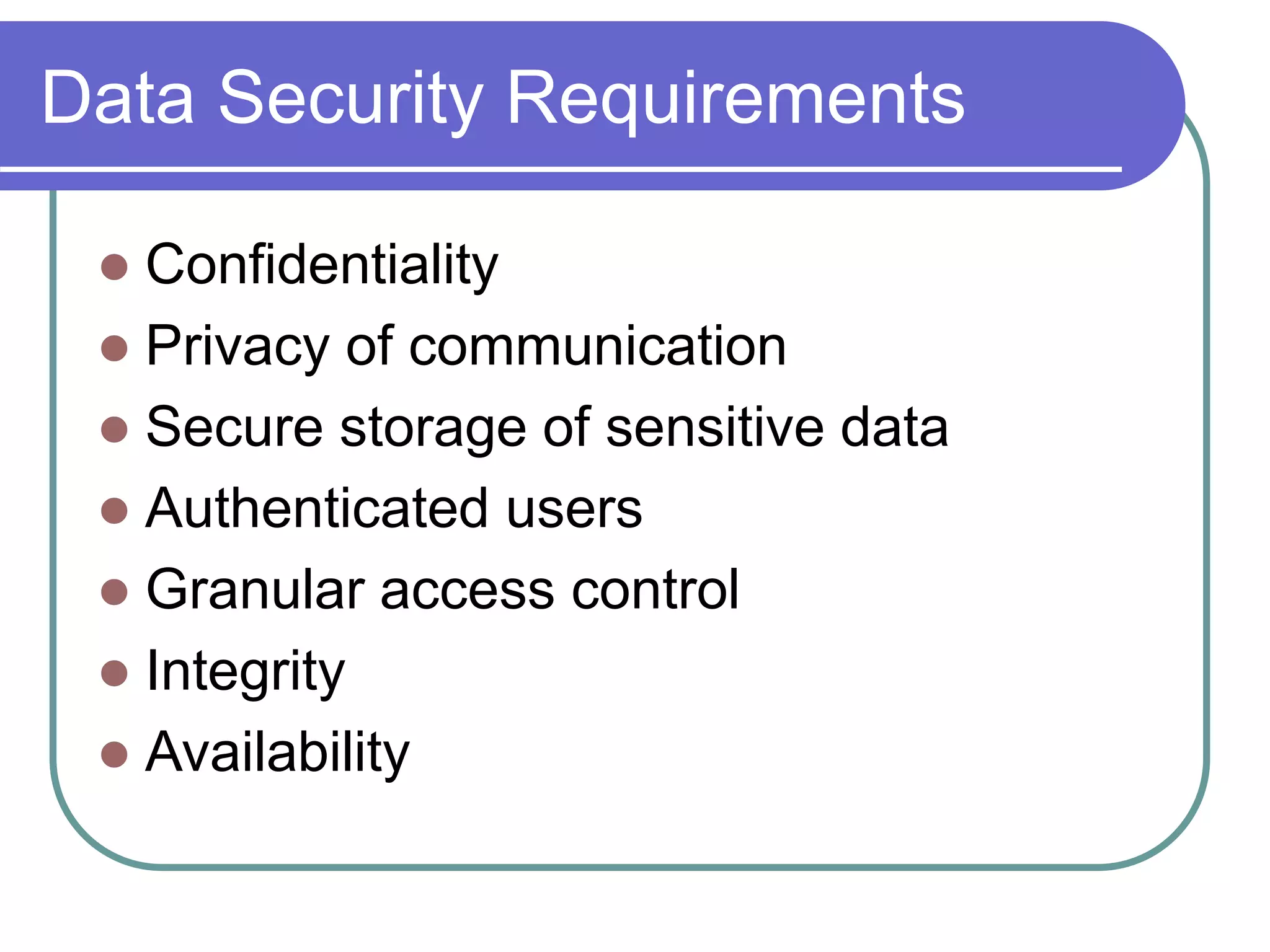
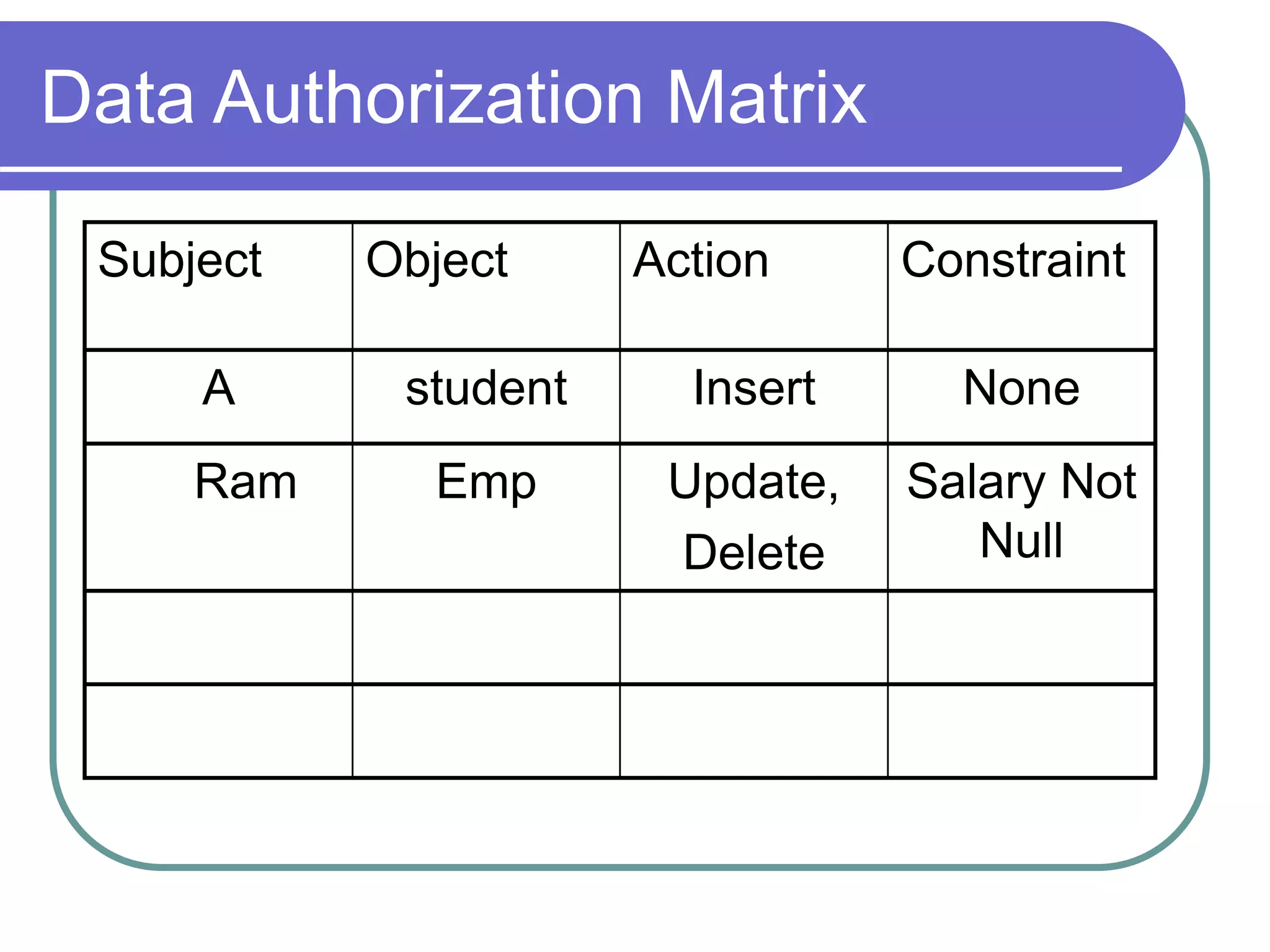
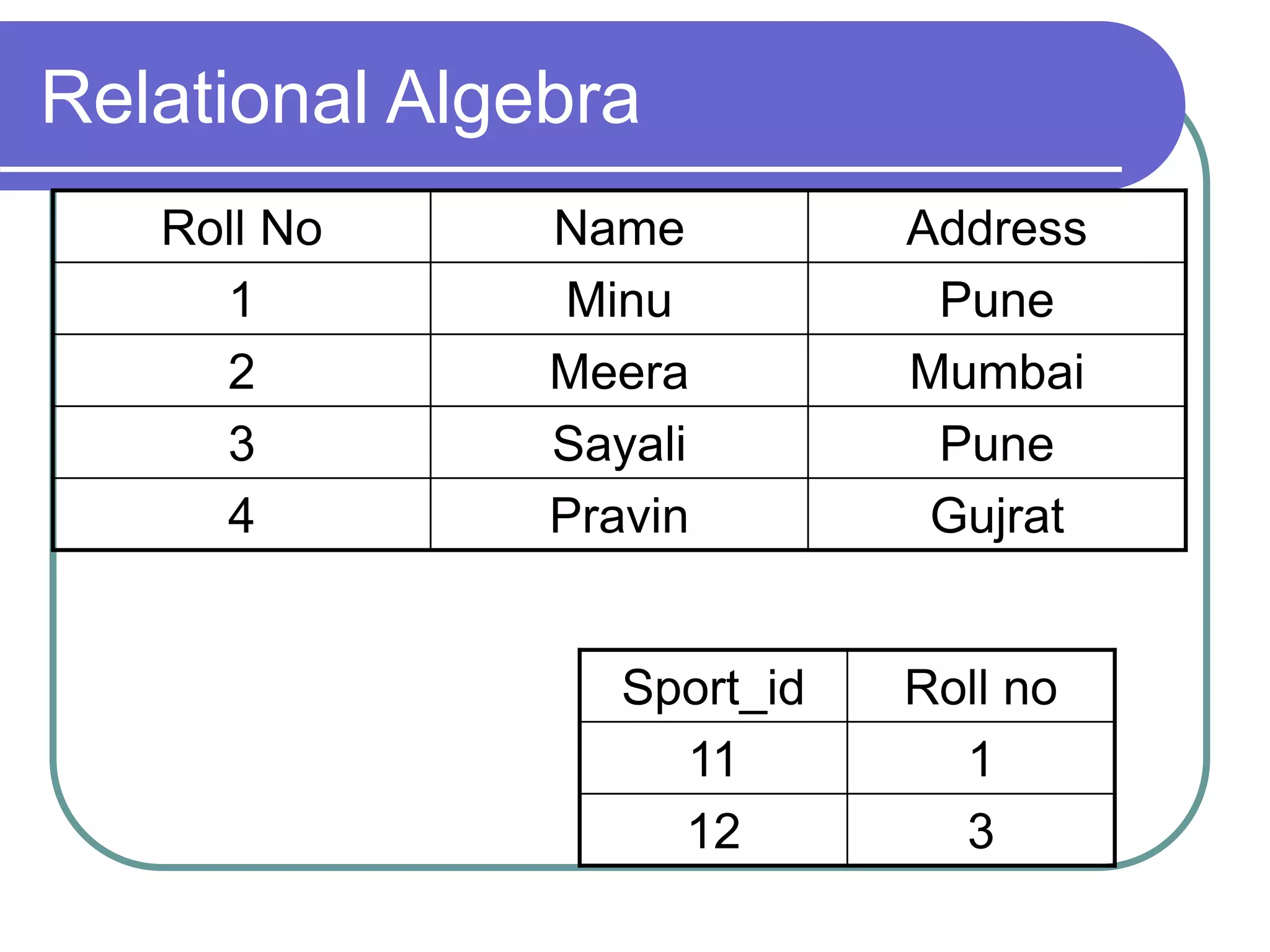
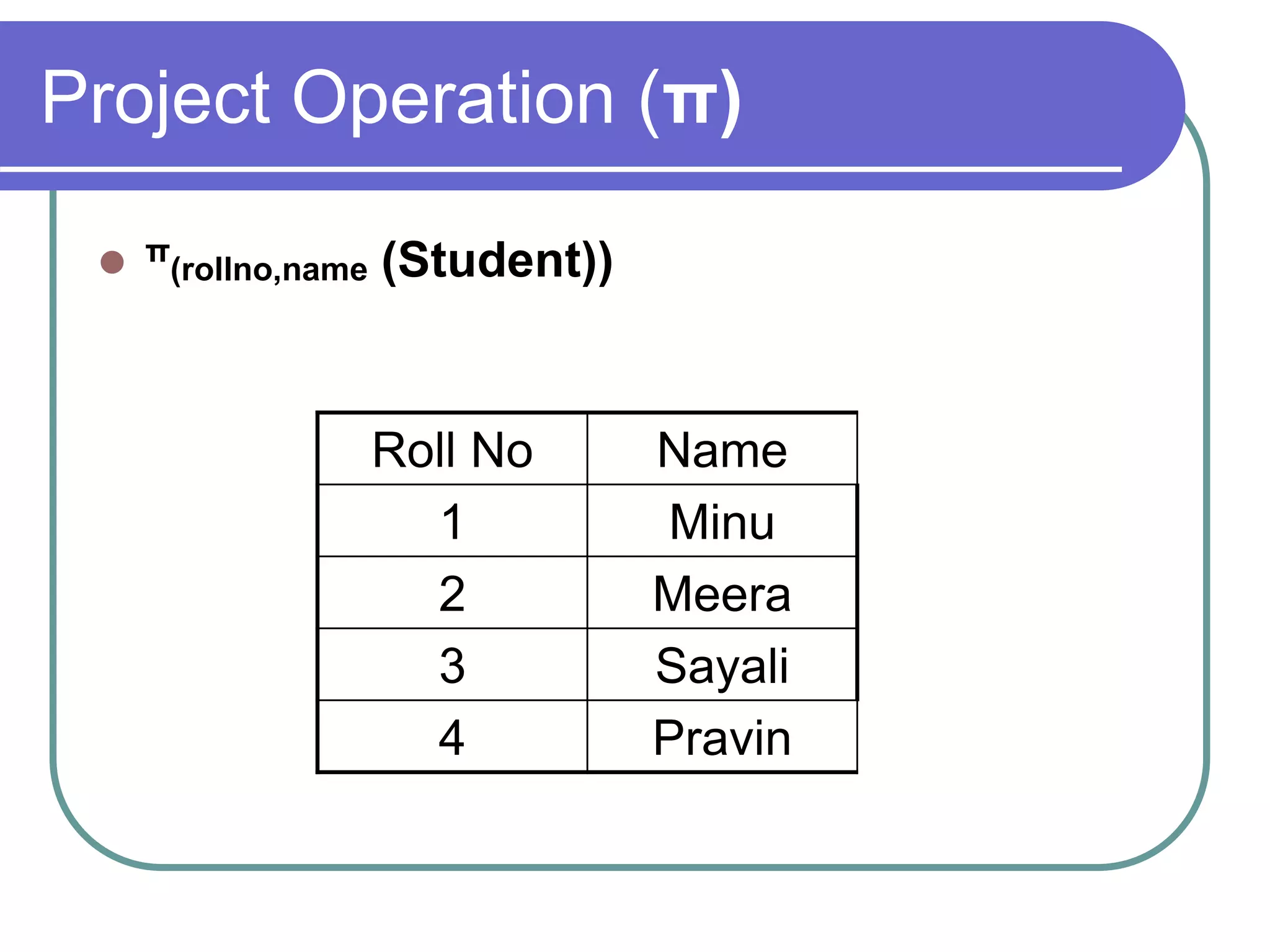
