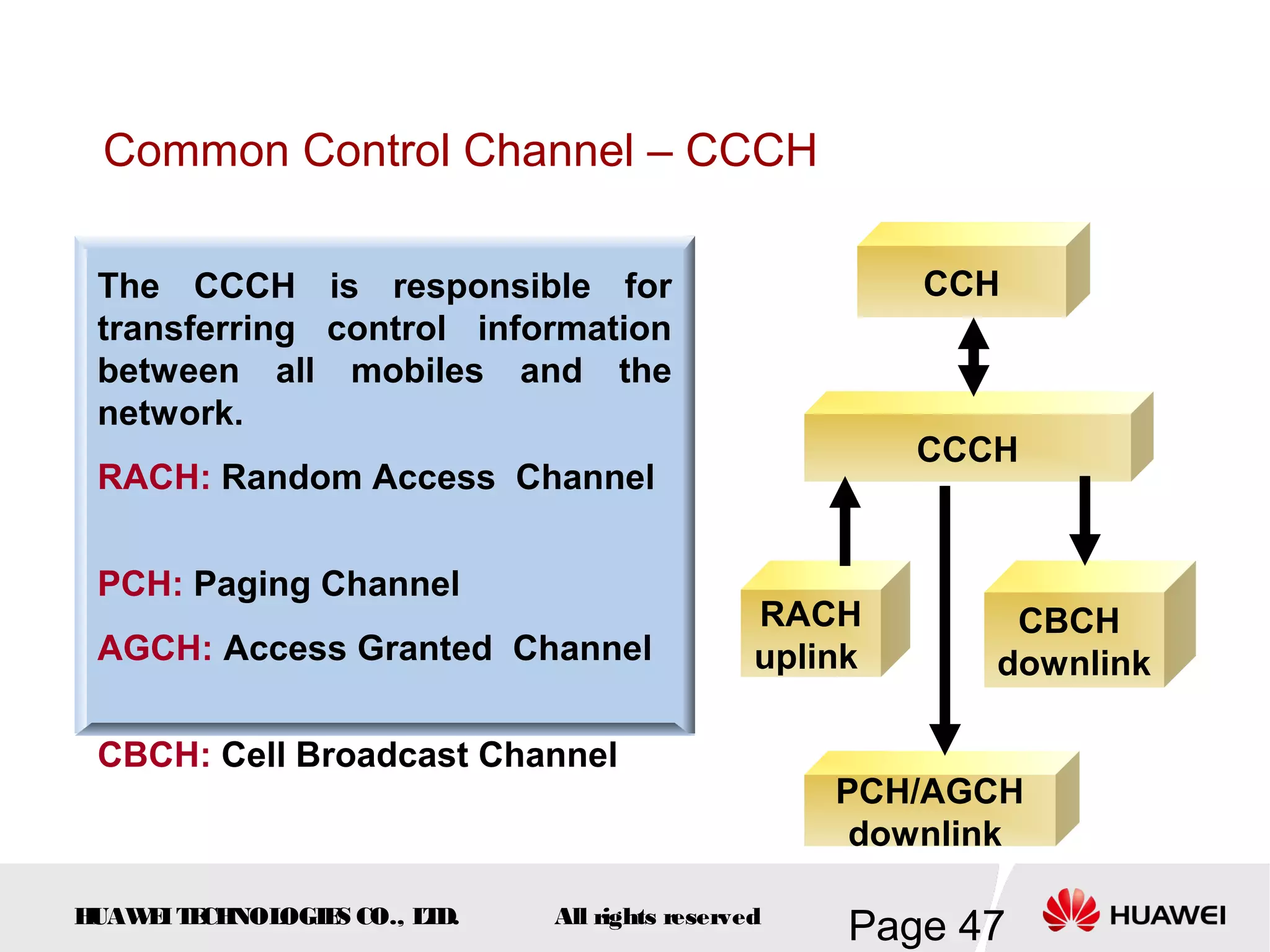
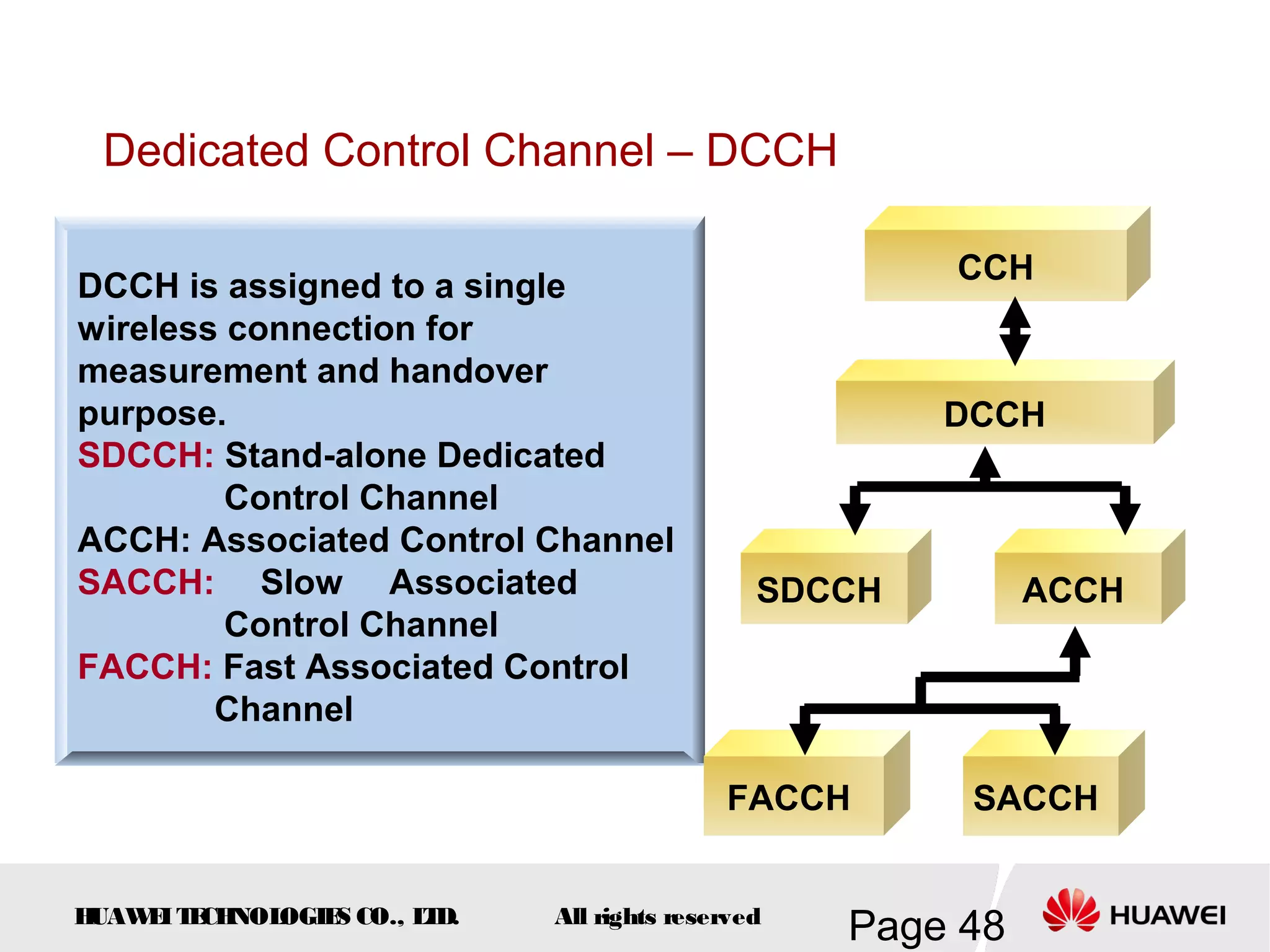
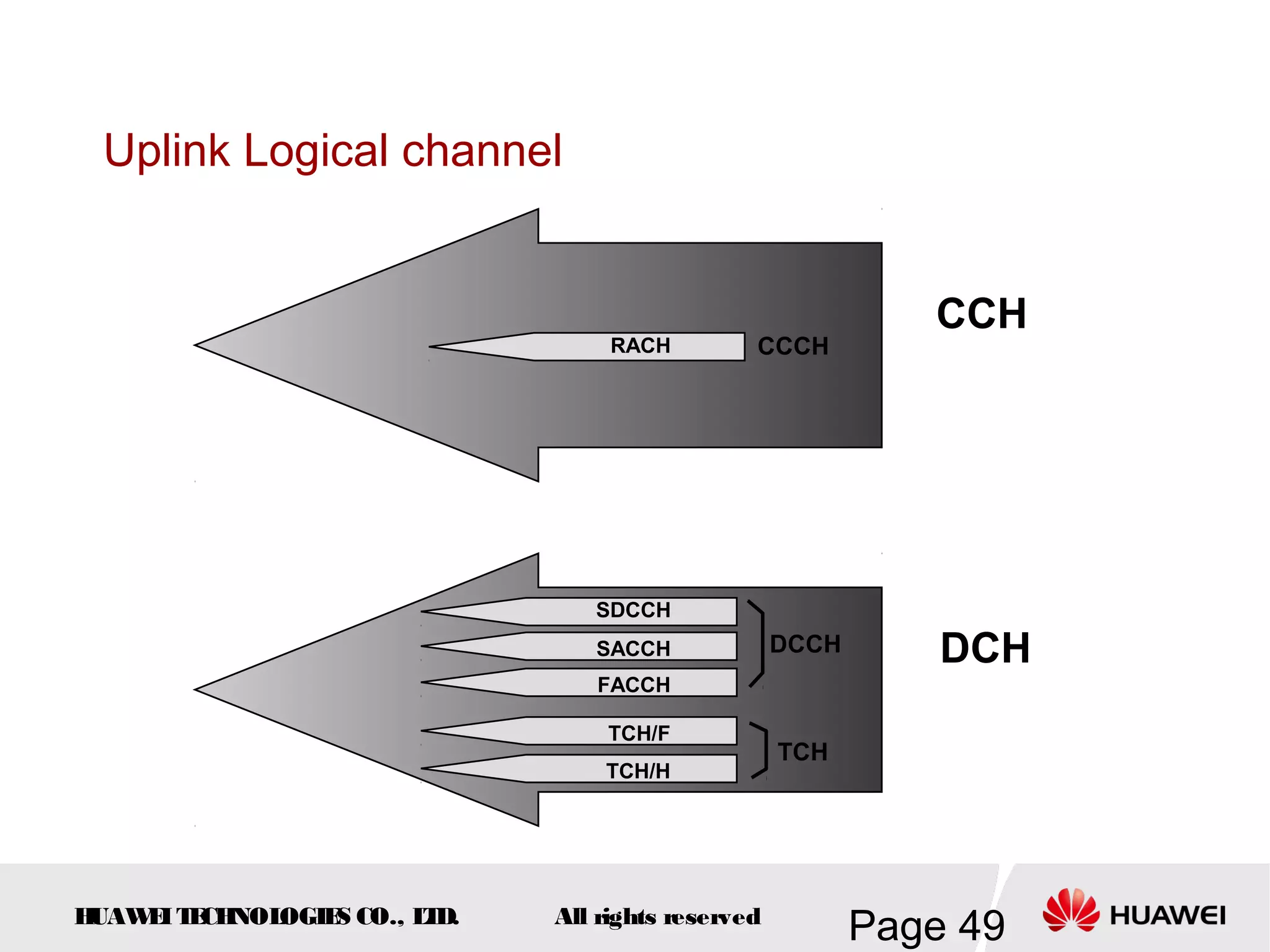
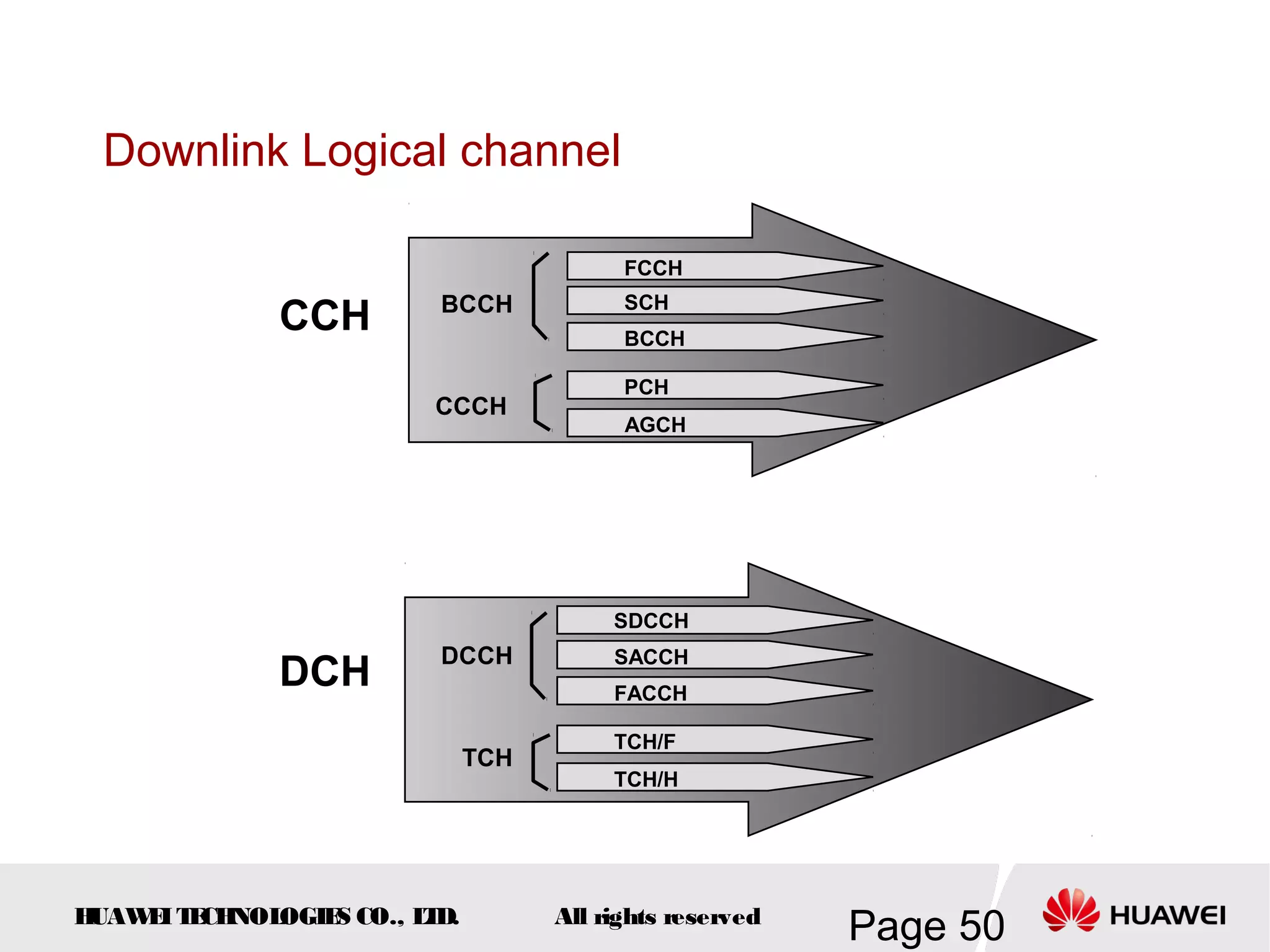
