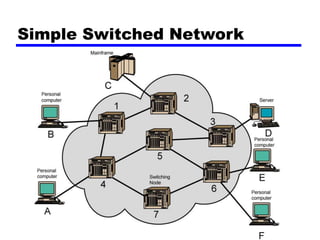
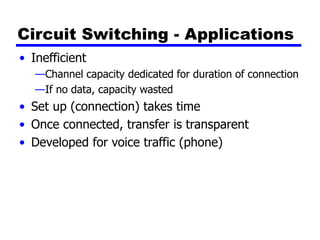
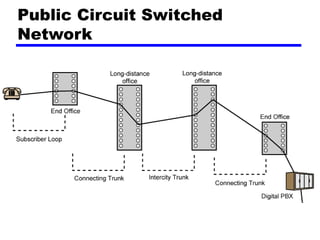
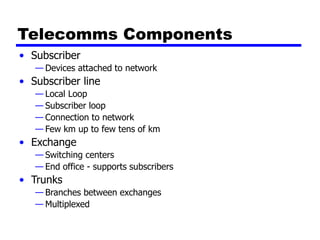
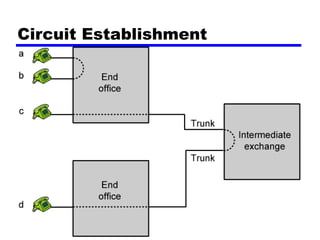
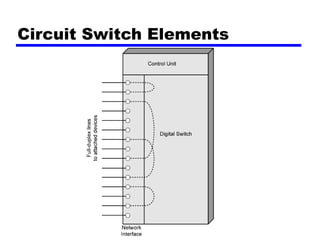
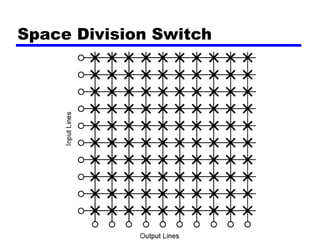
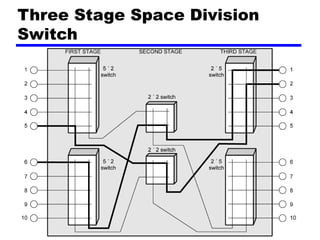
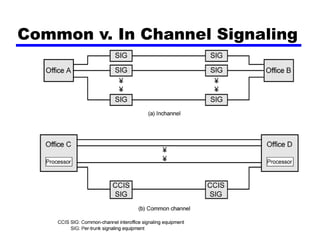
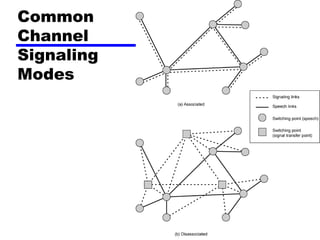
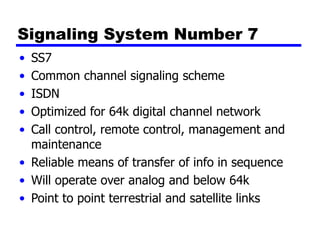
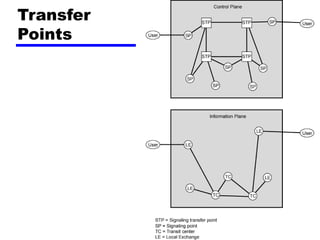
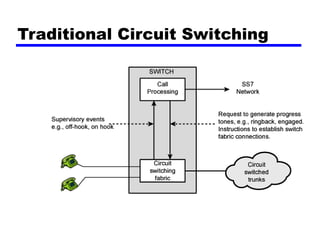
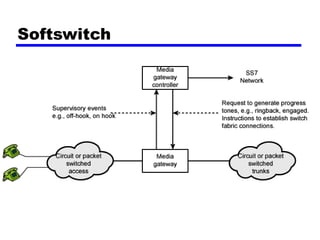
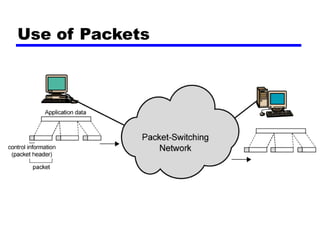
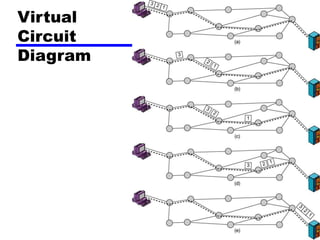
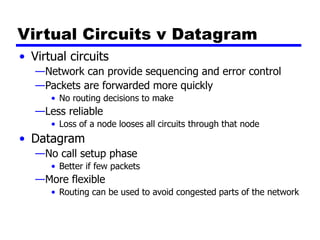
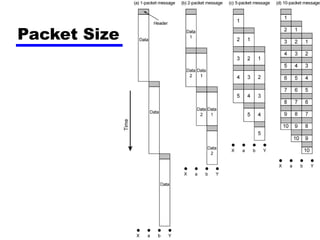
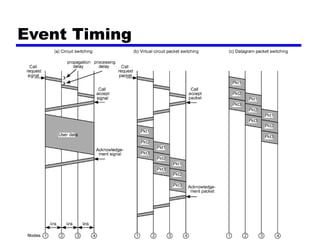
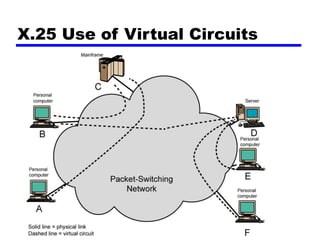
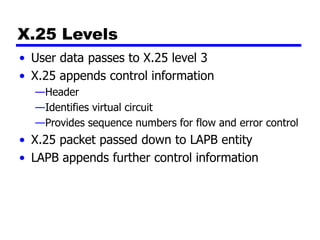
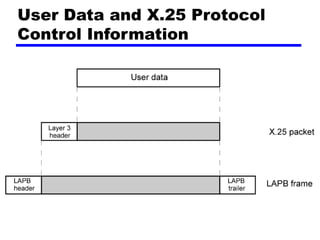
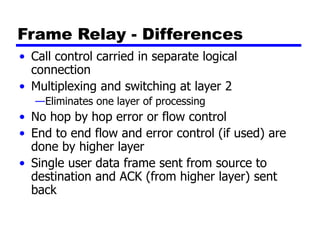
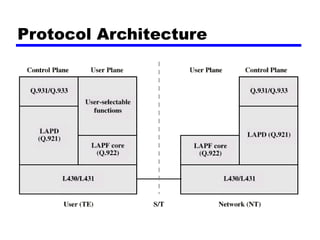
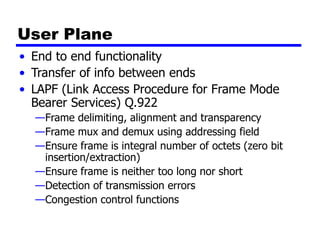
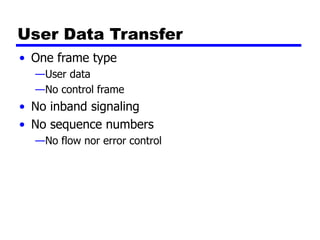
Circuit switching and packet switching are the two main switching techniques used in communications networks. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated communication path between two stations for the duration of the call. It is inefficient if the channel is idle but provides transparent transfer once connected. Packet switching breaks messages into packets that are transmitted individually and reassembled at the destination. It makes more efficient use of network resources but adds complexity for routing and reassembly. X.25 and Frame Relay are common standards used to implement packet switching networks.