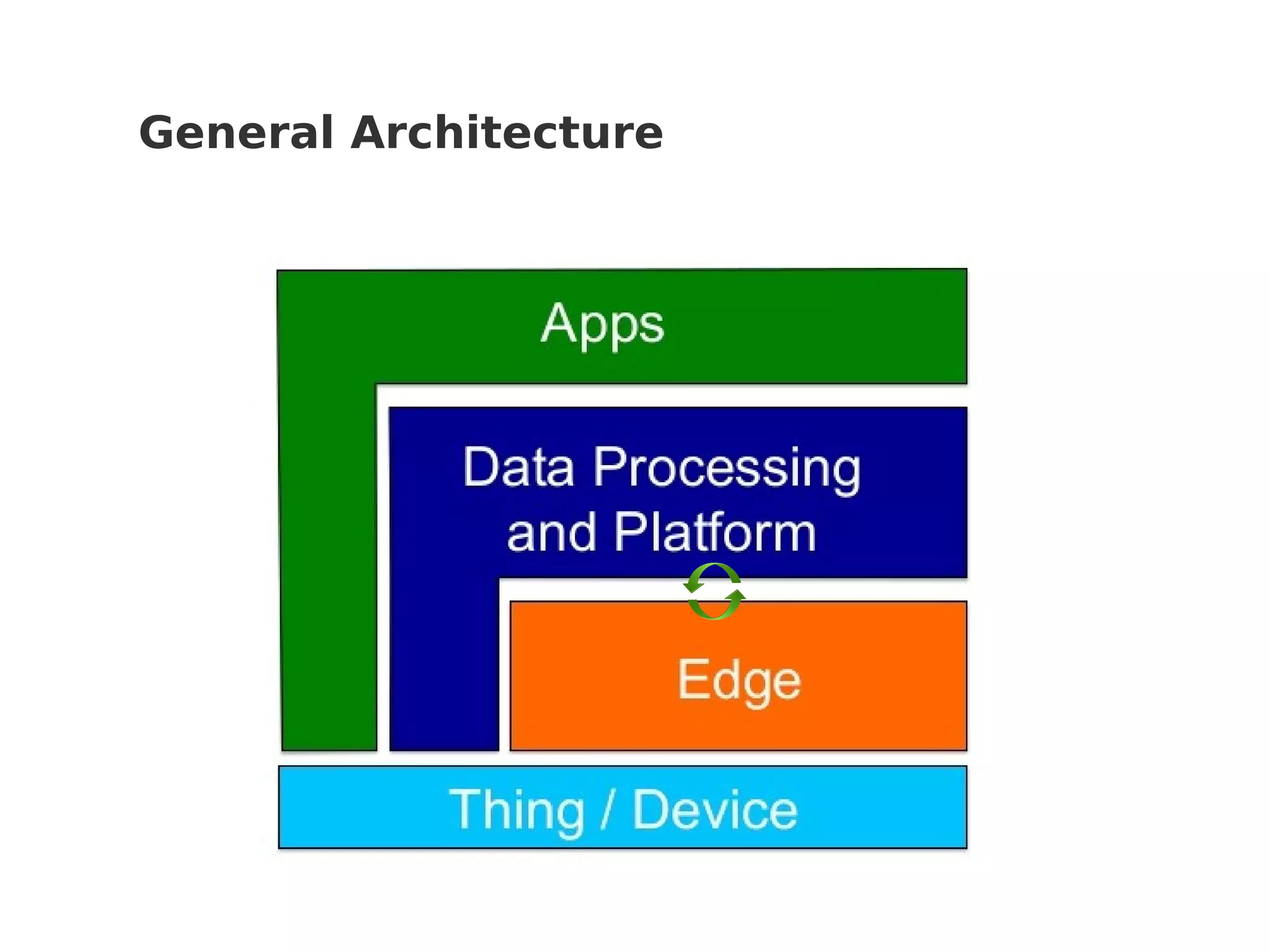
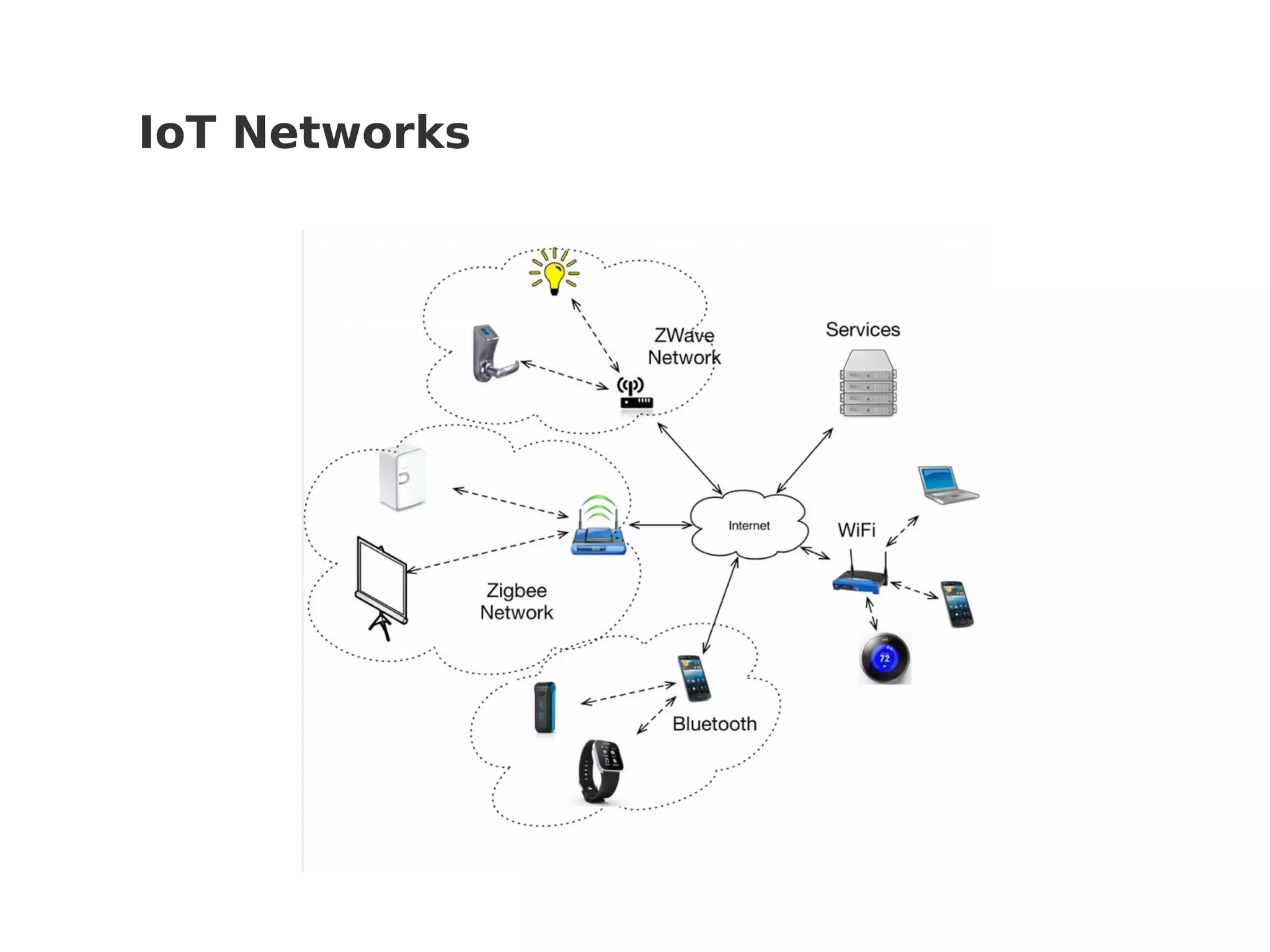
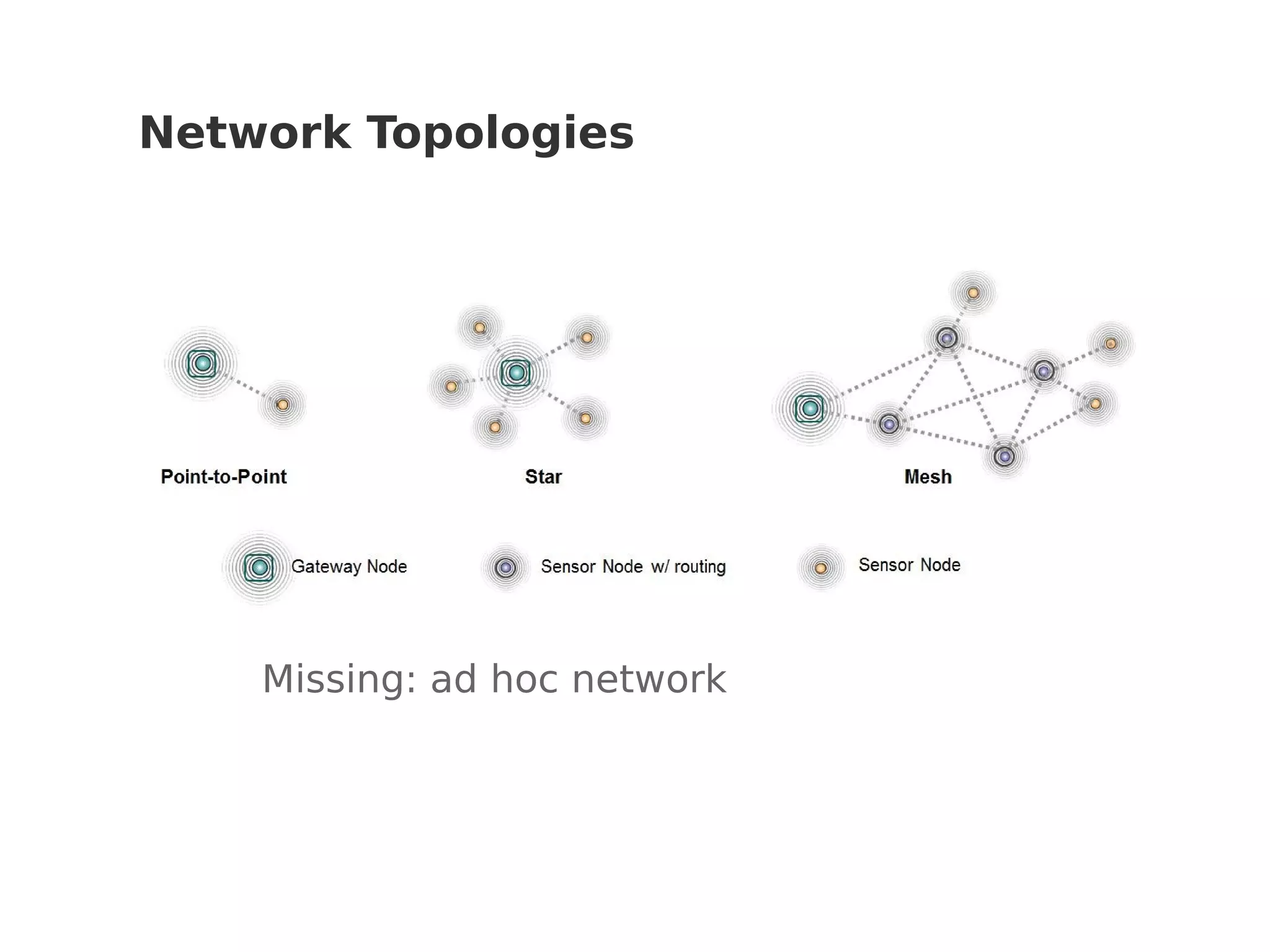