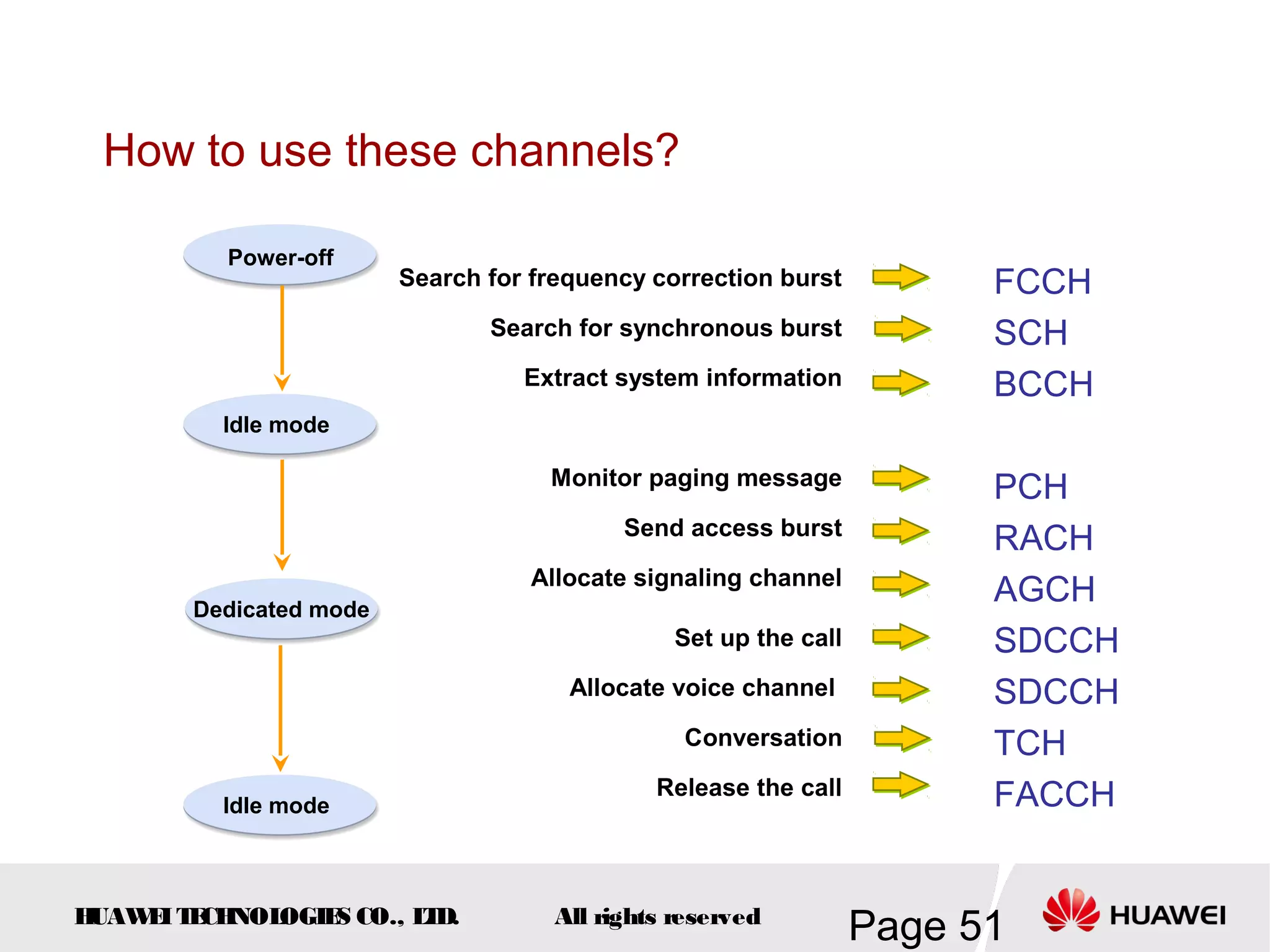
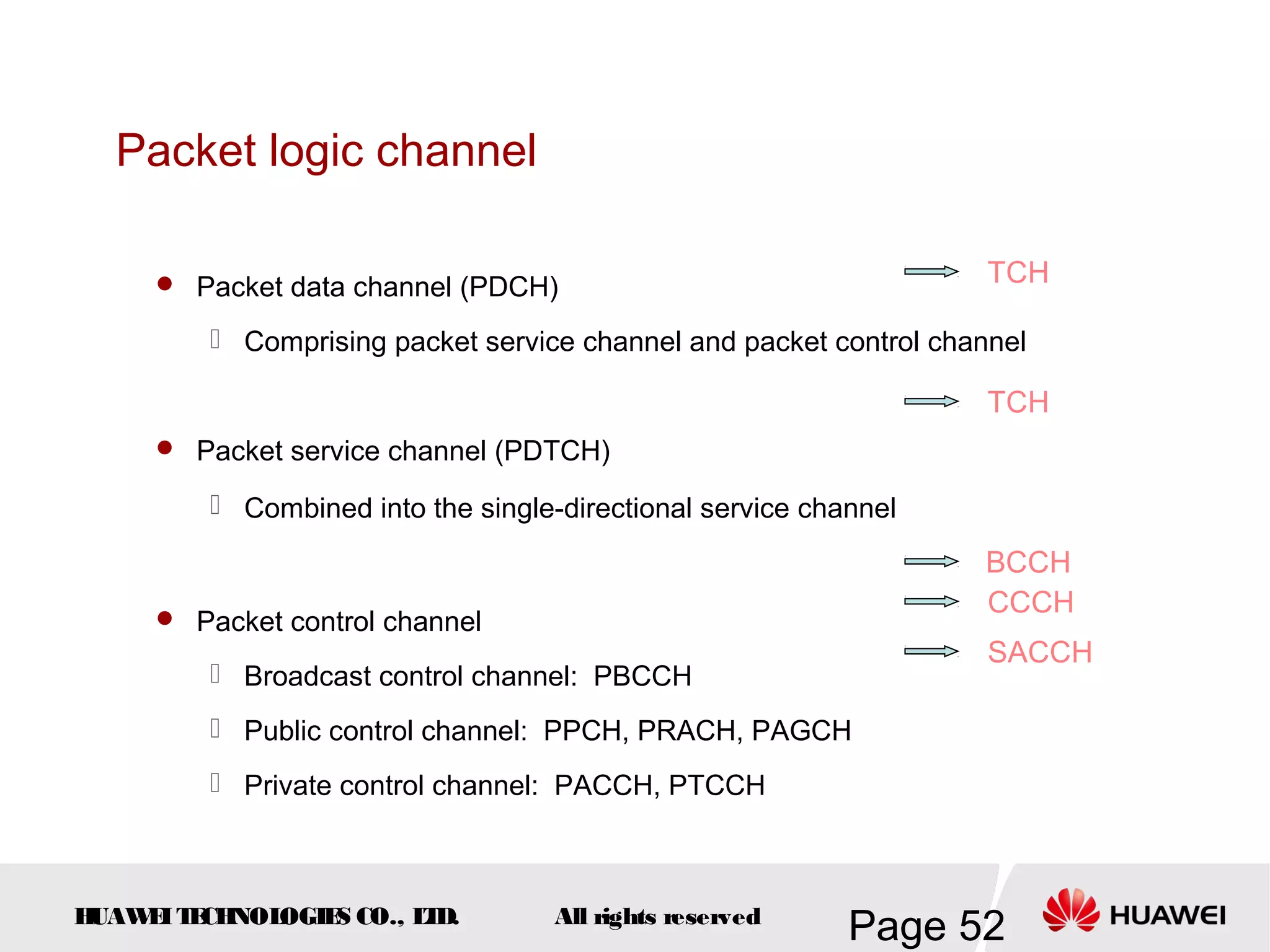
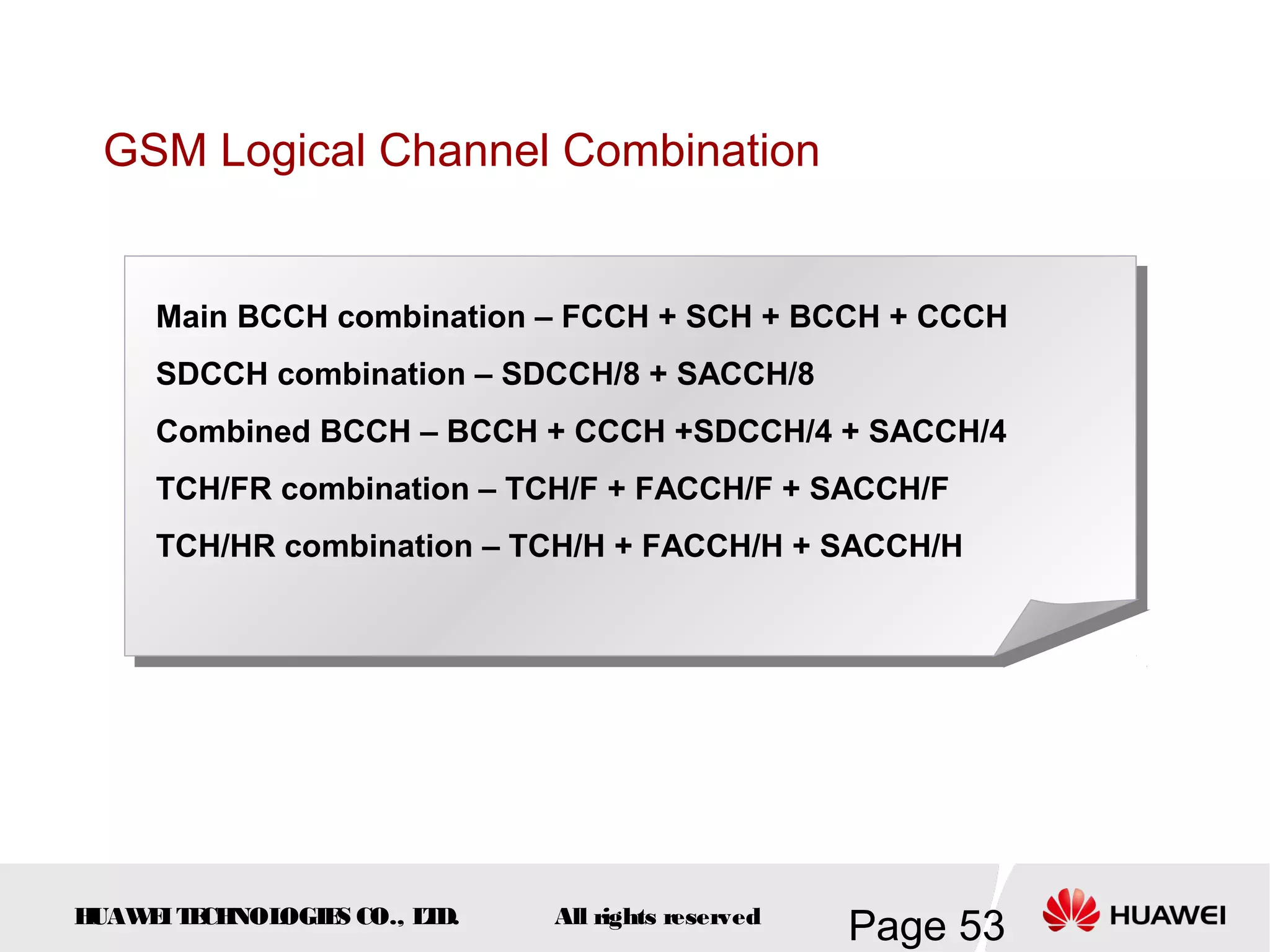
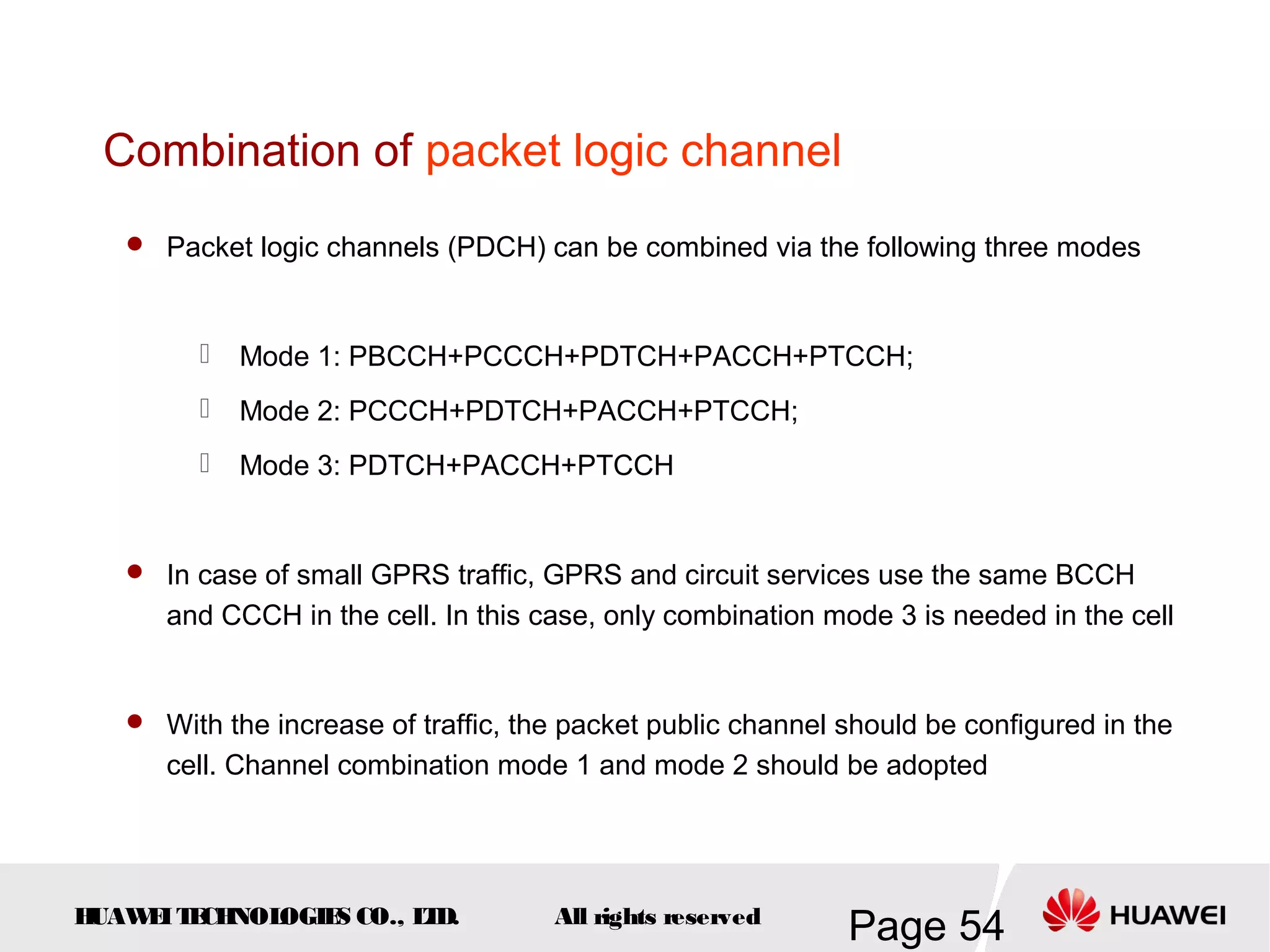
