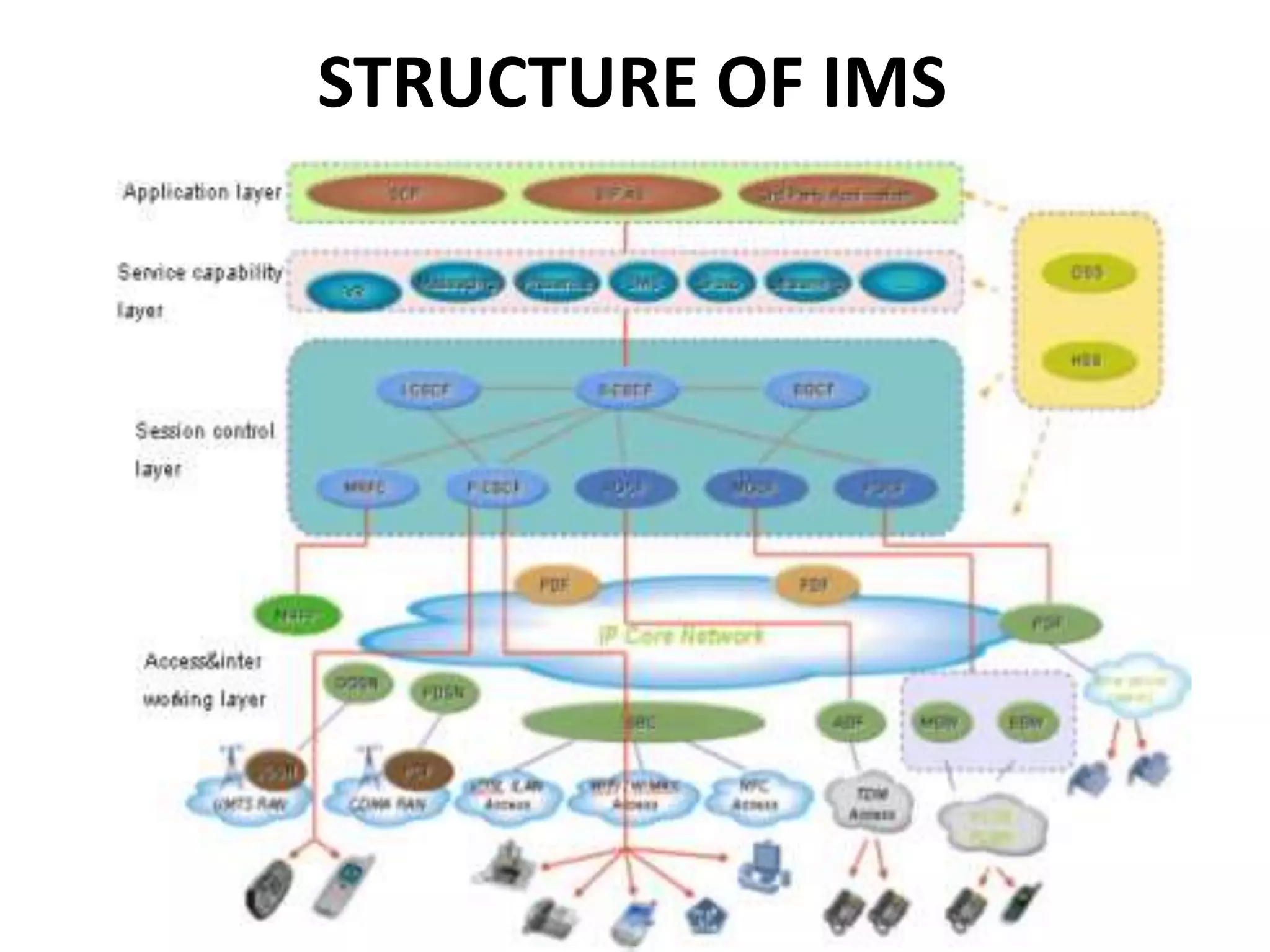
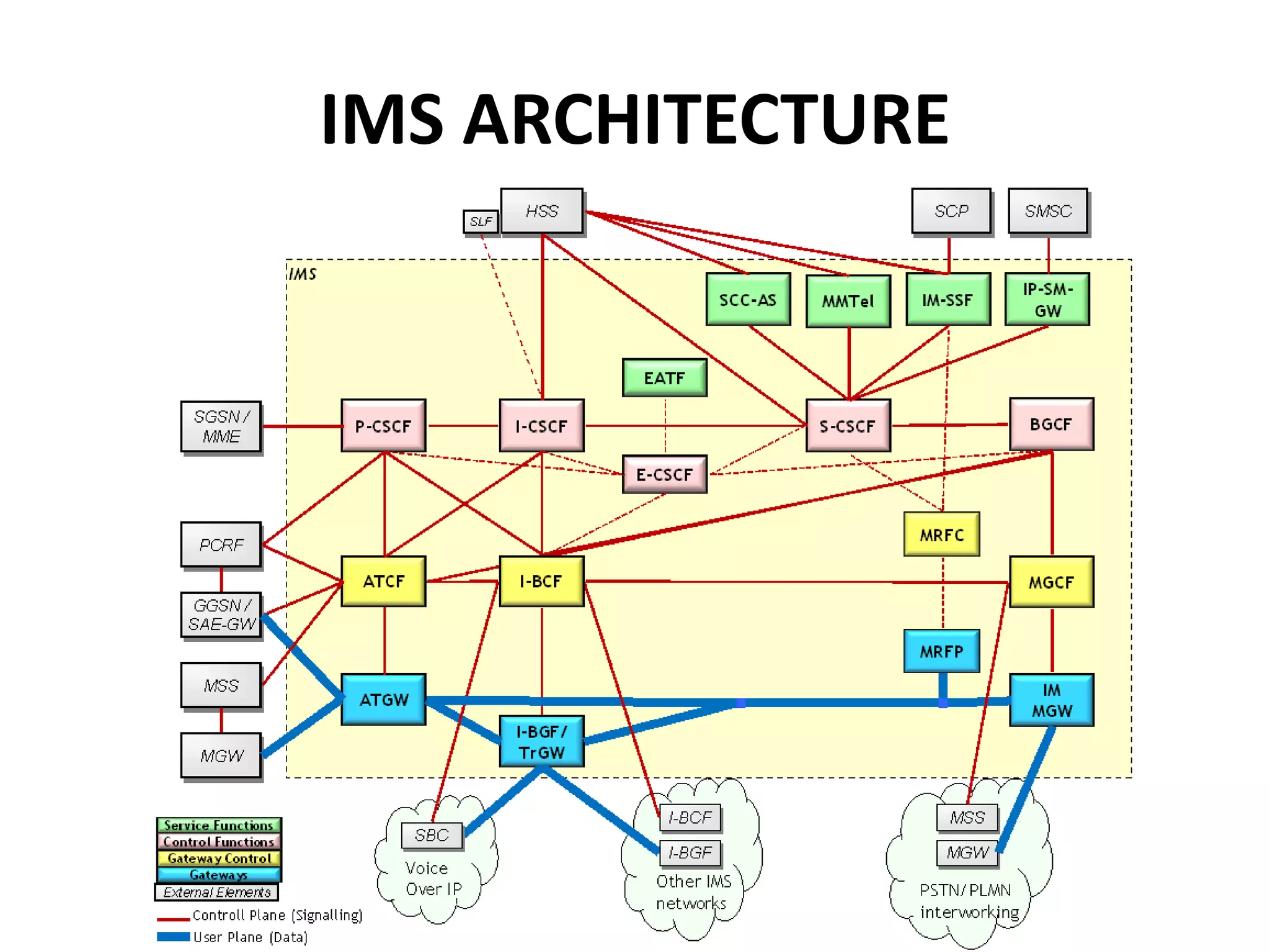
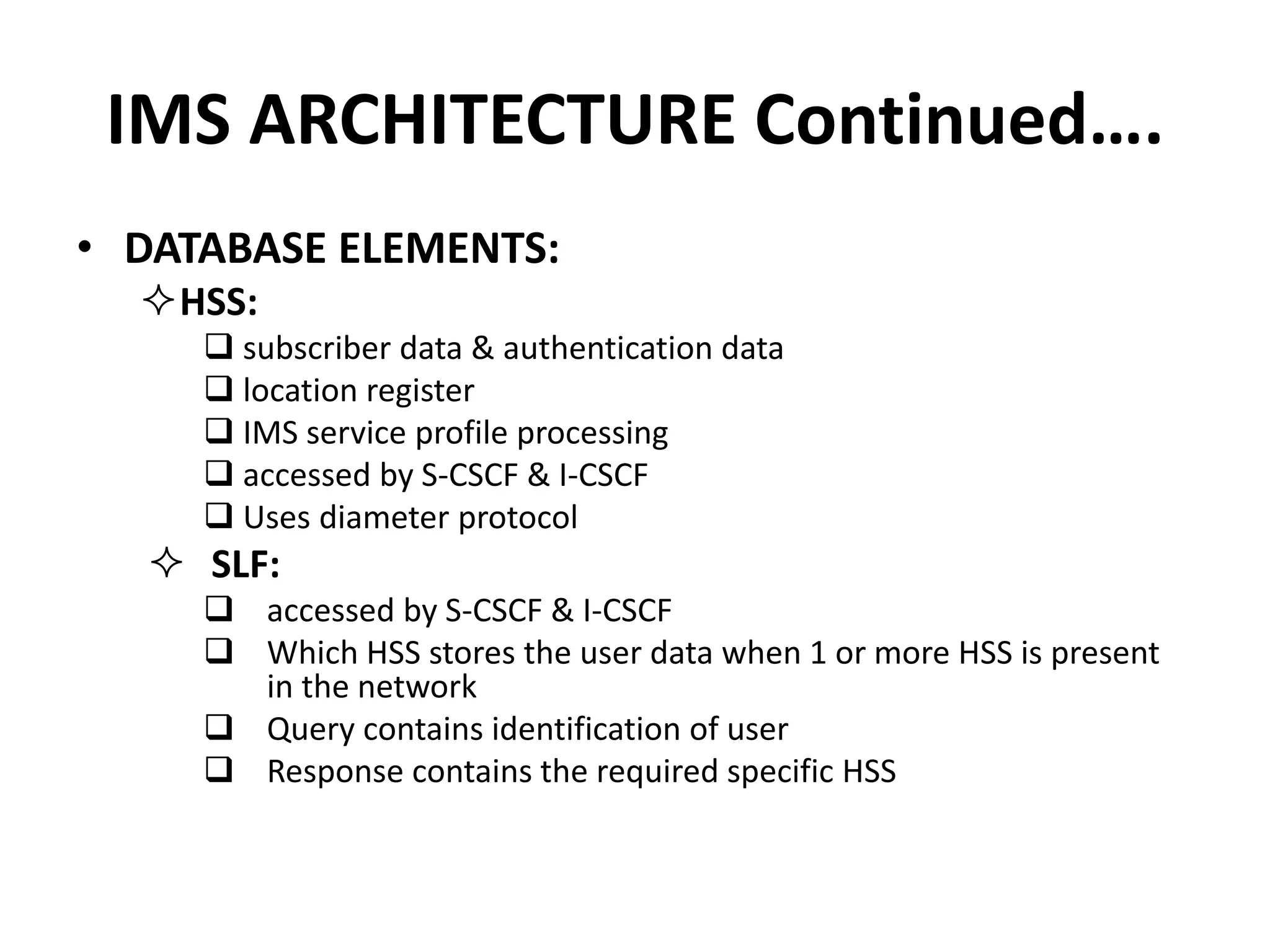
