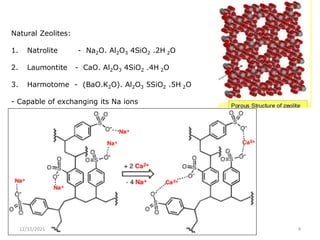
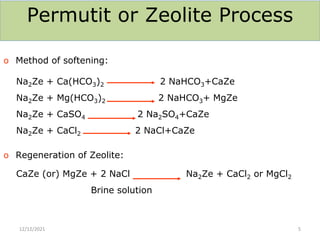
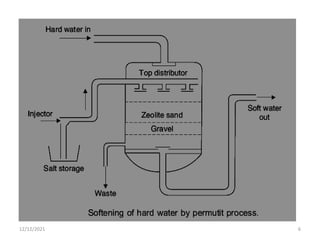
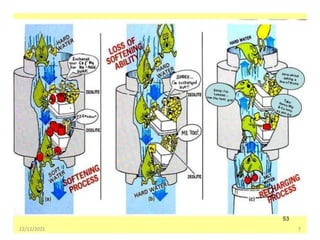
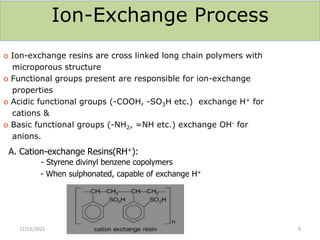
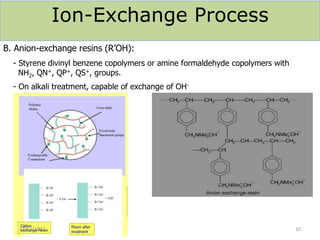
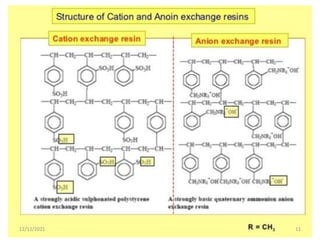
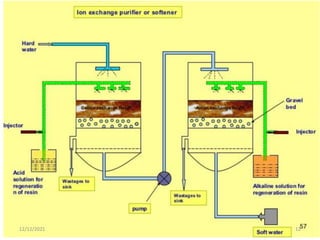
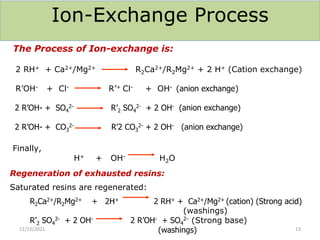
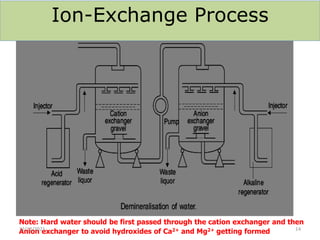
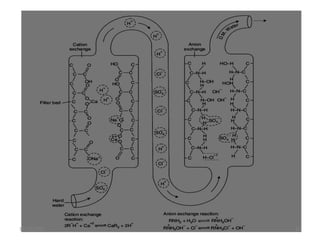
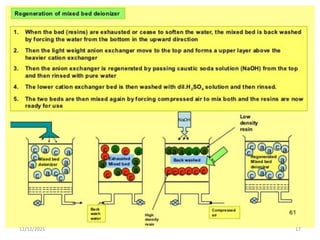
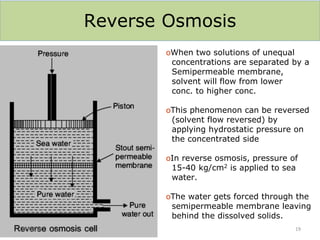
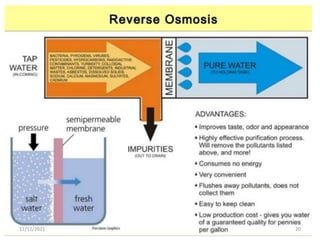
This document discusses various methods for water softening, including zeolite (permutit) process, ion exchange, mixed bed ion exchange, and reverse osmosis. The zeolite process uses hydrated sodium aluminium silicate to exchange sodium ions for calcium and magnesium ions in hard water. Ion exchange uses resins to exchange ions, with cation exchange resins exchanging hydrogen ions for calcium/magnesium ions and anion exchange resins exchanging hydroxide ions. Mixed bed deionizers contain both cation and anion resins. Reverse osmosis uses pressure to force water through a semi-permeable membrane, leaving dissolved solids behind. Each method has advantages such as reducing hardness or