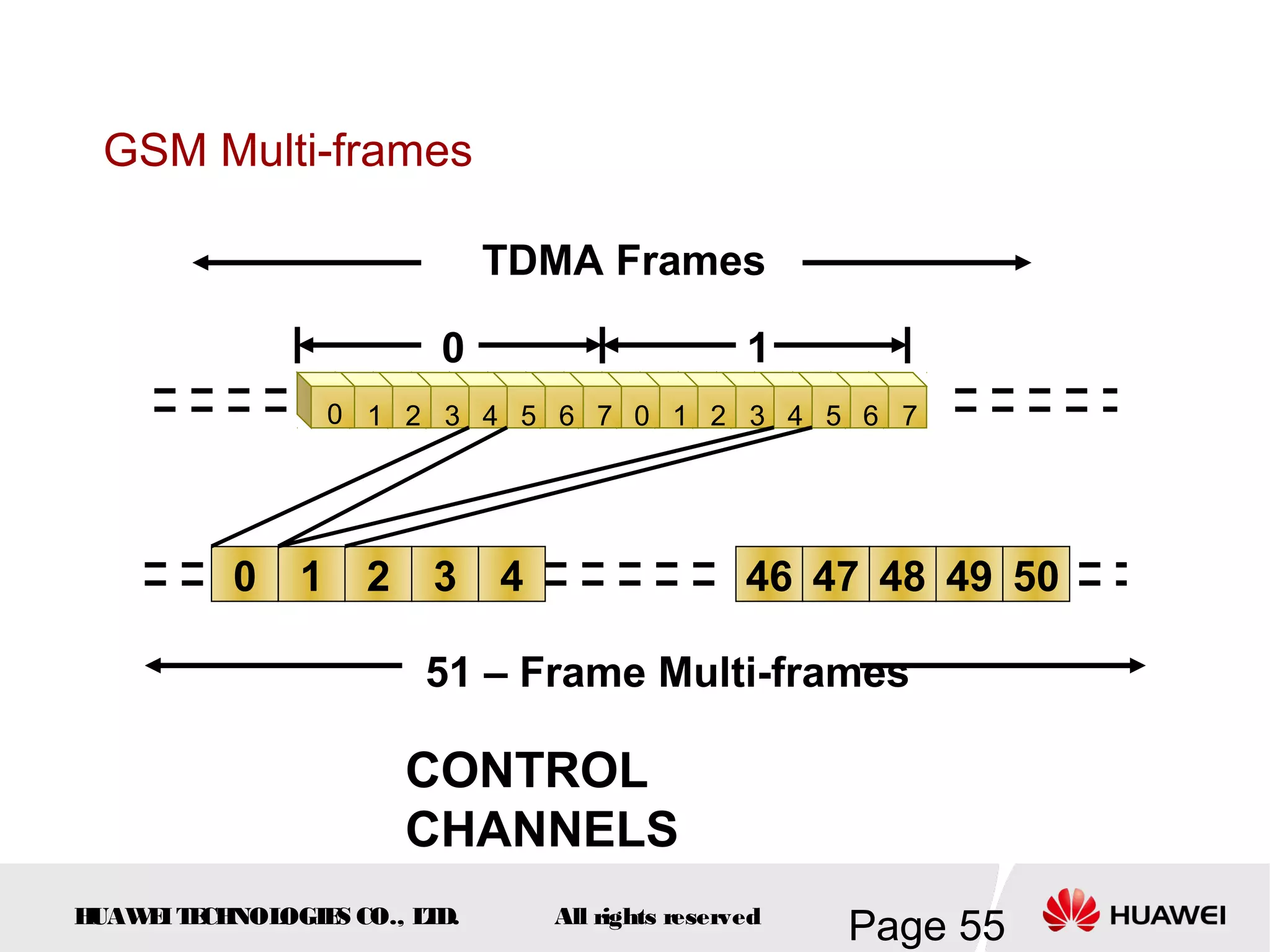
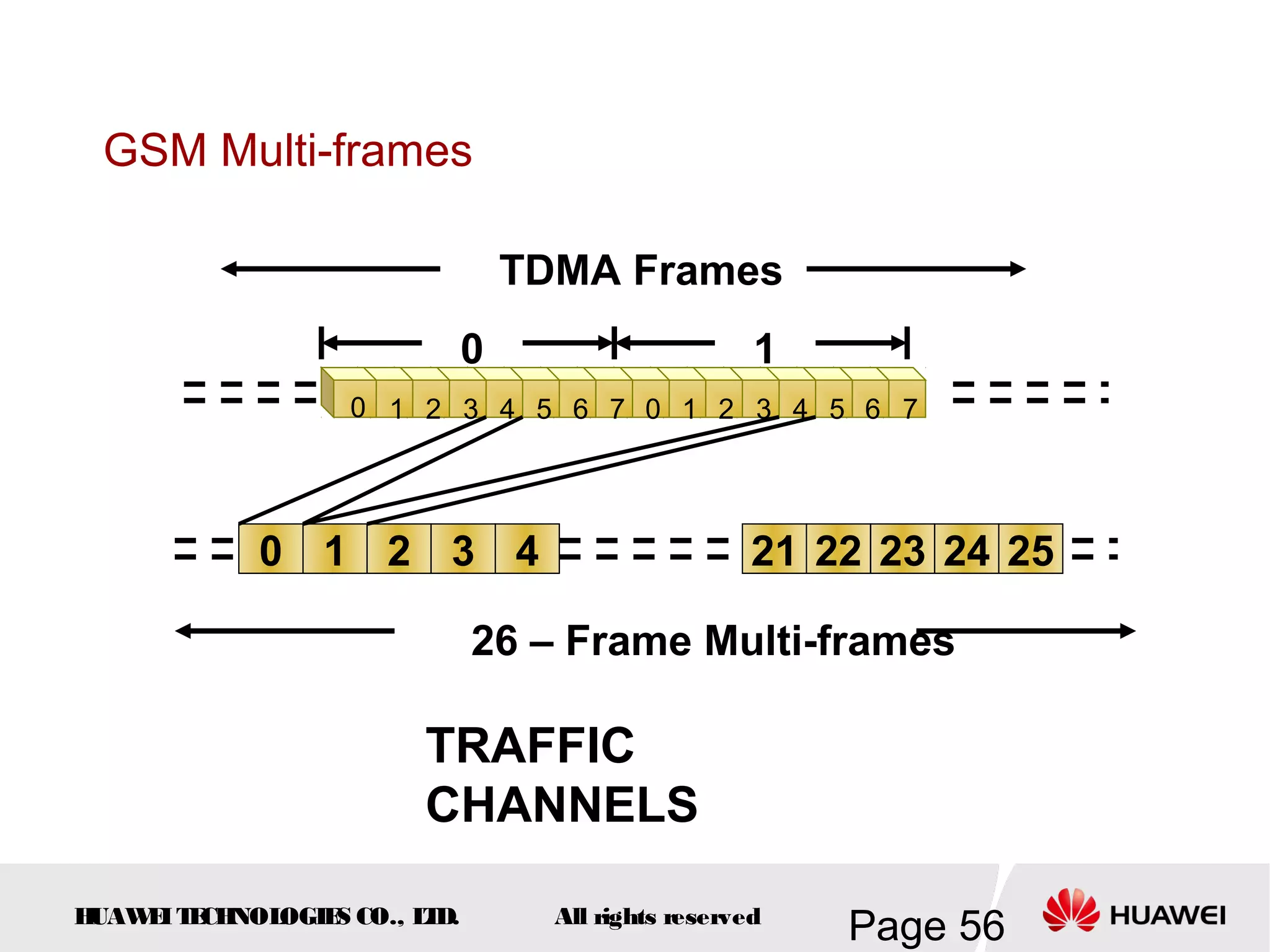
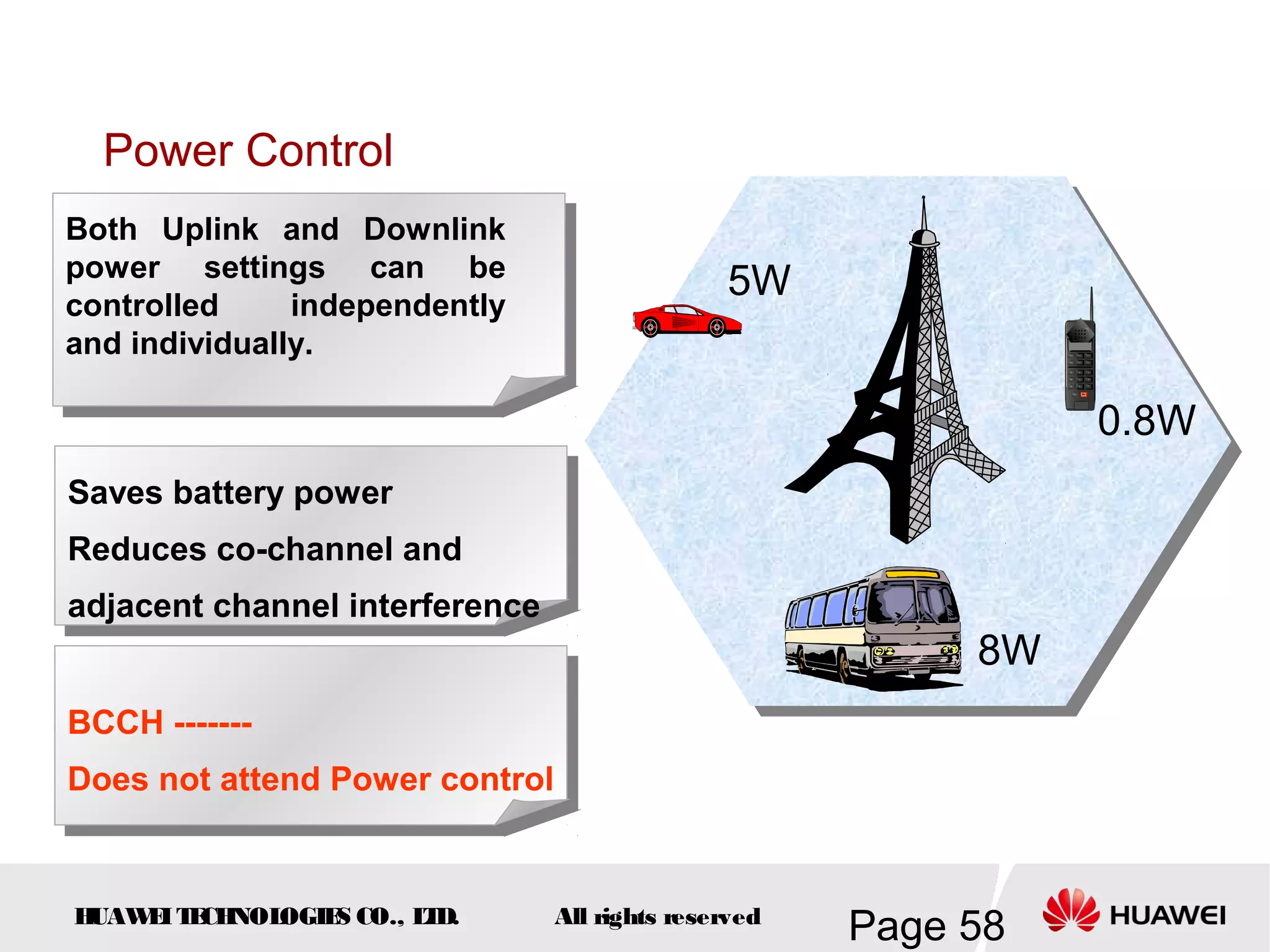
