Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX




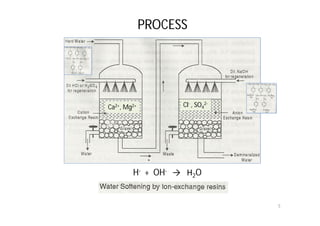


The ion exchange process removes hardness-causing ions from water by exchanging them for ions on cross-linked polymer resins. There are two main types of resins: cation exchange resins that replace calcium and magnesium ions with hydrogen ions, and anion exchange resins that replace chloride and sulfate ions with hydroxide ions. The process produces deionized water that is free from minerals and hardness ions.