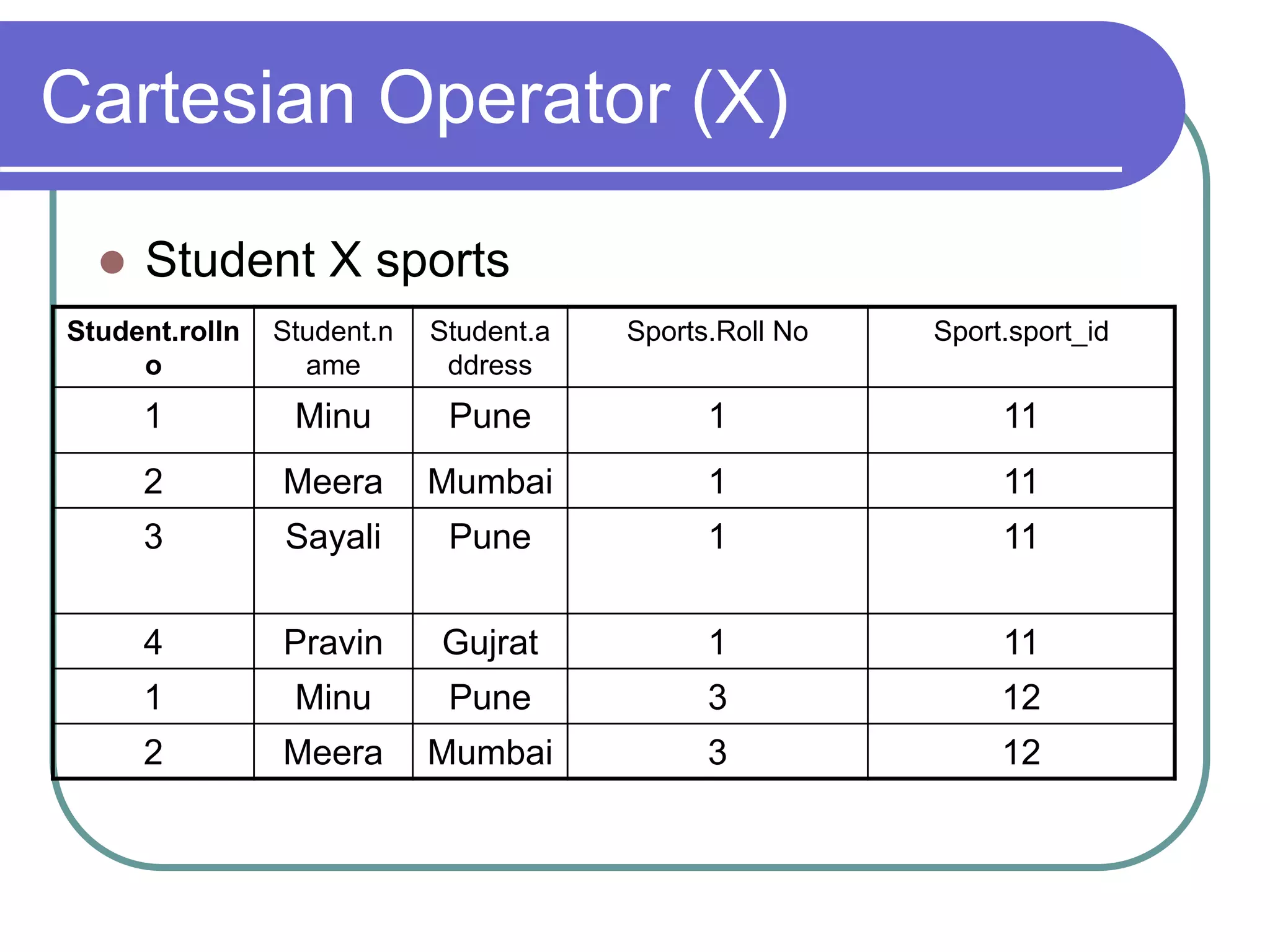
This document discusses the rules for relational databases defined by E.F. Codd, including that all data should be represented as values in tables, each data value can be logically accessed using a table name, primary key and column name, null values should be supported systematically, and the database description should be queryable using the same relational language as the data. It also covers relational algebra operations like select, project, union, difference, cartesian product, and aggregation functions.