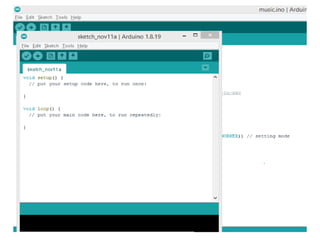
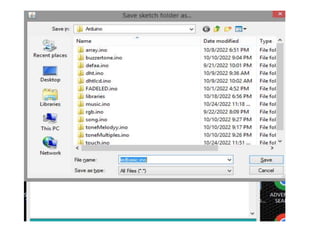
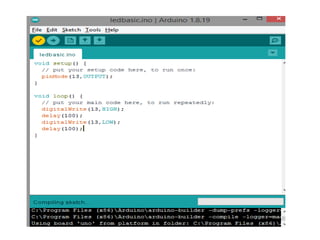
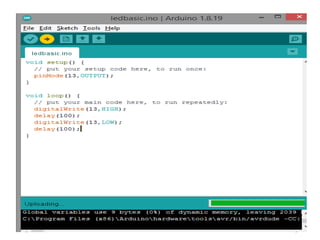
The document discusses the Arduino UNO board. It describes the components of the board including the ATmega328 microcontroller and digital and analog pins. It explains how to program the board using the Arduino IDE and connect it to a computer via USB. The steps to get started with the board are outlined, including installing drivers and uploading code to control digital pins using functions like pinMode(), digitalWrite(), and delay().