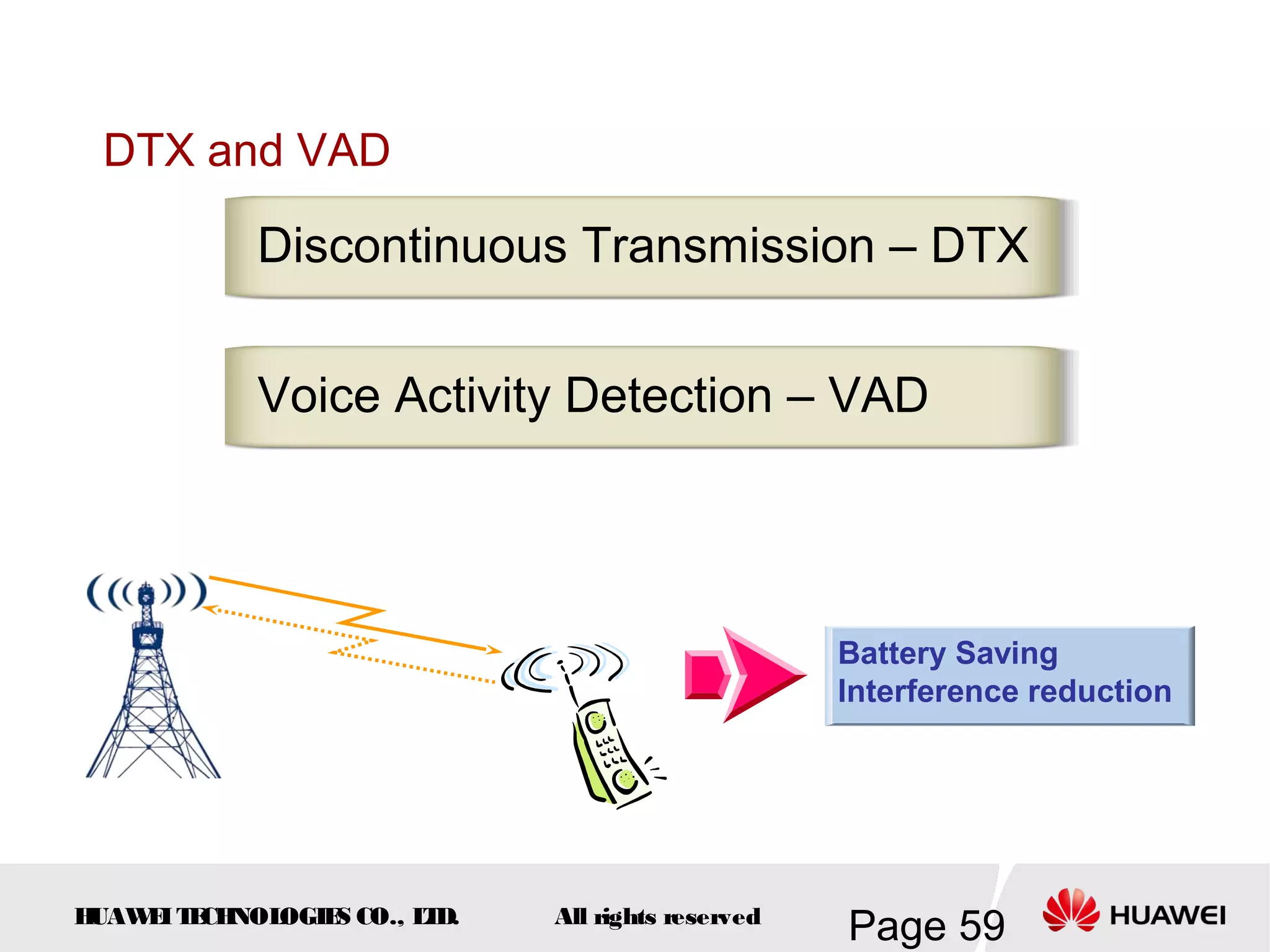
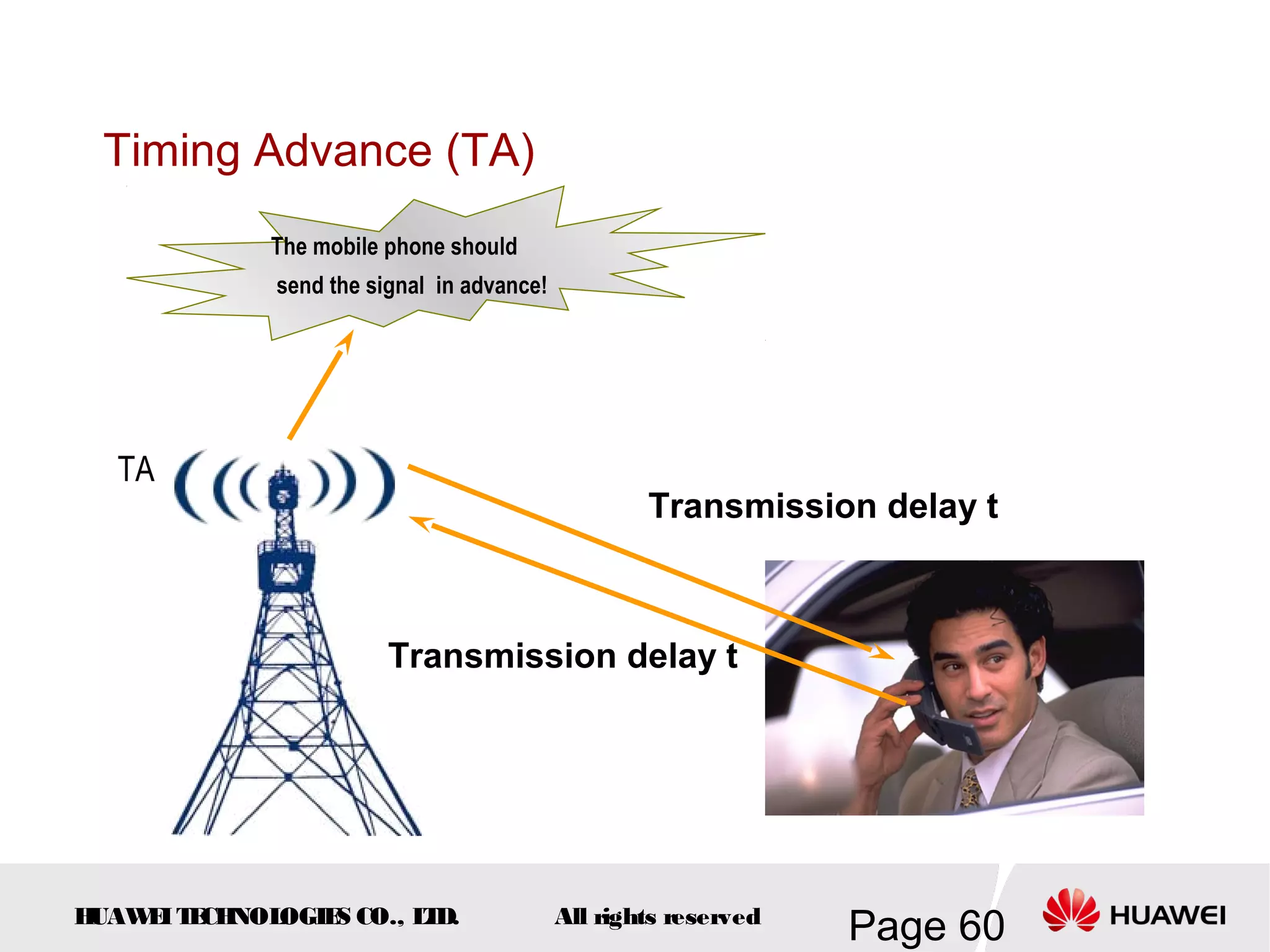
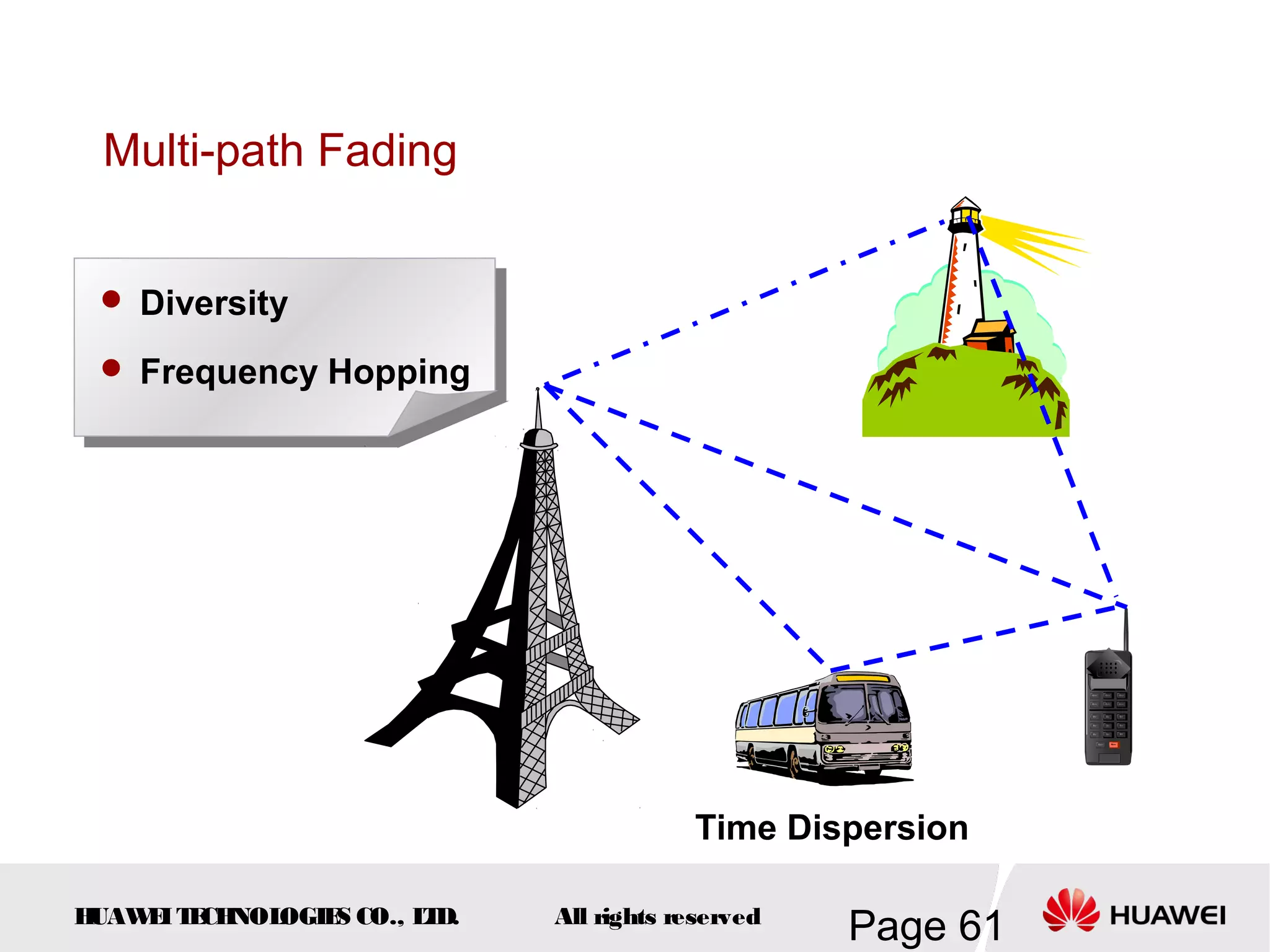
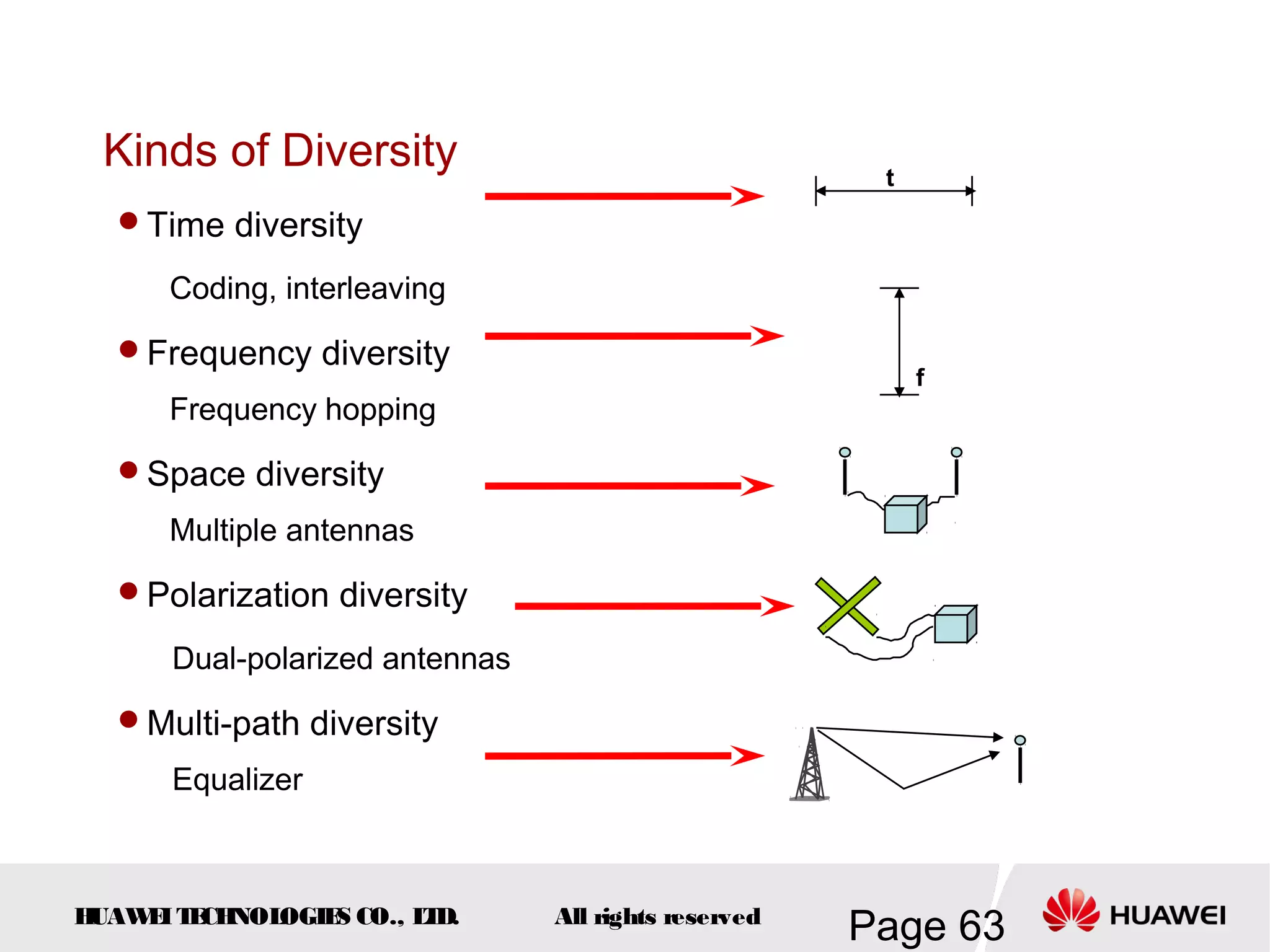