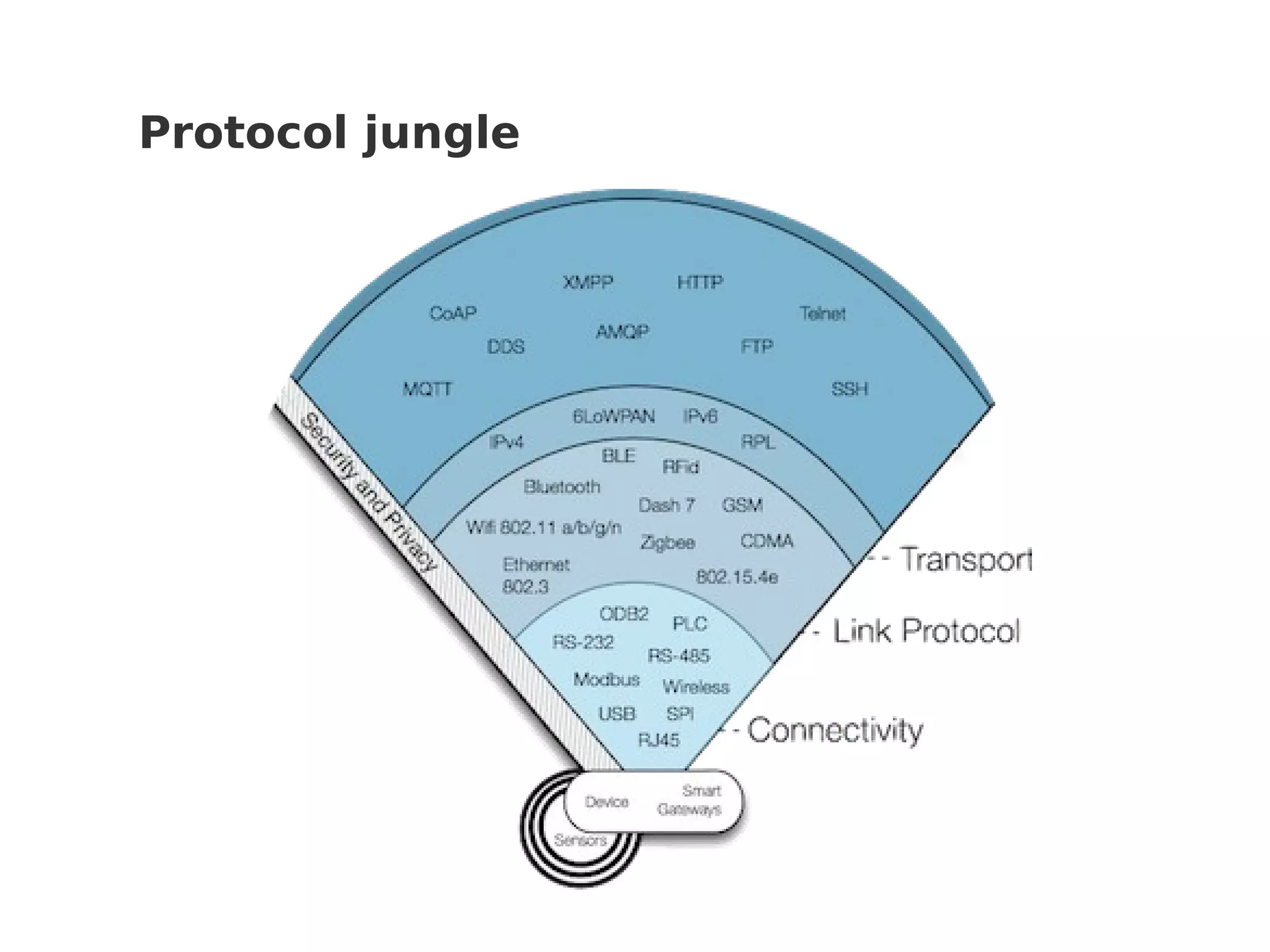
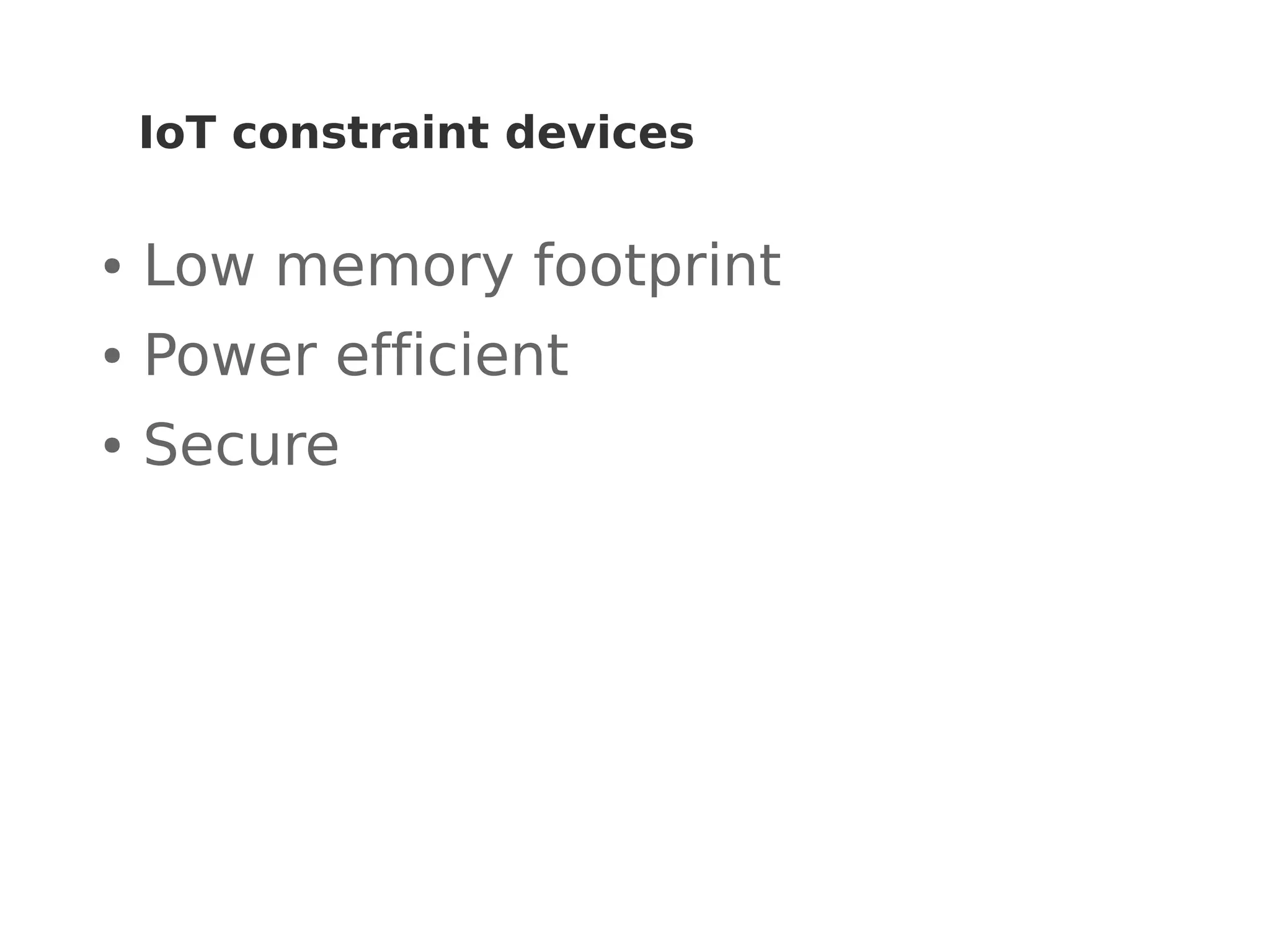
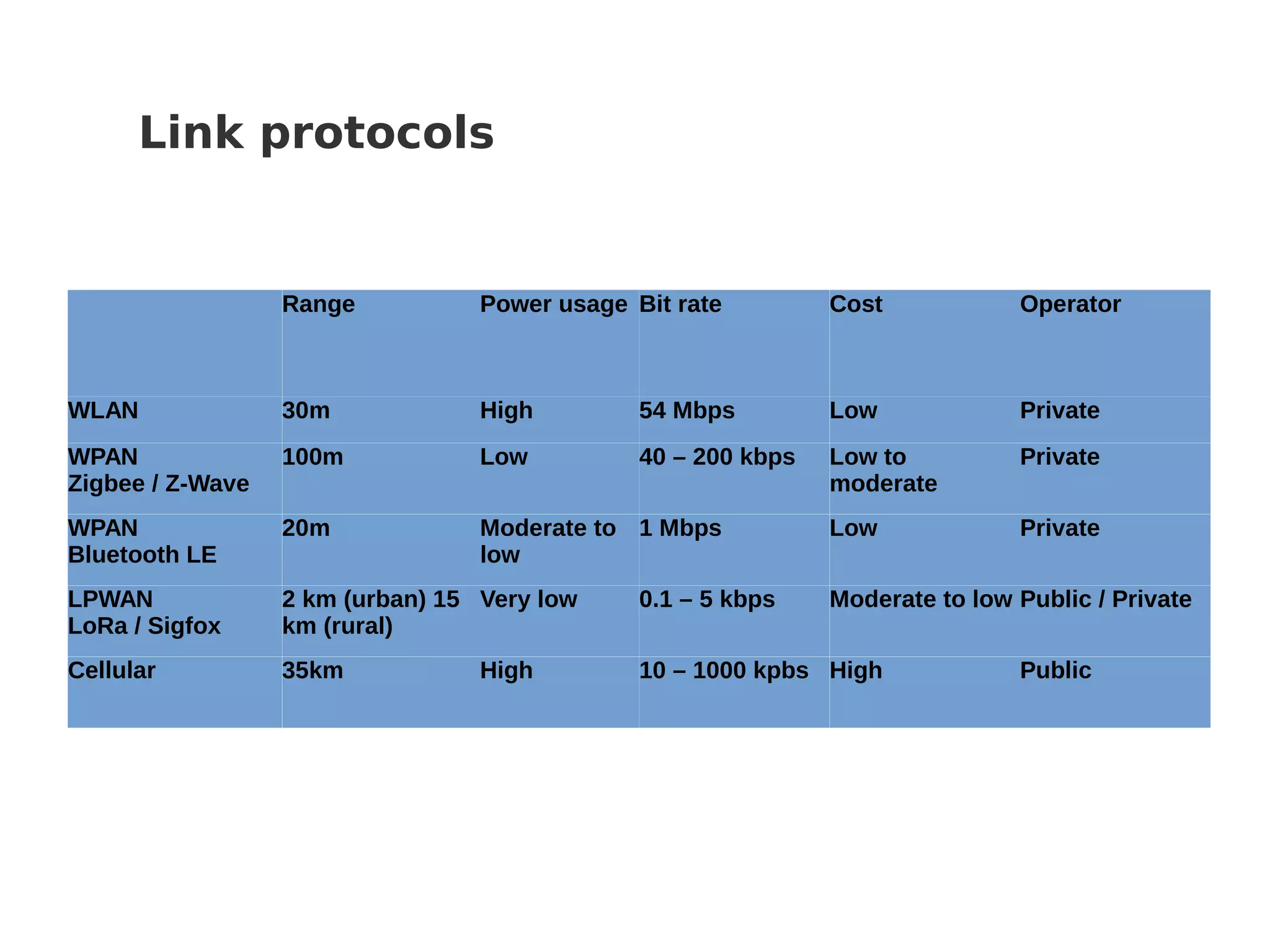
