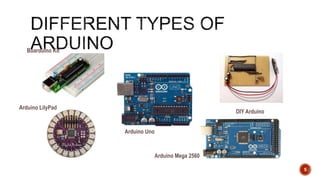
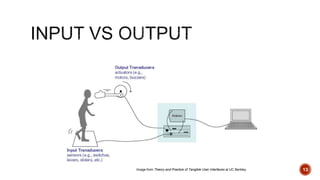
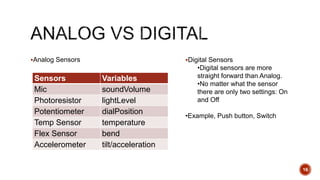
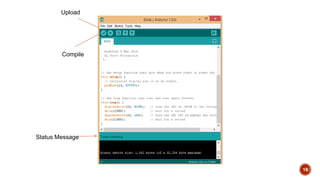
This document provides an overview of the Arduino Uno microcontroller board. It describes that the Arduino Uno contains an ATmega328 microprocessor and can be used to control electronics projects through input and output pins. The Arduino IDE software is used to write programs that can be compiled and uploaded to the board via a USB connection. The document explains the different pin types on the Arduino Uno and provides examples of how sensors and actuators can be connected to collect analog and digital data and control outputs.