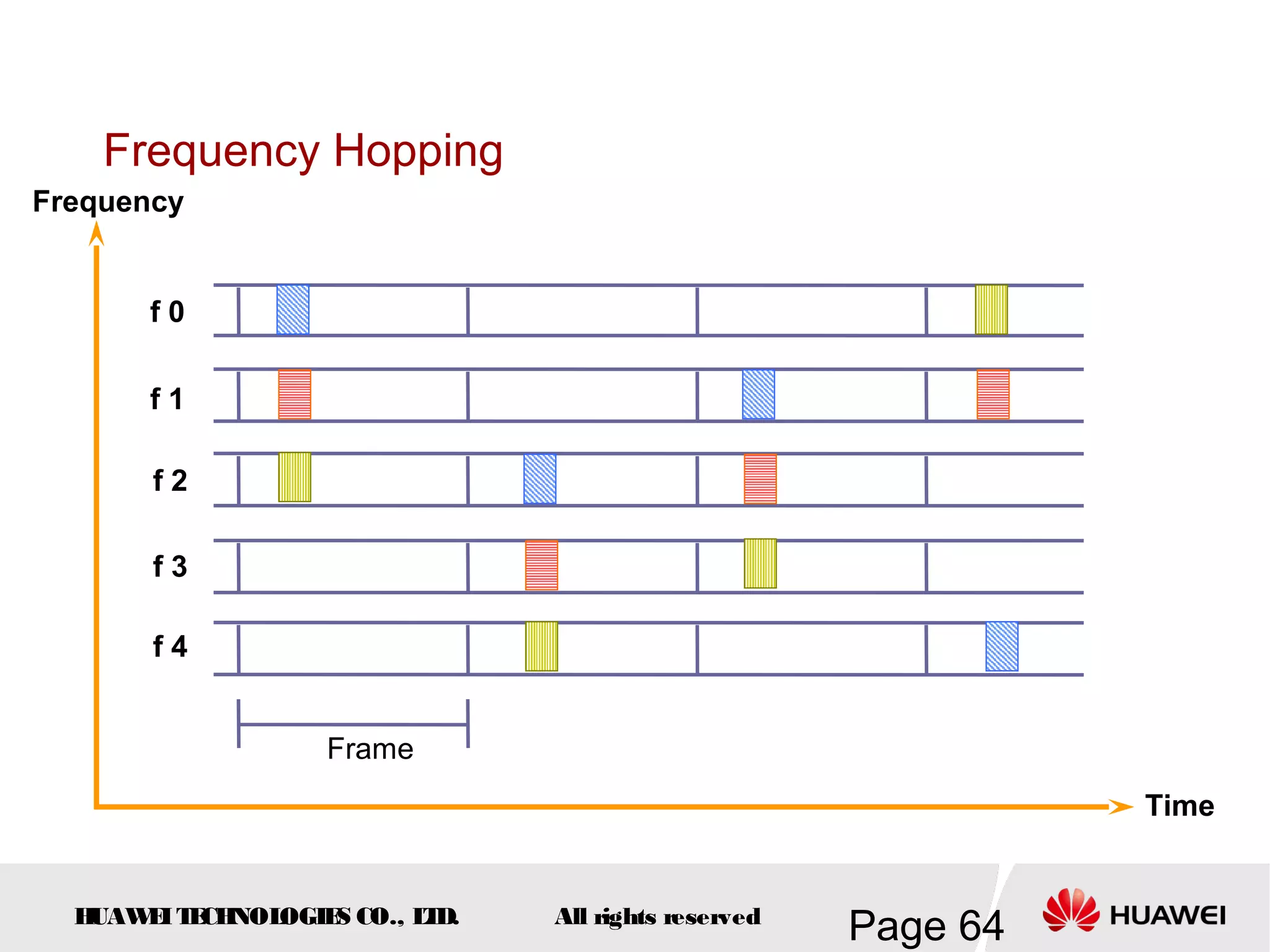
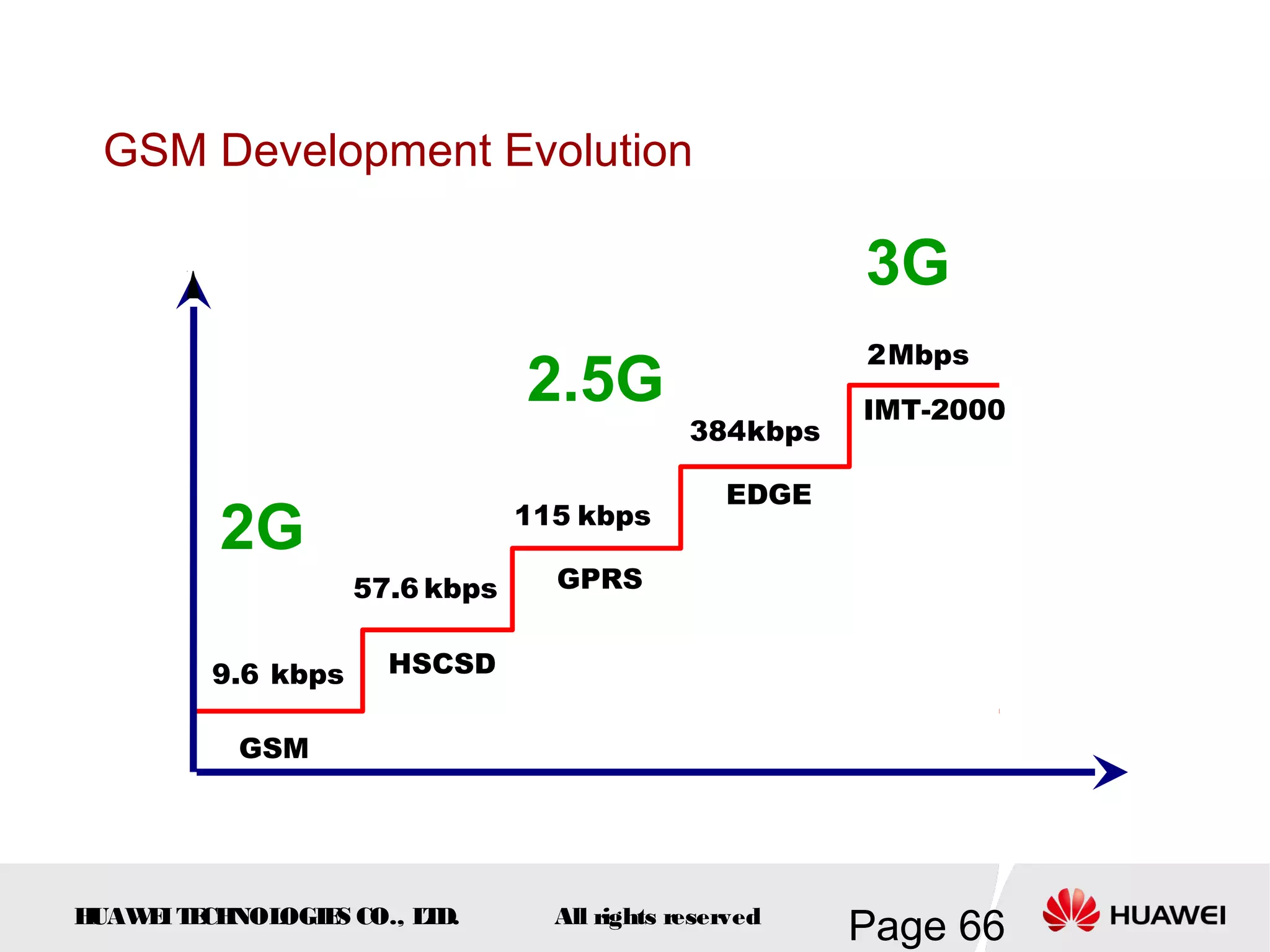
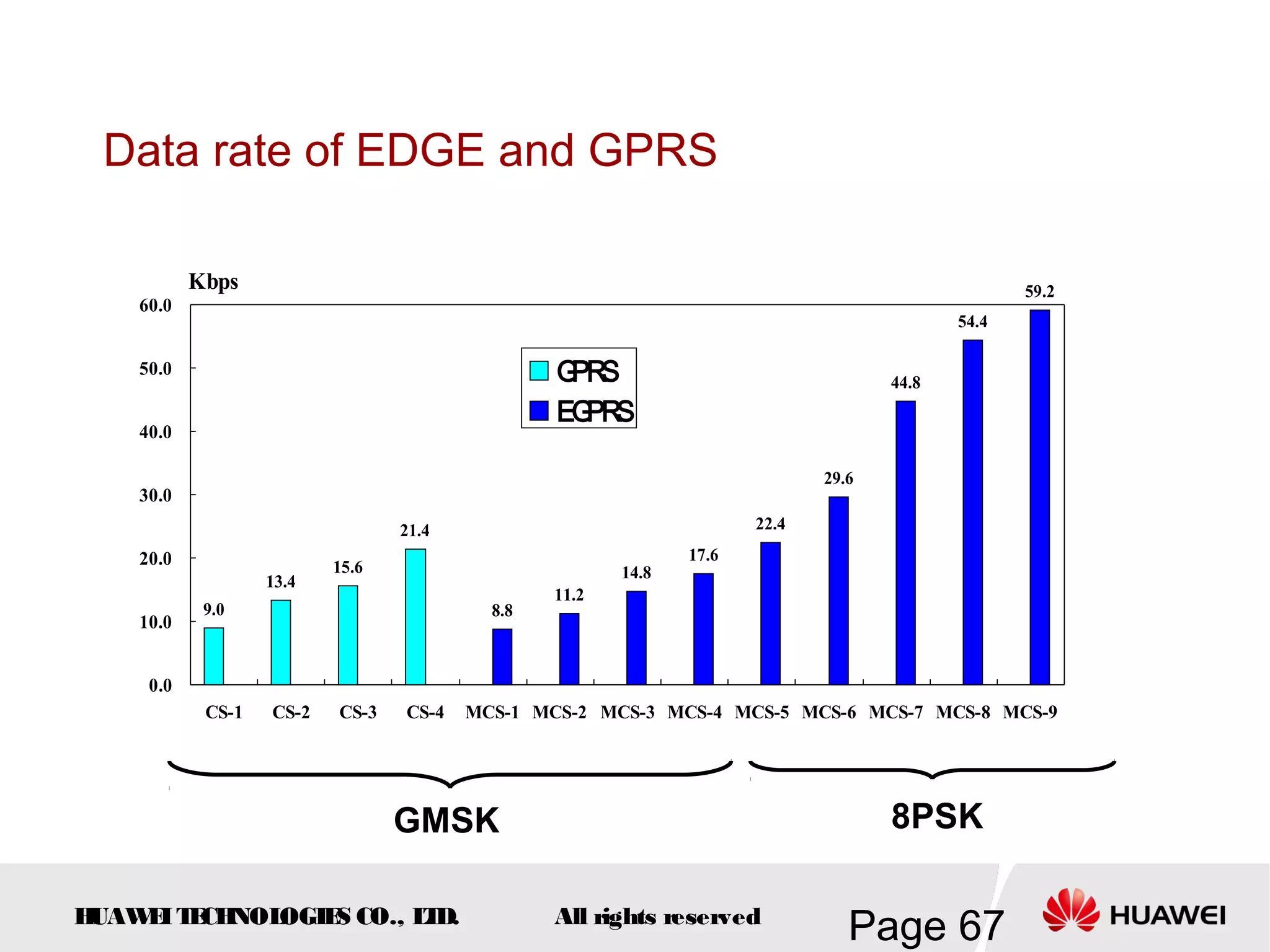
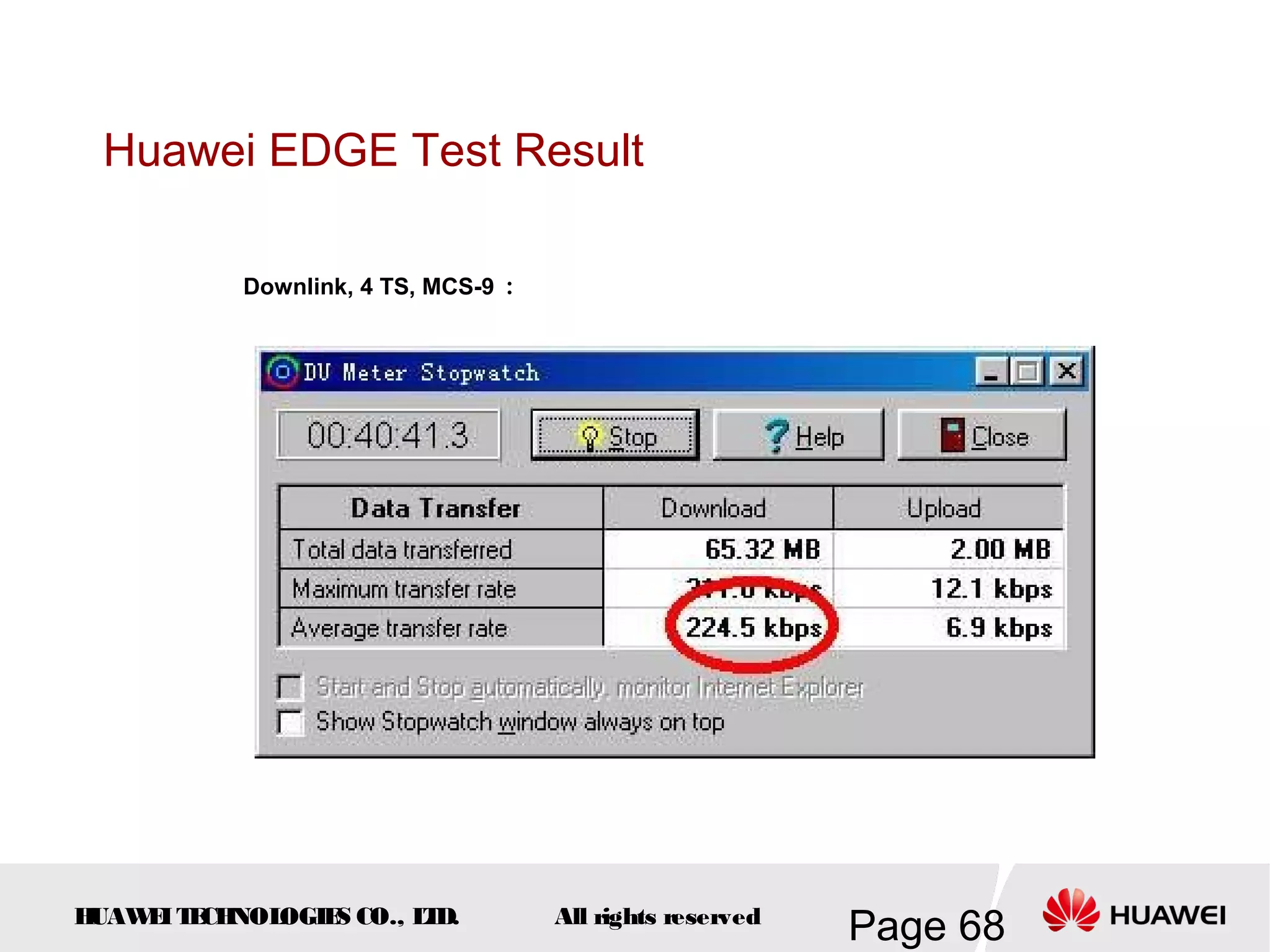
The document provides an overview of the GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) system, detailing its fundamental structure, operation, and key components. Key topics include frequency spectrum, cellular design, multiple access techniques, and the roles of various network entities like the Base Station Subsystem (BSS) and Mobile Switching Center (MSC). It outlines the history, development, and various channel management strategies within the GSM framework.