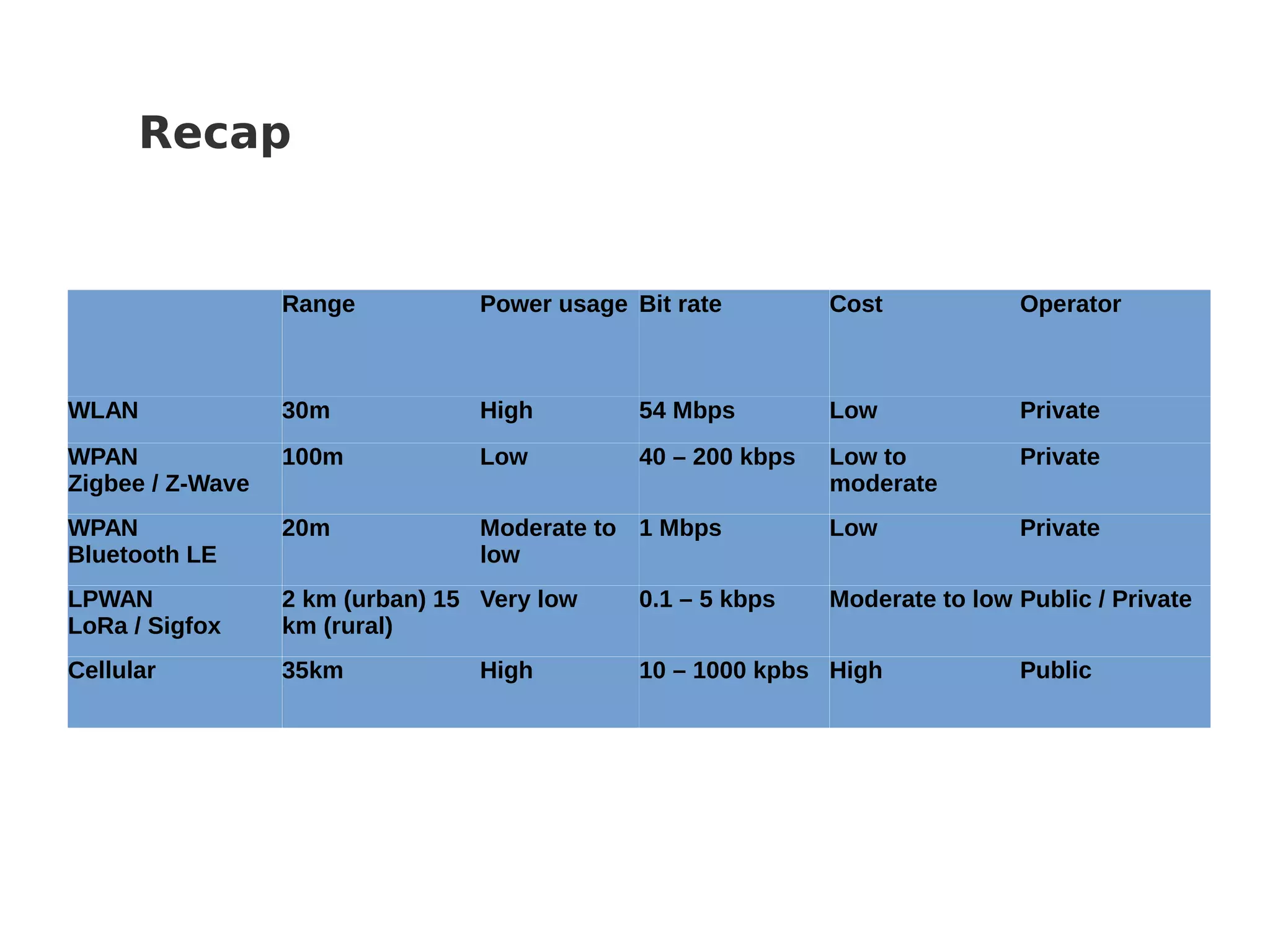
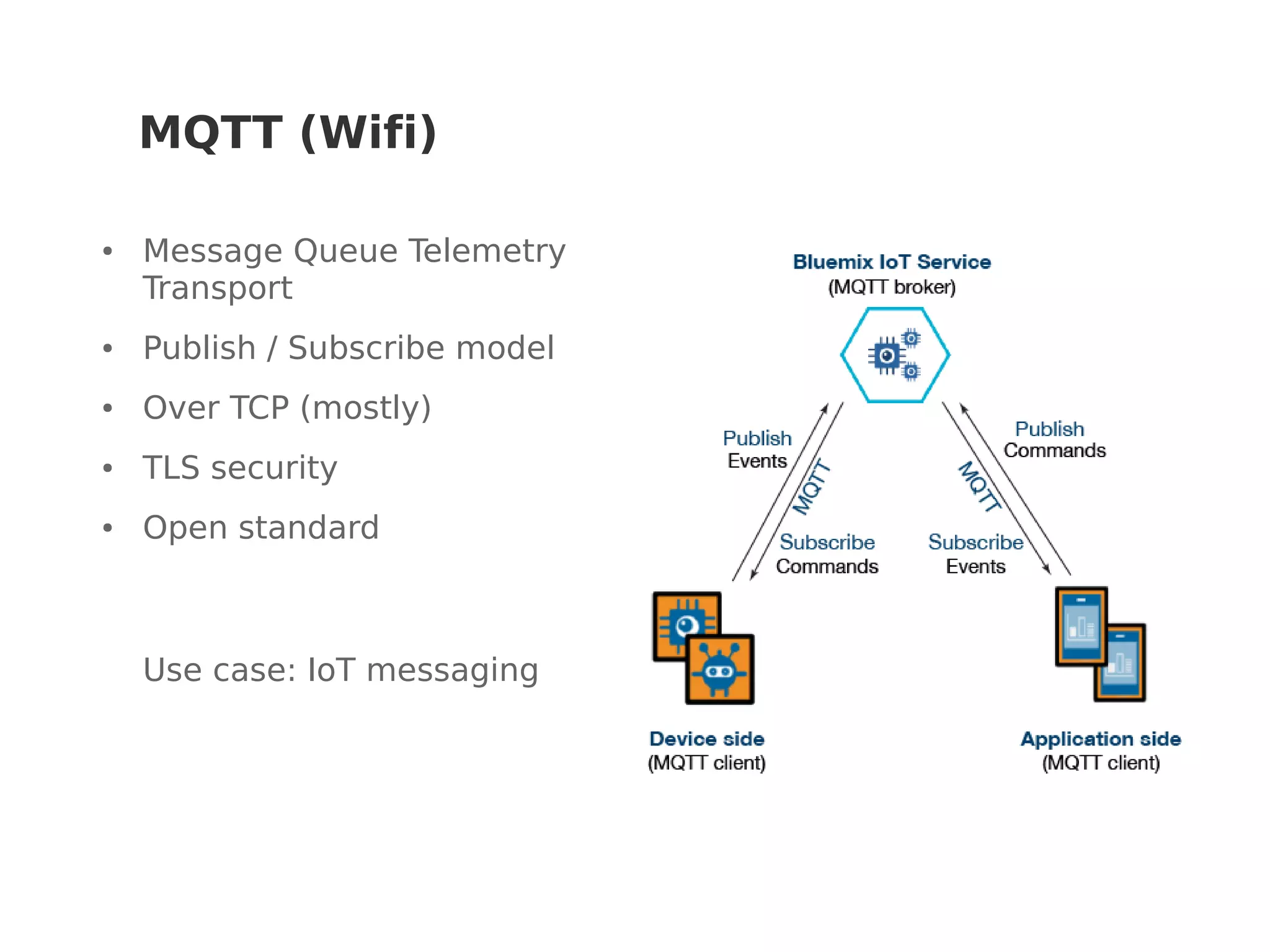
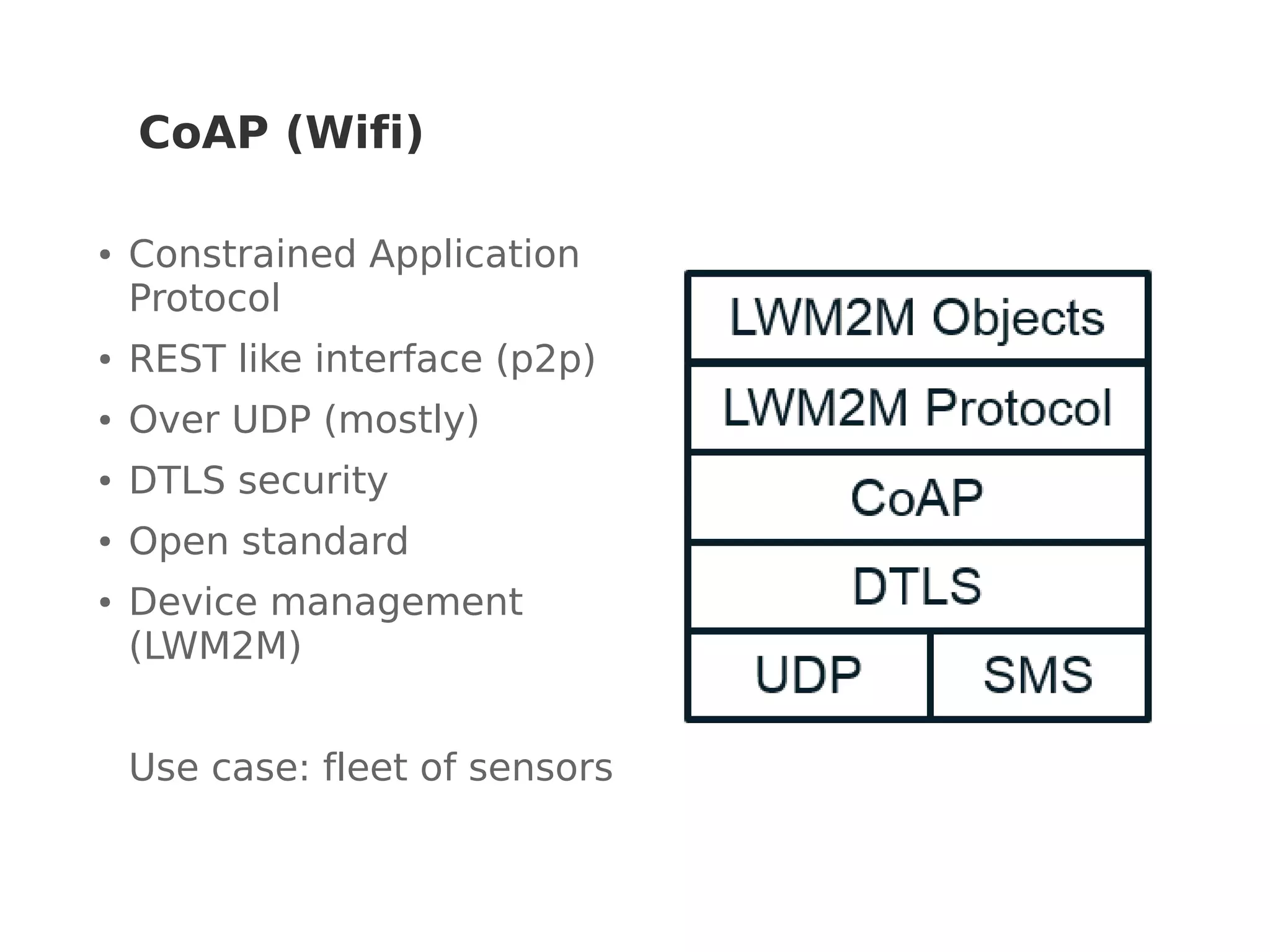
This document discusses various Internet of Things (IoT) protocols. It defines IoT as interconnected devices that can transmit and receive data over a network. It then covers common network topologies and constraints of IoT devices. Several wireless protocols are described in detail, including their typical range, power usage, data rates, and costs. Popular protocols for messaging (MQTT) and REST-like interfaces (CoAP) are also summarized. The document aims to provide an overview of the IoT protocol landscape to help people get started with IoT development.