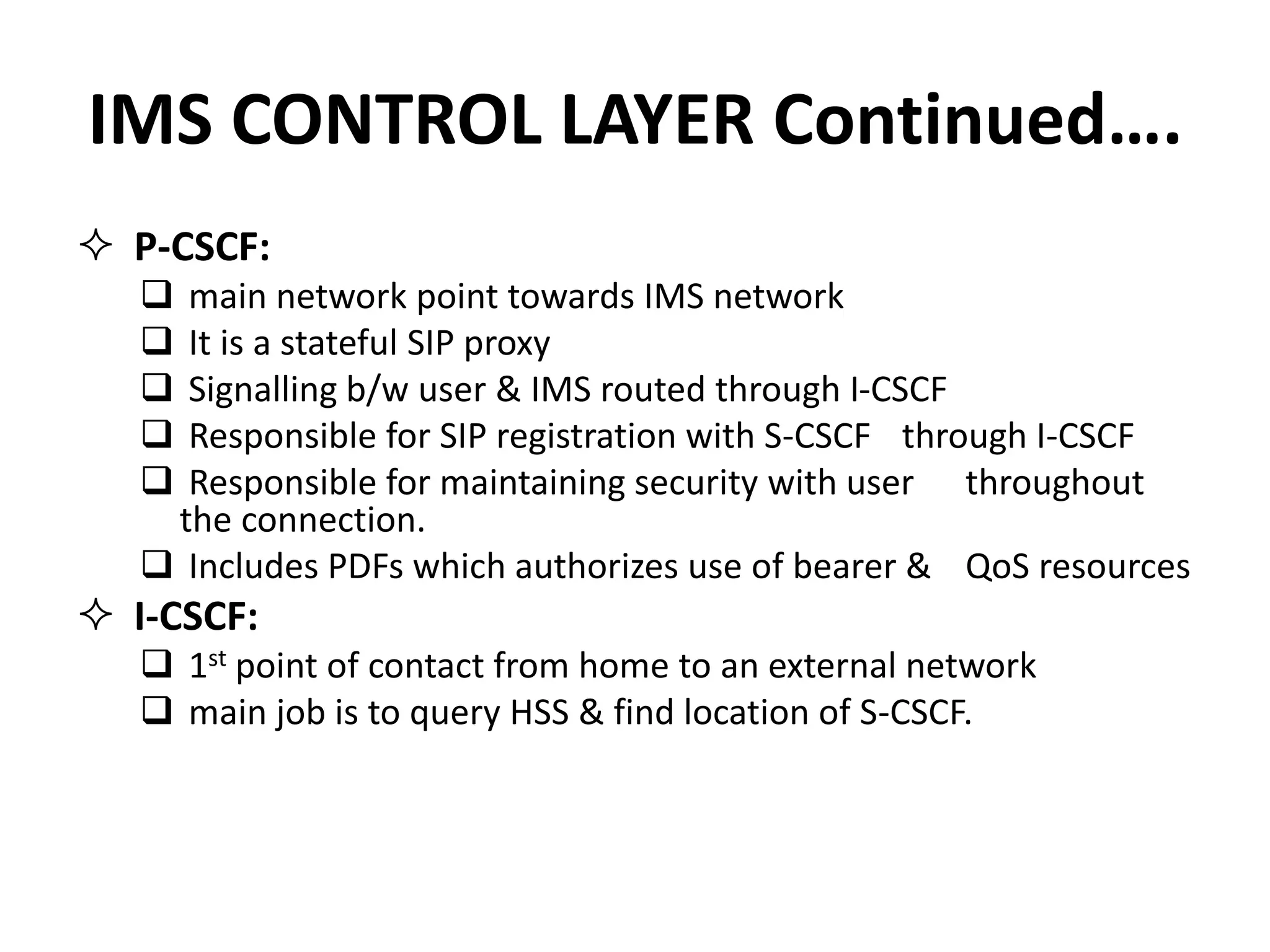
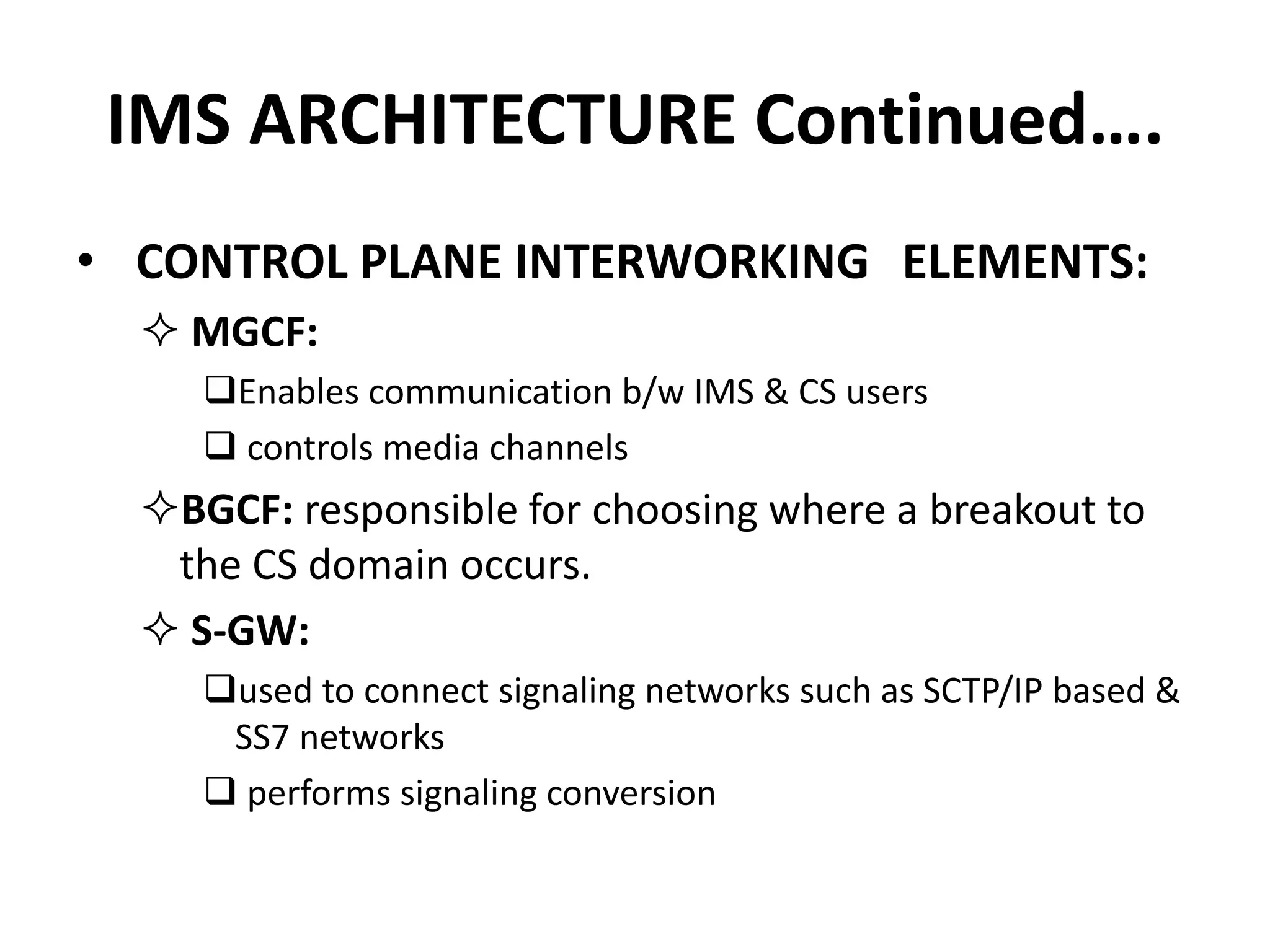
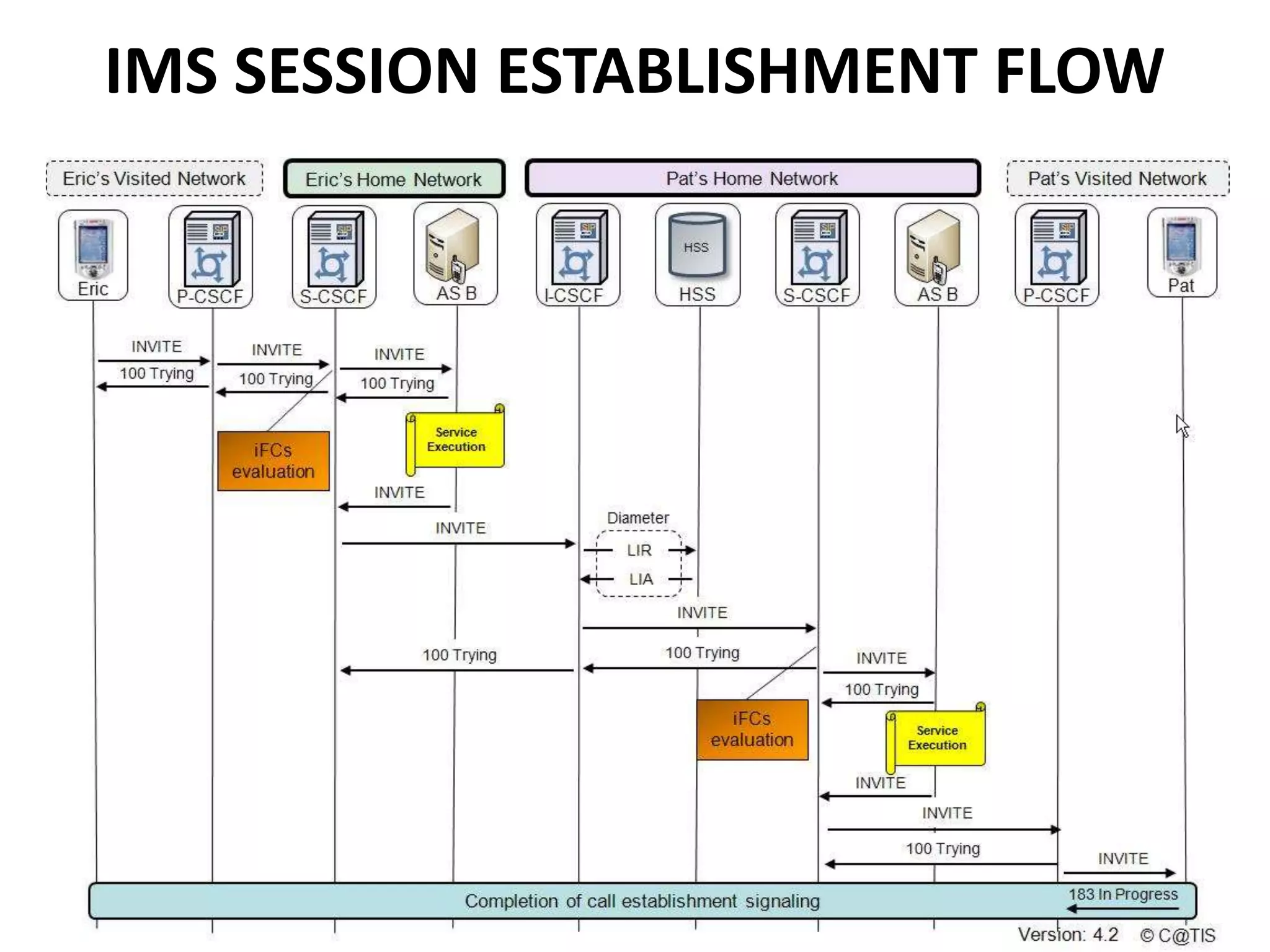
IMS is an architectural framework that uses SIP to deliver IP multimedia services to mobile users. It consists of common core elements, enablers, and support systems arranged in three layers. The control layer contains various nodes that handle signaling and session management, including the P-CSCF for access, I-CSCF for routing, and S-CSCF for authentication and services. Together these elements establish and manage multimedia sessions between IMS subscribers and networks.